Abstract
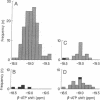
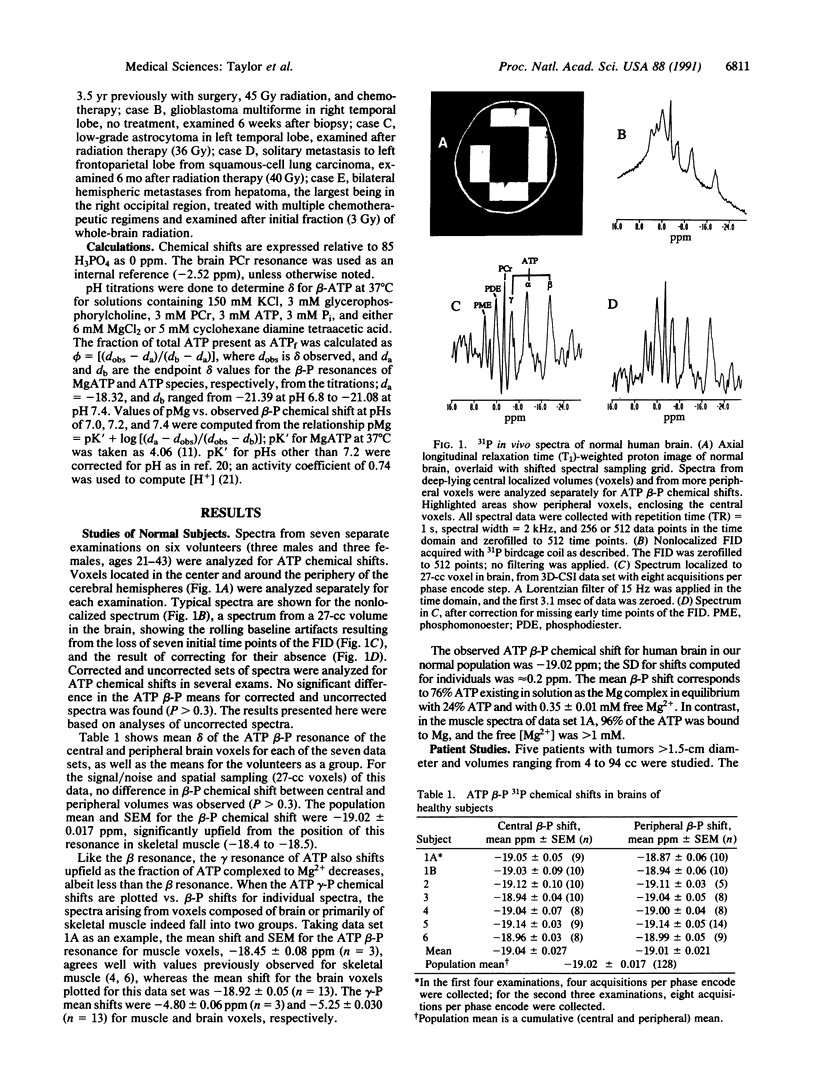
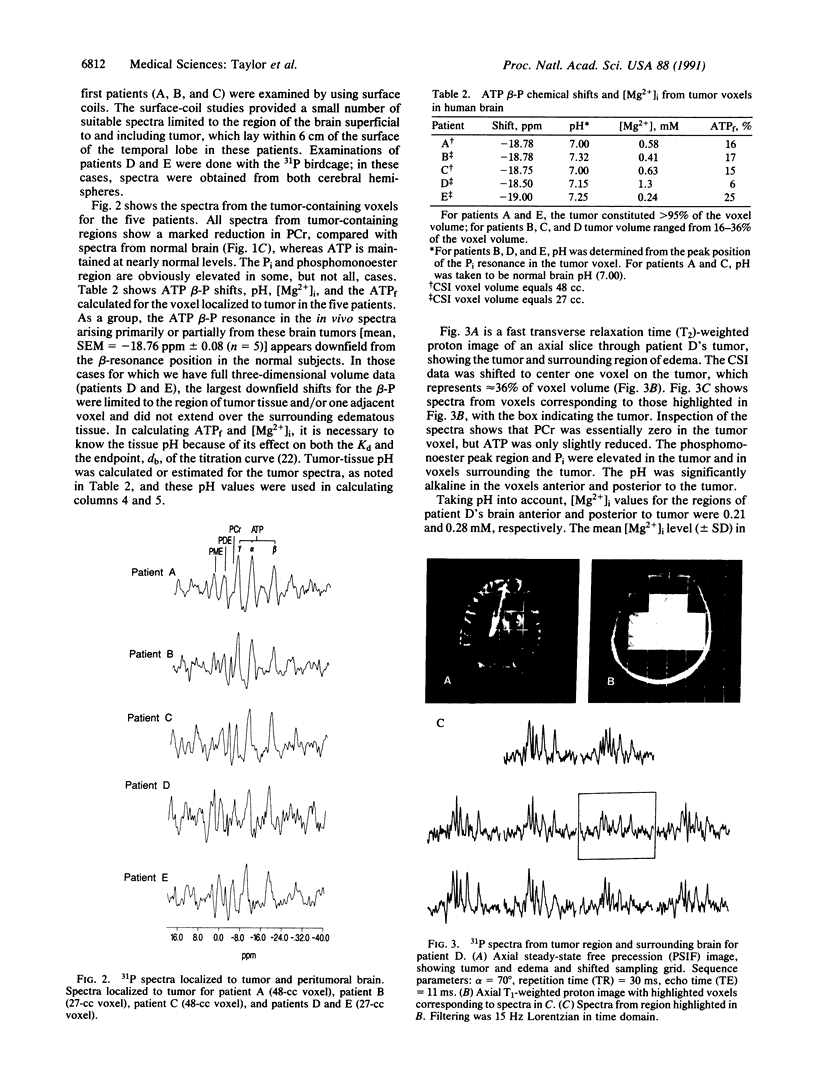
We have studied a series of normal subjects and patients with brain tumors, by using 31P three-dimensional chemical shift imaging to obtain localized 31P spectra of the brain. A significant proportion of brain cytosolic ATP in normal brain is not complexed to Mg2+, as indicated by the chemical shift delta of the beta-P resonance of ATP. The ATP beta-P resonance position in brain thus is sensitive to changes in intracellular free Mg2+ concentration and in the proportion of ATP complexed with Mg because this shift lies on the rising portion of the delta vs. Mg2+ titration curve for ATP. We have measured the ATP beta-P shift and compared intracellular free Mg2+ concentration and fractions of free ATP for normal individuals (n = 6) and a limited series of patients with brain tumors (n = 5). In four of the five spectra obtained from brain tissue containing a substantial proportion of tumor, intracellular free Mg2+ was increased, and the fraction of free ATP was decreased, compared with normal brain.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bachelard H. S., Goldfarb P. S. Adenine nucleotides and magnesium ions in relation to control of mammalian cerebral-cortex hexokinase. Biochem J. 1969 May;112(5):579–586. doi: 10.1042/bj1120579. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bottomley P. A., Hardy C. J. Rapid, reliable in vivo assays of human phosphate metabolites by nuclear magnetic resonance. Clin Chem. 1989 Mar;35(3):392–395. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brooks K. J., Bachelard H. S. Changes in intracellular free magnesium during hypoglycaemia and hypoxia in cerebral tissue as calculated from 31P-nuclear magnetic resonance spectra. J Neurochem. 1989 Aug;53(2):331–334. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1989.tb07338.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COHN M., HUGHES T. R., Jr Nuclear magnetic resonance spectra of adenosine di- and triphosphate. II. Effect of complexing with divalent metal ions. J Biol Chem. 1962 Jan;237:176–181. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corkey B. E., Duszynski J., Rich T. L., Matschinsky B., Williamson J. R. Regulation of free and bound magnesium in rat hepatocytes and isolated mitochondria. J Biol Chem. 1986 Feb 25;261(6):2567–2574. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Degani H., Horowitz A., Itzchak Y. Breast tumors: evaluation with P-31 MR spectroscopy. Radiology. 1986 Oct;161(1):53–55. doi: 10.1148/radiology.161.1.3020609. