Abstract
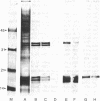
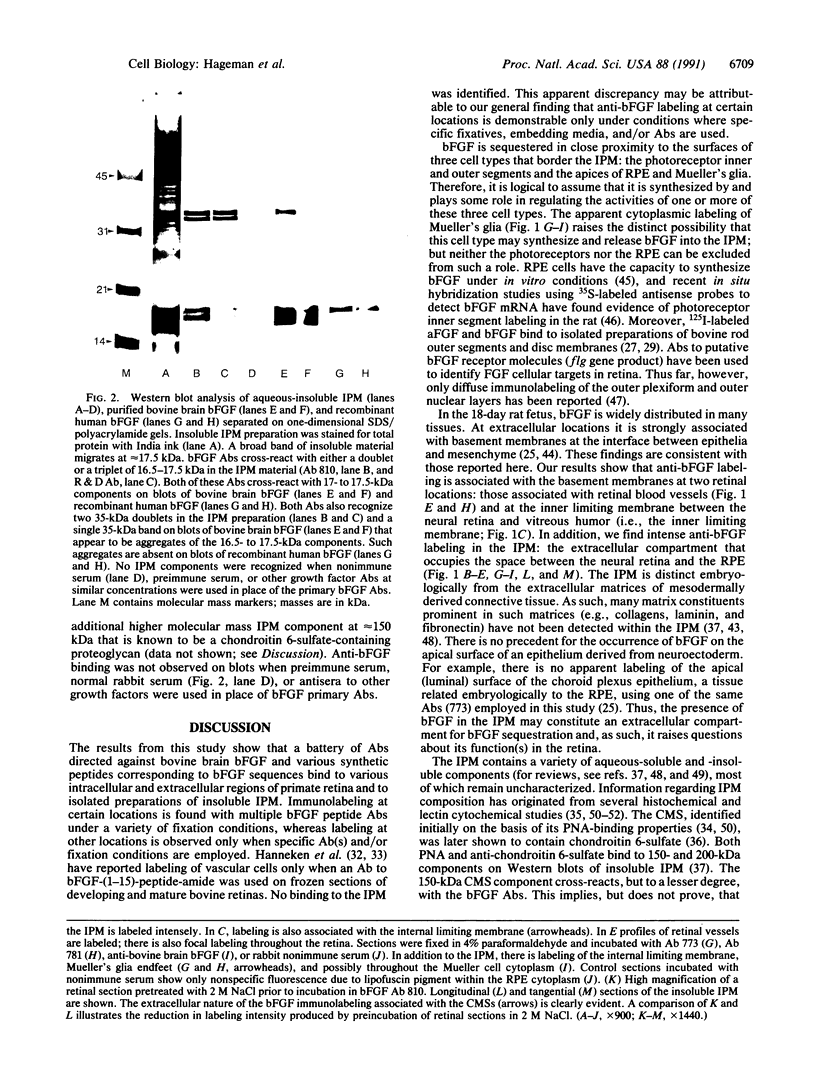
The interphotoreceptor matrix (IPM) occupies the extracellular space between the photoreceptors of the retina and the apical surface of the retinal pigmented epithelium. A large proportion of the IPM is composed of aqueous-insoluble glycoconjugates, including chondroitin sulfate-containing proteoglycans, the distribution of which exhibits both apical-basal and photoreceptor cell type-specific heterogeneities. The precise function of most insoluble IPM constituents is unknown, although the available evidence suggests some may contribute to retinal adhesion or photoreceptor survival. We have now identified basic fibroblast growth factor (bFGF), or an immunologically related protein from the FGF family, within the IPM. The IPM is labeled on sections of primate retinas by a battery of polyclonal antibodies (Abs) directed against various peptide sequences of bFGF and by an Ab to bovine brain bFGF. bFGF Abs also bind to purified preparations of aqueous-insoluble IPM. All bFGF Abs utilized cross-react with equivalent low molecular mass components of 16.5-17.5 kDa on Western blots of insoluble IPM proteins, purified bFGF, and recombinant bFGF. The Abs do not bind any aqueous-soluble IPM components, suggesting that the bFGF is normally bound to an insoluble IPM constituent(s) in situ. The fact that bFGF is sequestered in the IPM and is located in such close proximity to the photoreceptors, the retinal pigmented epithelium, and Mueller's glia raises the strong possibility that it is synthesized by and regulates the activities of one or more of these three cell types in vivo.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adler A. J., Klucznik K. M. Proteins and glycoproteins of the bovine interphotoreceptor matrix: composition and fractionation. Exp Eye Res. 1982 Mar;34(3):423–434. doi: 10.1016/0014-4835(82)90088-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adler A. J., Severin K. M. Proteins of the bovine interphotoreceptor matrix: tissues of origin. Exp Eye Res. 1981 Jun;32(6):755–769. doi: 10.1016/0014-4835(81)90025-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson K. J., Dam D., Lee S., Cotman C. W. Basic fibroblast growth factor prevents death of lesioned cholinergic neurons in vivo. Nature. 1988 Mar 24;332(6162):360–361. doi: 10.1038/332360a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baird A., Esch F., Gospodarowicz D., Guillemin R. Retina- and eye-derived endothelial cell growth factors: partial molecular characterization and identity with acidic and basic fibroblast growth factors. Biochemistry. 1985 Dec 31;24(27):7855–7860. doi: 10.1021/bi00348a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baird A., Esch F., Mormède P., Ueno N., Ling N., Böhlen P., Ying S. Y., Wehrenberg W. B., Guillemin R. Molecular characterization of fibroblast growth factor: distribution and biological activities in various tissues. Recent Prog Horm Res. 1986;42:143–205. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-571142-5.50008-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baird A., Schubert D., Ling N., Guillemin R. Receptor- and heparin-binding domains of basic fibroblast growth factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Apr;85(7):2324–2328. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.7.2324. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgess W. H., Maciag T. The heparin-binding (fibroblast) growth factor family of proteins. Annu Rev Biochem. 1989;58:575–606. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.58.070189.003043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caruelle D., Groux-Muscatelli B., Gaudric A., Sestier C., Coscas G., Caruelle J. P., Barritault D. Immunological study of acidic fibroblast growth factor (aFGF) distribution in the eye. J Cell Biochem. 1989 Feb;39(2):117–128. doi: 10.1002/jcb.240390204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chader G. J. Interphotoreceptor retinoid-binding protein (IRBP): a model protein for molecular biological and clinically relevant studies. Friedenwald lecture. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1989 Jan;30(1):7–22. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Damon D. H., D'Amore P. A., Wagner J. A. Sulfated glycosaminoglycans modify growth factor-induced neurite outgrowth in PC12 cells. J Cell Physiol. 1988 May;135(2):293–300. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041350217. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiMario J., Buffinger N., Yamada S., Strohman R. C. Fibroblast growth factor in the extracellular matrix of dystrophic (mdx) mouse muscle. Science. 1989 May 12;244(4905):688–690. doi: 10.1126/science.2717945. