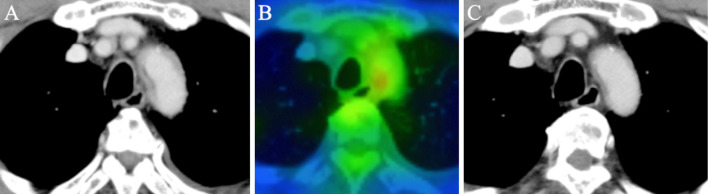
A 73-year-old man presented with a 1-month history of fever and numbness of the bilateral upper and lower extremities. Laboratory tests showed positive myeloperoxidase-antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody (ANCA) results (296 U/mL). Computed tomography (CT) showed wall thickening in the thoracic aorta and common carotid arteries (Picture A), and gallium single-photon emission CT/CT showed accumulation in the thickened wall (Picture B). He had exudative pleurisy and mononeuritis multiplex, and no evidence of other diseases, except ANCA-associated vasculitis, including giant cell arteritis. Tests for human leucocyte antigen (HLA)-B52 were positive, as is frequently observed in cases of Takayasu arteritis (1). The involvement of large vessels in ANCA-associated vasculitis is rare (2). Few reports have described the association between HLA and aortitis with ANCA-associated vasculitis. We believe that the ANCA-associated vasculitis developed concurrently with aortitis in the present case, due to the patient's genetic tendency for aortic inflammation. The patient was treated with prednisolone and intravenous cyclophosphamide, which successfully led to remission (Picture C).
Picture.
The authors state that they have no Conflict of Interest (COI).
References
- 1. Terao C, Yoshifuji H, Ohmura K, et al. Association of Takayasu arteritis with HLA-B 67:01 and two amino acids in HLA-B protein. Rheumatology 52: 1769-1774, 2013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2. Chirinos JA, Tamariz LJ, Lopes G, et al. Large vessel involvement in ANCA-associated vasculitides: report of a case and review of the literature. Clin Rheumatol 23: 152-159, 2004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]