Abstract
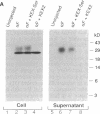
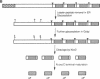
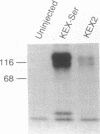
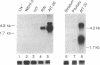
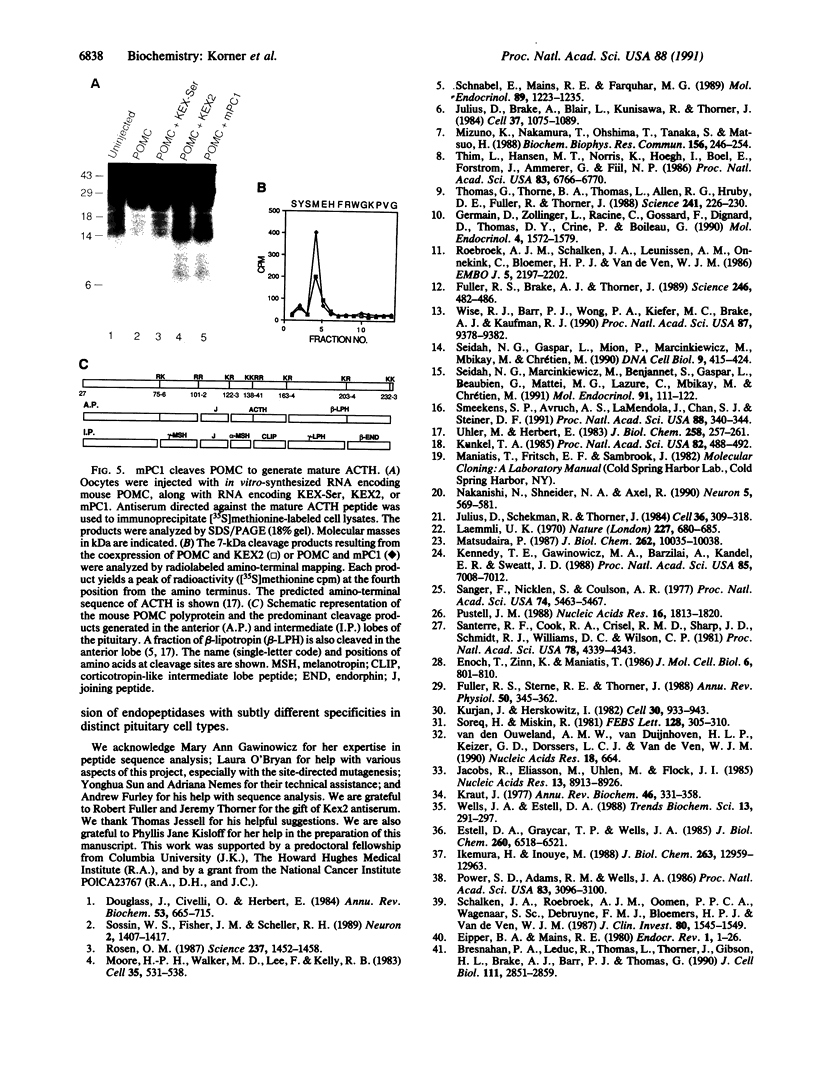
We have combined gene cloning with an assay for prohormone biosynthesis and processing in Xenopus oocytes to identify the genes that encode mammalian prohormone processing enzymes. The coinjection of RNA encoding murine prohormone convertase 1 (mPC1), a mammalian endoprotease, along with proopiomelanocortin RNA into an oocyte results in the appropriate cleavage after paired basic residues in the proopiomelanocortin polyprotein necessary to generate corticotropin. The ability of mPC1 to generate corticotropin, along with the observation that mPC1 is specifically expressed in endocrine and neuronal cells, suggests that the mPC1 gene encodes the endopeptidase responsible for the pathway of proopiomelanocortin cleavage observed in the anterior pituitary.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bresnahan P. A., Leduc R., Thomas L., Thorner J., Gibson H. L., Brake A. J., Barr P. J., Thomas G. Human fur gene encodes a yeast KEX2-like endoprotease that cleaves pro-beta-NGF in vivo. J Cell Biol. 1990 Dec;111(6 Pt 2):2851–2859. doi: 10.1083/jcb.111.6.2851. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Douglass J., Civelli O., Herbert E. Polyprotein gene expression: generation of diversity of neuroendocrine peptides. Annu Rev Biochem. 1984;53:665–715. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.53.070184.003313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eipper B. A., Mains R. E. Structure and biosynthesis of pro-adrenocorticotropin/endorphin and related peptides. Endocr Rev. 1980 Winter;1(1):1–27. doi: 10.1210/edrv-1-1-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Enoch T., Zinn K., Maniatis T. Activation of the human beta-interferon gene requires an interferon-inducible factor. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Mar;6(3):801–810. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.3.801. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Estell D. A., Graycar T. P., Wells J. A. Engineering an enzyme by site-directed mutagenesis to be resistant to chemical oxidation. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jun 10;260(11):6518–6521. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuller R. S., Brake A. J., Thorner J. Intracellular targeting and structural conservation of a prohormone-processing endoprotease. Science. 1989 Oct 27;246(4929):482–486. doi: 10.1126/science.2683070. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuller R. S., Sterne R. E., Thorner J. Enzymes required for yeast prohormone processing. Annu Rev Physiol. 1988;50:345–362. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.50.030188.002021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Germain D., Zollinger L., Racine C., Gossard F., Dignard D., Thomas D. Y., Crine P., Boileau G. The yeast KEX-2-processing endoprotease is active in the Golgi apparatus of transfected NIH 3T3 fibroblasts. Mol Endocrinol. 1990 Oct;4(10):1572–1579. doi: 10.1210/mend-4-10-1572. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikemura H., Inouye M. In vitro processing of pro-subtilisin produced in Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1988 Sep 15;263(26):12959–12963. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobs M., Eliasson M., Uhlén M., Flock J. I. Cloning, sequencing and expression of subtilisin Carlsberg from Bacillus licheniformis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Dec 20;13(24):8913–8926. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.24.8913. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Julius D., Brake A., Blair L., Kunisawa R., Thorner J. Isolation of the putative structural gene for the lysine-arginine-cleaving endopeptidase required for processing of yeast prepro-alpha-factor. Cell. 1984 Jul;37(3):1075–1089. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90442-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Julius D., Schekman R., Thorner J. Glycosylation and processing of prepro-alpha-factor through the yeast secretory pathway. Cell. 1984 Feb;36(2):309–318. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90224-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kennedy T. E., Gawinowicz M. A., Barzilai A., Kandel E. R., Sweatt J. D. Sequencing of proteins from two-dimensional gels by using in situ digestion and transfer of peptides to polyvinylidene difluoride membranes: application to proteins associated with sensitization in Aplysia. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Sep;85(18):7008–7012. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.18.7008. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kraut J. Serine proteases: structure and mechanism of catalysis. Annu Rev Biochem. 1977;46:331–358. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.46.070177.001555. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel T. A. Rapid and efficient site-specific mutagenesis without phenotypic selection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jan;82(2):488–492. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.2.488. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurjan J., Herskowitz I. Structure of a yeast pheromone gene (MF alpha): a putative alpha-factor precursor contains four tandem copies of mature alpha-factor. Cell. 1982 Oct;30(3):933–943. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90298-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsudaira P. Sequence from picomole quantities of proteins electroblotted onto polyvinylidene difluoride membranes. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jul 25;262(21):10035–10038. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizuno K., Nakamura T., Ohshima T., Tanaka S., Matsuo H. Yeast KEX2 genes encodes an endopeptidase homologous to subtilisin-like serine proteases. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 Oct 14;156(1):246–254. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(88)80832-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore H. P., Walker M. D., Lee F., Kelly R. B. Expressing a human proinsulin cDNA in a mouse ACTH-secreting cell. Intracellular storage, proteolytic processing, and secretion on stimulation. Cell. 1983 Dec;35(2 Pt 1):531–538. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90187-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakanishi N., Shneider N. A., Axel R. A family of glutamate receptor genes: evidence for the formation of heteromultimeric receptors with distinct channel properties. Neuron. 1990 Nov;5(5):569–581. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(90)90212-x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Power S. D., Adams R. M., Wells J. A. Secretion and autoproteolytic maturation of subtilisin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 May;83(10):3096–3100. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.10.3096. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pustell J. M. Interactive molecular biology computing. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Mar 11;16(5):1813–1820. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.5.1813. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roebroek A. J., Schalken J. A., Leunissen J. A., Onnekink C., Bloemers H. P., Van de Ven W. J. Evolutionary conserved close linkage of the c-fes/fps proto-oncogene and genetic sequences encoding a receptor-like protein. EMBO J. 1986 Sep;5(9):2197–2202. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04484.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosen O. M. After insulin binds. Science. 1987 Sep 18;237(4821):1452–1458. doi: 10.1126/science.2442814. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Santerre R. F., Cook R. A., Crisel R. M., Sharp J. D., Schmidt R. J., Williams D. C., Wilson C. P. Insulin synthesis in a clonal cell line of simian virus 40-transformed hamster pancreatic beta cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jul;78(7):4339–4343. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.7.4339. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schalken J. A., Roebroek A. J., Oomen P. P., Wagenaar S. S., Debruyne F. M., Bloemers H. P., Van de Ven W. J. fur gene expression as a discriminating marker for small cell and nonsmall cell lung carcinomas. J Clin Invest. 