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faktorovich E. G., Steinberg R. H., Yasumura D., Matthes M. T., LaVail M. M. Photoreceptor degeneration in inherited retinal dystrophy delayed by basic fibroblast growth factor. Nature. 1990 Sep 6;347(6288):83–86. doi: 10.1038/347083a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finklestein S. P., Apostolides P. J., Caday C. G., Prosser J., Philips M. F., Klagsbrun M. Increased basic fibroblast growth factor (bFGF) immunoreactivity at the site of focal brain wounds. Brain Res. 1988 Sep 20;460(2):253–259. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(88)90370-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Folkman J., Klagsbrun M., Sasse J., Wadzinski M., Ingber D., Vlodavsky I. A heparin-binding angiogenic protein--basic fibroblast growth factor--is stored within basement membrane. Am J Pathol. 1988 Feb;130(2):393–400. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glaser B. M., D'Amore P. A., Michels R. G., Patz A., Fenselau A. Demonstration of vasoproliferative activity from mammalian retina. J Cell Biol. 1980 Feb;84(2):298–304. doi: 10.1083/jcb.84.2.298. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonzalez A. M., Buscaglia M., Ong M., Baird A. Distribution of basic fibroblast growth factor in the 18-day rat fetus: localization in the basement membranes of diverse tissues. J Cell Biol. 1990 Mar;110(3):753–765. doi: 10.1083/jcb.110.3.753. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gospodarowicz D., Cheng J. Heparin protects basic and acidic FGF from inactivation. J Cell Physiol. 1986 Sep;128(3):475–484. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041280317. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gospodarowicz D., Ferrara N., Schweigerer L., Neufeld G. Structural characterization and biological functions of fibroblast growth factor. Endocr Rev. 1987 May;8(2):95–114. doi: 10.1210/edrv-8-2-95. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gospodarowicz D., Neufeld G., Schweigerer L. Fibroblast growth factor. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 1986 Aug;46(3):187–204. doi: 10.1016/0303-7207(86)90001-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hageman G. S., Johnson L. V. Biochemical characterization of the major peanut-agglutinin-binding glycoproteins in vertebrate retinae. J Comp Neurol. 1986 Jul 22;249(4):499-510, 482-3. doi: 10.1002/cne.902490406. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hageman G. S., Johnson L. V. Chondroitin 6-sulfate glycosaminoglycan is a major constituent of primate cone photoreceptor matrix sheaths. Curr Eye Res. 1987 Apr;6(4):639–646. doi: 10.3109/02713688709025225. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanneken A., Lutty G. A., McLeod D. S., Robey F., Harvey A. K., Hjelmeland L. M. Localization of basic fibroblast growth factor to the developing capillaries of the bovine retina. J Cell Physiol. 1989 Jan;138(1):115–120. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041380116. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herman I. M., D'Amore P. A. Capillary endothelial cell migration: loss of stress fibres in response to retina-derived growth factor. J Muscle Res Cell Motil. 1984 Dec;5(6):697–709. doi: 10.1007/BF00713928. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janet T., Miehe M., Pettmann B., Labourdette G., Sensenbrenner M. Ultrastructural localization of fibroblast growth factor in neurons of rat brain. Neurosci Lett. 1987 Sep 23;80(2):153–157. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(87)90645-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson L. V., Blanks J. C. Application of acrylamide as an embedding medium in studies of lectin and antibody binding in the vertebrate retina. Curr Eye Res. 1984 Jul;3(7):969–974. doi: 10.3109/02713688409167215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson L. V., Hageman G. S., Blanks J. C. Interphotoreceptor matrix domains ensheath vertebrate cone photoreceptor cells. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1986 Feb;27(2):129–135. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joseph-Silverstein J., Consigli S. A., Lyser K. M., Ver Pault C. Basic fibroblast growth factor in the chick embryo: immunolocalization to striated muscle cells and their precursors. J Cell Biol. 1989 Jun;108(6):2459–2466. doi: 10.1083/jcb.108.6.2459. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LaVail M. M., Pinto L. H., Yasumura D. The interphotoreceptor matrix in rats with inherited retinal dystrophy. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1981 Nov;21(5):658–668. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu L. M., Nicoll C. S. Evidence for a role of basic fibroblast growth factor in rat embryonic growth and differentiation. Endocrinology. 