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Degani H., Shaer A., Victor T. A., Kaye A. M. Estrogen-induced changes in high-energy phosphate metabolism in rat uterus: 31P NMR studies. Biochemistry. 1984 Jun 5;23(12):2572–2577. doi: 10.1021/bi00307a006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elin R. J. Assessment of magnesium status. Clin Chem. 1987 Nov;33(11):1965–1970. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grubbs R. D., Maguire M. E. Magnesium as a regulatory cation: criteria and evaluation. Magnesium. 1987;6(3):113–127. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gupta R. K., Gupta P., Yushok W. D., Rose Z. B. On the noninvasive measurement of intracellular free magnesium by 31P NMR spectroscopy. Physiol Chem Phys Med NMR. 1983;15(3):265–280. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Headrick J. P., Willis R. J. Effect of inotropic stimulation on cytosolic Mg2+ in isolated rat heart: a 31P magnetic resonance study. Magn Reson Med. 1989 Dec;12(3):328–338. doi: 10.1002/mrm.1910120305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hubesch B., Sappey-Marinier D., Roth K., Meyerhoff D. J., Matson G. B., Weiner M. W. P-31 MR spectroscopy of normal human brain and brain tumors. Radiology. 1990 Feb;174(2):401–409. doi: 10.1148/radiology.174.2.2296651. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jangaard N. O., Unkeless J., Atkinson D. E. The inhibition of citrate synthase by adenosine triphosphate. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1968 Jan 8;151(1):225–235. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(68)90177-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kushmerick M. J., Dillon P. F., Meyer R. A., Brown T. R., Krisanda J. M., Sweeney H. L. 31P NMR spectroscopy, chemical analysis, and free Mg2+ of rabbit bladder and uterine smooth muscle. J Biol Chem. 1986 Nov 5;261(31):14420–14429. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luyten P. R., Groen J. P., Vermeulen J. W., den Hollander J. A. Experimental approaches to image localized human 31P NMR spectroscopy. Magn Reson Med. 1989 Jul;11(1):1–21. doi: 10.1002/mrm.1910110102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malloy C. R., Cunningham C. C., Radda G. K. The metabolic state of the rat liver in vivo measured by 31P-NMR spectroscopy. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1986 Jan 23;885(1):1–11. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(86)90032-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyerhoff D. J., Boska M. D., Thomas A. M., Weiner M. W. Alcoholic liver disease: quantitative image-guided P-31 MR spectroscopy. Radiology. 1989 Nov;173(2):393–400. doi: 10.1148/radiology.173.2.2798871. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy E., Steenbergen C., Levy L. A., Raju B., London R. E. Cytosolic free magnesium levels in ischemic rat heart. J Biol Chem. 1989 Apr 5;264(10):5622–5627. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Sullivan W. J., Smithers G. W. Stability constants for biologically important metal-ligand complexes. Methods Enzymol. 1979;63:294–336. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(79)63014-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petroff O. A., Prichard J. W., Behar K. L., Alger J. R., den Hollander J. A., Shulman R. G. Cerebral intracellular pH by 31P nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Neurology. 1985 Jun;35(6):781–788. doi: 10.1212/wnl.35.6.781. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips R. C., George P., Rutman R. J. Thermodynamic studies of the formation and ionization of the magnesium(II) complexes of ADP and ATP over the pH range 5 to 9. J Am Chem Soc. 1966 Jun 20;88(12):2631–2640. doi: 10.1021/ja00964a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramadan N. M., Halvorson H., Vande-Linde A., Levine S. R., Helpern J. A., Welch K. M. Low brain magnesium in migraine. Headache. 1989 Jul;29(7):416–419. doi: 10.1111/j.1526-4610.1989.hed2907416.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsien R. Y., Rink T. J. Neutral carrier ion-selective microelectrodes for measurement of intracellular free calcium. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Jul;599(2):623–638. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(80)90205-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Veloso D., Guynn R. W., Oskarsson M., Veech R. L. The concentrations of free and bound magnesium in rat tissues. Relative constancy of free Mg 2+ concentrations. J Biol Chem. 1973 Jul 10;248(13):4811–4819. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vigneron D. B., Nelson S. J., Murphy-Boesch J., Kelley D. A., Kessler H. B., Brown T. R., Taylor J. S. Chemical shift imaging of human brain: axial, sagittal, and coronal P-31 metabolite images. Radiology. 1990 Dec;177(3):643–649. doi: 10.1148/radiology.177.3.2243963. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vink R., McIntosh T. K., Demediuk P., Weiner M. W., Faden A. I. Decline in intracellular free Mg2+ is associated with irreversible tissue injury after brain trauma. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jan 15;263(2):757–761. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wray S., Tofts P. S. Direct in vivo measurement of absolute metabolite concentrations using 31P nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1986 May 29;886(3):399–405. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(86)90175-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]