Abstract
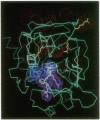
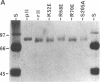
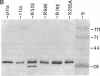
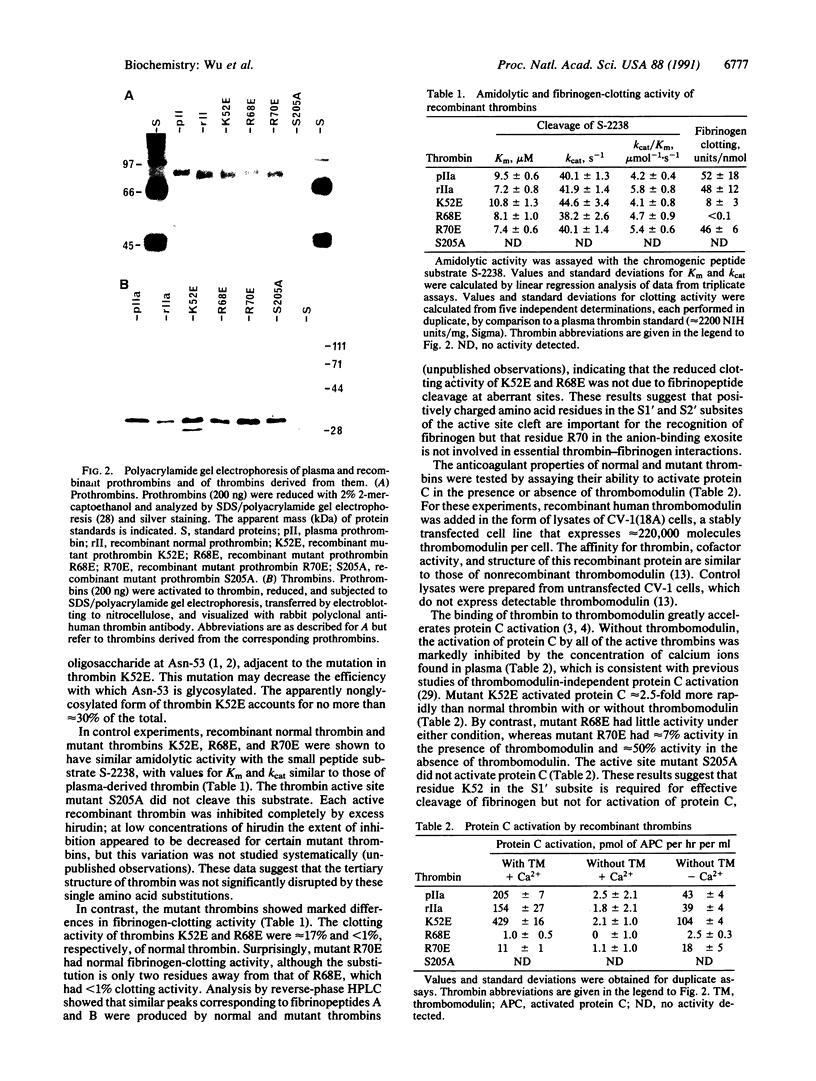
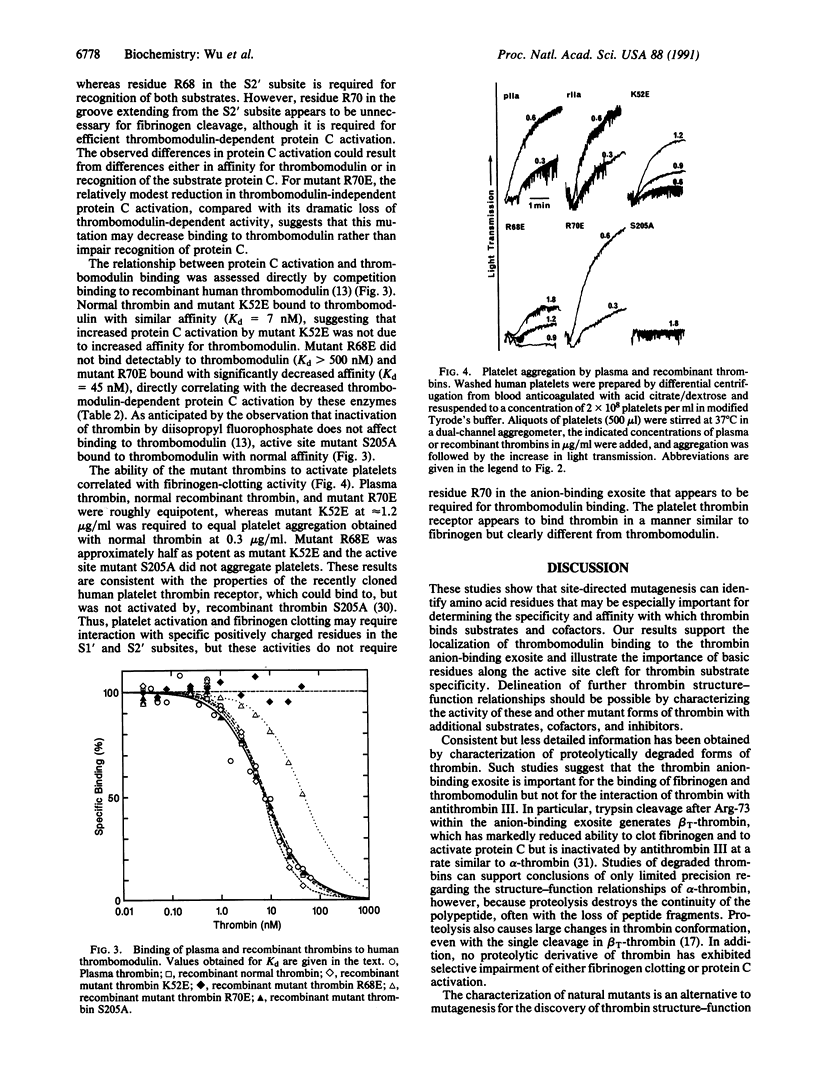
Thrombin is a serine protease that acts as a procoagulant by clotting fibrinogen and activating platelets and as an anticoagulant by activating protein C in a thrombomodulin-dependent reaction. Fibrinogen and thrombomodulin bind competitively to an anion-binding exosite on thrombin. We prepared recombinant normal human thrombin and mutant thrombins with single amino acid substitutions in order to localize and distinguish the fibrinogen- and thrombomodulin-binding sites. Normal and mutant thrombins had similar amidolytic activity. Thrombin K52E had approximately 2.5-fold increased protein C-activating activity but only approximately 17% of normal fibrinogen-clotting activity. Thrombin R70E had normal fibrinogen-clotting activity but only approximately 7% of normal protein C-activating activity. Thrombin R68E had markedly reduced activity in both assays. Decreased activation of protein C correlated with decreased binding affinity for thrombomodulin, and ability to activate platelets correlated directly with fibrinogen-clotting activity. These results demonstrate that thrombins with predominantly anticoagulant or procoagulant activity can be created by mutagenesis and that thrombomodulin- and fibrinogen-binding sites on thrombin may overlap but are not identical.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bajaj S. P., Spitzer S. G., Welsh W. J., Warn-Cramer B. J., Kasper C. K., Birktoft J. J. Experimental and theoretical evidence supporting the role of Gly363 in blood coagulation factor IXa (Gly193 in chymotrypsin) for proper activation of the proenzyme. J Biol Chem. 1990 Feb 15;265(5):2956–2961. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berliner L. J., Birktoft J. J., Miller T. L., Musci G., Scheffler J. E., Shen Y. Y., Sugawara Y. Thrombin: active-site topography. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1986;485:80–95. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1986.tb34570.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berliner L. J., Sugawara Y., Fenton J. W., 2nd Human alpha-thrombin binding to nonpolymerized fibrin-Sepharose: evidence for an anionic binding region. Biochemistry. 1985 Nov 19;24(24):7005–7009. doi: 10.1021/bi00345a038. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bode W., Mayr I., Baumann U., Huber R., Stone S. R., Hofsteenge J. The refined 1.9 A crystal structure of human alpha-thrombin: interaction with D-Phe-Pro-Arg chloromethylketone and significance of the Tyr-Pro-Pro-Trp insertion segment. EMBO J. 1989 Nov;8(11):3467–3475. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08511.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borowski M., Furie B. C., Goldsmith G. H., Furie B. Metal and phospholipid binding properties of partially carboxylated human prothrombin variants. J Biol Chem. 1985 Aug 5;260(16):9258–9264. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boshart M., Weber F., Jahn G., Dorsch-Häsler K., Fleckenstein B., Schaffner W. A very strong enhancer is located upstream of an immediate early gene of human cytomegalovirus. Cell. 1985 Jun;41(2):521–530. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80025-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dittman W. A., Majerus P. W. Structure and function of thrombomodulin: a natural anticoagulant. Blood. 1990 Jan 15;75(2):329–336. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esmon C. T., Owen W. G. Identification of an endothelial cell cofactor for thrombin-catalyzed activation of protein C. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Apr;78(4):2249–2252. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.4.2249. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esmon N. L., DeBault L. E., Esmon C. T. Proteolytic formation and properties of gamma-carboxyglutamic acid-domainless protein C. J Biol Chem. 1983 May 10;258(9):5548–5553. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fenton J. W., 2nd Thrombin specificity. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1981;370:468–495. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1981.tb29757.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham F. L., van der Eb A. J. A new technique for the assay of infectivity of human adenovirus 5 DNA. Virology. 1973 Apr;52(2):456–467. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90341-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grütter M. G., Priestle J. P., Rahuel J., Grossenbacher H., Bode W., Hofsteenge J., Stone S. R. Crystal structure of the thrombin-hirudin complex: a novel mode of serine protease inhibition. EMBO J. 1990 Aug;9(8):2361–2365. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07410.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henriksen R. A., Mann K. G. Identification of the primary structural defect in the dysthrombin thrombin Quick I: substitution of cysteine for arginine-382. Biochemistry. 1988 Dec 27;27(26):9160–9165. doi: 10.1021/bi00426a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hofsteenge J., Braun P. J., Stone S. R. Enzymatic properties of proteolytic derivatives of human alpha-thrombin. Biochemistry. 1988 Mar 22;27(6):2144–2151. doi: 10.1021/bi00406a049. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kisiel W., Davie E. W. Isolation and characterization of bovine factor VII. Biochemistry. 1975 Nov 4;14(22):4928–4934. doi: 10.1021/bi00693a023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kisiel W., Hanahan D. J. Purification and characterization of human Factor II. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Mar 30;304(1):103–113. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(73)90119-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maraganore J. M., Chao B., Joseph M. L., Jablonski J., Ramachandran K. L. Anticoagulant activity of synthetic hirudin peptides. J Biol Chem. 1989 May 25;264(15):8692–8698. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker B. A., Stark G. R. Regulation of simian virus 40 transcription: sensitive analysis of the RNA species present early in infections by virus or viral DNA. J Virol. 1979 Aug;31(2):360–369. doi: 10.1128/jvi.31.2.360-369.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rydel T. J., Ravichandran K. G., Tulinsky A., Bode W., Huber R., Roitsch C., Fenton J. W., 2nd The structure of a complex of recombinant hirudin and human alpha-thrombin. Science. 1990 Jul 20;249(4966):277–280. doi: 10.1126/science.2374926. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saiki R. K., Gelfand D. H., Stoffel S., Scharf S. J., Higuchi R., Horn G. T., Mullis K. B., Erlich H. A. Primer-directed enzymatic amplification of DNA with a thermostable DNA polymerase. Science. 1988 Jan 29;239(4839):487–491. doi: 10.1126/science.2448875. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shuman M. A., Majerus P. W. The measurement of thrombin in clotting blood by radioimmunoassay. J Clin Invest. 1976 Nov;58(5):1249–1258. doi: 10.1172/JCI108579. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern P. J., Berg P. Transformation of mammalian cells to antibiotic resistance with a bacterial gene under control of the SV40 early region promoter. J Mol Appl Genet. 1982;1(4):327–341. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sprague J., Condra J. H., Arnheiter H., Lazzarini R. A. Expression of a recombinant DNA gene coding for the vesicular stomatitis virus nucleocapsid protein. J Virol. 1983 Feb;45(2):773–781. doi: 10.1128/jvi.45.2.773-781.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsiang M., Lentz S. R., Dittman W. A., Wen D., Scarpati E. M., Sadler J. E. Equilibrium binding of thrombin to recombinant human thrombomodulin: effect of hirudin, fibrinogen, factor Va, and peptide analogues. Biochemistry. 1990 Nov 27;29(47):10602–10612. doi: 10.1021/bi00499a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vehar G. A., Davie E. W. Preparation and properties of bovine factor VIII (antihemophilic factor). Biochemistry. 1980 Feb 5;19(3):401–410. doi: 10.1021/bi00544a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vu T. K., Hung D. T., Wheaton V. I., Coughlin S. R. Molecular cloning of a functional thrombin receptor reveals a novel proteolytic mechanism of receptor activation. Cell. 1991 Mar 22;64(6):1057–1068. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90261-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker F. J., Sexton P. W., Esmon C. T. The inhibition of blood coagulation by activated Protein C through the selective inactivation of activated Factor V. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Dec 7;571(2):333–342. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(79)90103-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]