1987 Dec;80(6):1545–1549. doi: 10.1172/JCI113240. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schnabel E., Mains R. E., Farquhar M. G. Proteolytic processing of pro-ACTH/endorphin begins in the Golgi complex of pituitary corticotropes and AtT-20 cells. Mol Endocrinol. 1989 Aug;3(8):1223–1235. doi: 10.1210/mend-3-8-1223. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seidah N. G., Gaspar L., Mion P., Marcinkiewicz M., Mbikay M., Chrétien M. cDNA sequence of two distinct pituitary proteins homologous to Kex2 and furin gene products: tissue-specific mRNAs encoding candidates for pro-hormone processing proteinases. DNA Cell Biol. 1990 Jul-Aug;9(6):415–424. doi: 10.1089/dna.1990.9.415. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seidah N. G., Marcinkiewicz M., Benjannet S., Gaspar L., Beaubien G., Mattei M. G., Lazure C., Mbikay M., Chrétien M. Cloning and primary sequence of a mouse candidate prohormone convertase PC1 homologous to PC2, Furin, and Kex2: distinct chromosomal localization and messenger RNA distribution in brain and pituitary compared to PC2. Mol Endocrinol. 1991 Jan;5(1):111–122. doi: 10.1210/mend-5-1-111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smeekens S. P., Avruch A. S., LaMendola J., Chan S. J., Steiner D. F. Identification of a cDNA encoding a second putative prohormone convertase related to PC2 in AtT20 cells and islets of Langerhans. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jan 15;88(2):340–344. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.2.340. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soreq H., Miskin R. Secreted proteins in the medium of microinjected Xenopus oocytes are degraded by oocyte proteases. FEBS Lett. 1981 Jun 15;128(2):305–310. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(81)80104-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sossin W. S., Fisher J. M., Scheller R. H. Cellular and molecular biology of neuropeptide processing and packaging. Neuron. 1989 May;2(5):1407–1417. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(89)90186-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thim L., Hansen M. T., Norris K., Hoegh I., Boel E., Forstrom J., Ammerer G., Fiil N. P. Secretion and processing of insulin precursors in yeast. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Sep;83(18):6766–6770. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.18.6766. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas G., Thorne B. A., Thomas L., Allen R. G., Hruby D. E., Fuller R., Thorner J. Yeast KEX2 endopeptidase correctly cleaves a neuroendocrine prohormone in mammalian cells. Science. 1988 Jul 8;241(4862):226–230. doi: 10.1126/science.3291117. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uhler M., Herbert E. Complete amino acid sequence of mouse pro-opiomelanocortin derived from the nucleotide sequence of pro-opiomelanocortin cDNA. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jan 10;258(1):257–261. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wells J. A., Estell D. A. Subtilisin--an enzyme designed to be engineered. Trends Biochem Sci. 1988 Aug;13(8):291–297. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(88)90121-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wise R. J., Barr P. J., Wong P. A., Kiefer M. C., Brake A. J., Kaufman R. J. Expression of a human proprotein processing enzyme: correct cleavage of the von Willebrand factor precursor at a paired basic amino acid site. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Dec;87(23):9378–9382. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.23.9378. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van den Ouweland A. M., van Duijnhoven H. L., Keizer G. D., Dorssers L. C., Van de Ven W. J. Structural homology between the human fur gene product and the subtilisin-like protease encoded by yeast KEX2. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Feb 11;18(3):664–664. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.3.664. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]