Figure 4. H89 inhibits type I IFN signaling pathway.
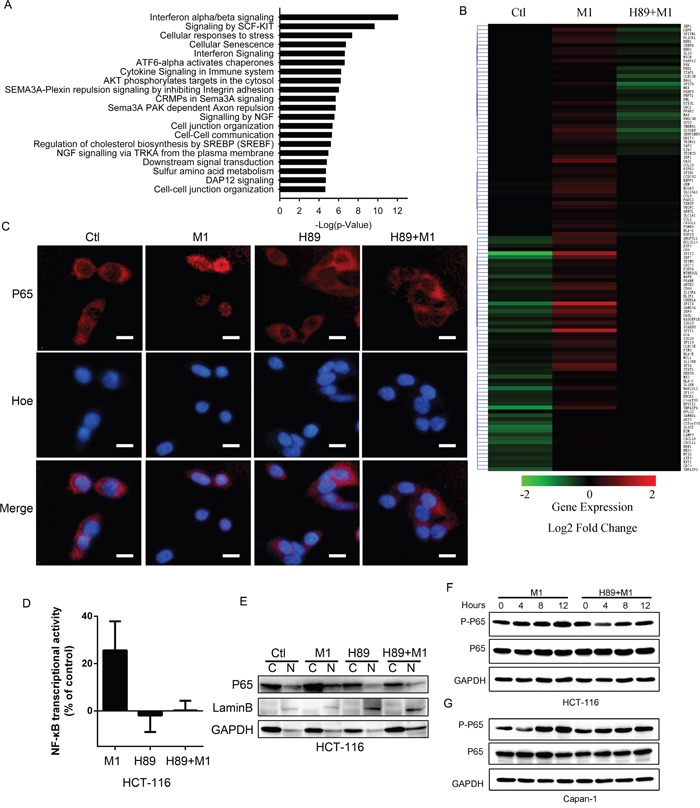
A. Gene Ontology analysis of the pathways overrepresented among genes differentially expressed between HCT-116 stimulated with vehicle or with M1. B. Heatmap of the expression of ISGs induced by M1 virus infection. C. Immunofluorescent staining of p65. HCT-116 cancer cells were pretreated with H89 for one hour and then infected with M1 virus (1PFU/cell) for four hours. D. NF-κB transcriptional activity determination. HCT-116 cells co-transfected with plasmids of pNF-κB-luciferase plus pRL-TK renilla and analyzed by luciferase reporter activity assays. E. Subcellular fractions of NF-B in cancer cells. Cytoplasmic and nuclear fractions were analyzed by IB analyses. Nuclear protein laminB was used as a nuclear (N) protein marker and GAPDH was used as a cytoplasmic (C) protein marker. F and G. Expression of phosphorylated p65 with western blot. HCT-116 and Capan-1 cancer cells were pretreated with H89 (10μM) or not and then infected with M1 virus (1 PFU/cell). Protein expressions were determined 0, 4, 8, 12 hours postinfection.