1988 Oct;123(4):2027–2031. doi: 10.1210/endo-123-4-2027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maciag T., Mehlman T., Friesel R., Schreiber A. B. Heparin binds endothelial cell growth factor, the principal endothelial cell mitogen in bovine brain. Science. 1984 Aug 31;225(4665):932–935. doi: 10.1126/science.6382607. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mascarelli F., Raulais D., Courtois Y. Fibroblast growth factor phosphorylation and receptors in rod outer segments. EMBO J. 1989 Aug;8(8):2265–2273. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08351.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison R. S., Sharma A., de Vellis J., Bradshaw R. A. Basic fibroblast growth factor supports the survival of cerebral cortical neurons in primary culture. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Oct;83(19):7537–7541. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.19.7537. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noji S., Matsuo T., Koyama E., Yamaai T., Nohno T., Matsuo N., Taniguchi S. Expression pattern of acidic and basic fibroblast growth factor genes in adult rat eyes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1990 Apr 16;168(1):343–349. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(90)91714-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pettmann B., Labourdette G., Weibel M., Sensenbrenner M. The brain fibroblast growth factor (FGF) is localized in neurons. Neurosci Lett. 1986 Jul 24;68(2):175–180. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(86)90137-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plouët J., Mascarelli F., Loret M. D., Faure J. P., Courtois Y. Regulation of eye derived growth factor binding to membranes by light, ATP or GTP in photoreceptor outer segments. EMBO J. 1988 Feb;7(2):373–376. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02823.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Risau W. Developing brain produces an angiogenesis factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jun;83(11):3855–3859. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.11.3855. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Risau W., Ekblom P. Production of a heparin-binding angiogenesis factor by the embryonic kidney. J Cell Biol. 1986 Sep;103(3):1101–1107. doi: 10.1083/jcb.103.3.1101. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross M., Ballard F. J. Regulation of protein metabolism and DNA synthesis by fibroblast growth factor in BHK-21 cells. Biochem J. 1988 Jan 15;249(2):363–368. doi: 10.1042/bj2490363. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schubert D., Ling N., Baird A. Multiple influences of a heparin-binding growth factor on neuronal development. J Cell Biol. 1987 Mar;104(3):635–643. doi: 10.1083/jcb.104.3.635. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schweigerer L., Malerstein B., Neufeld G., Gospodarowicz D. Basic fibroblast growth factor is synthesized in cultured retinal pigment epithelial cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1987 Mar 30;143(3):934–940. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(87)90340-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seed J., Olwin B. B., Hauschka S. D. Fibroblast growth factor levels in the whole embryo and limb bud during chick development. Dev Biol. 1988 Jul;128(1):50–57. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(88)90265-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shing Y., Folkman J., Sullivan R., Butterfield C., Murray J., Klagsbrun M. Heparin affinity: purification of a tumor-derived capillary endothelial cell growth factor. Science. 1984 Mar 23;223(4642):1296–1299. doi: 10.1126/science.6199844. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sievers J., Hausmann B., Unsicker K., Berry M. Fibroblast growth factors promote the survival of adult rat retinal ganglion cells after transection of the optic nerve. Neurosci Lett. 1987 May 6;76(2):157–162. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(87)90708-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sporn M. B., Roberts A. B. Peptide growth factors are multifunctional. Nature. 1988 Mar 17;332(6161):217–219. doi: 10.1038/332217a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uehara F., Sameshima M., Muramatsu T., Ohba N. Localization of fluorescence-labeled lectin binding sites on photoreceptor cells of the monkey retina. Exp Eye Res. 1983 Jan;36(1):113–123. doi: 10.1016/0014-4835(83)90094-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walicke P. A. Interactions between basic fibroblast growth factor (FGF) and glycosoaminoglycans in promoting neurite outgrowth. Exp Neurol. 1988 Oct;102(1):144–148. doi: 10.1016/0014-4886(88)90087-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]