Abstract
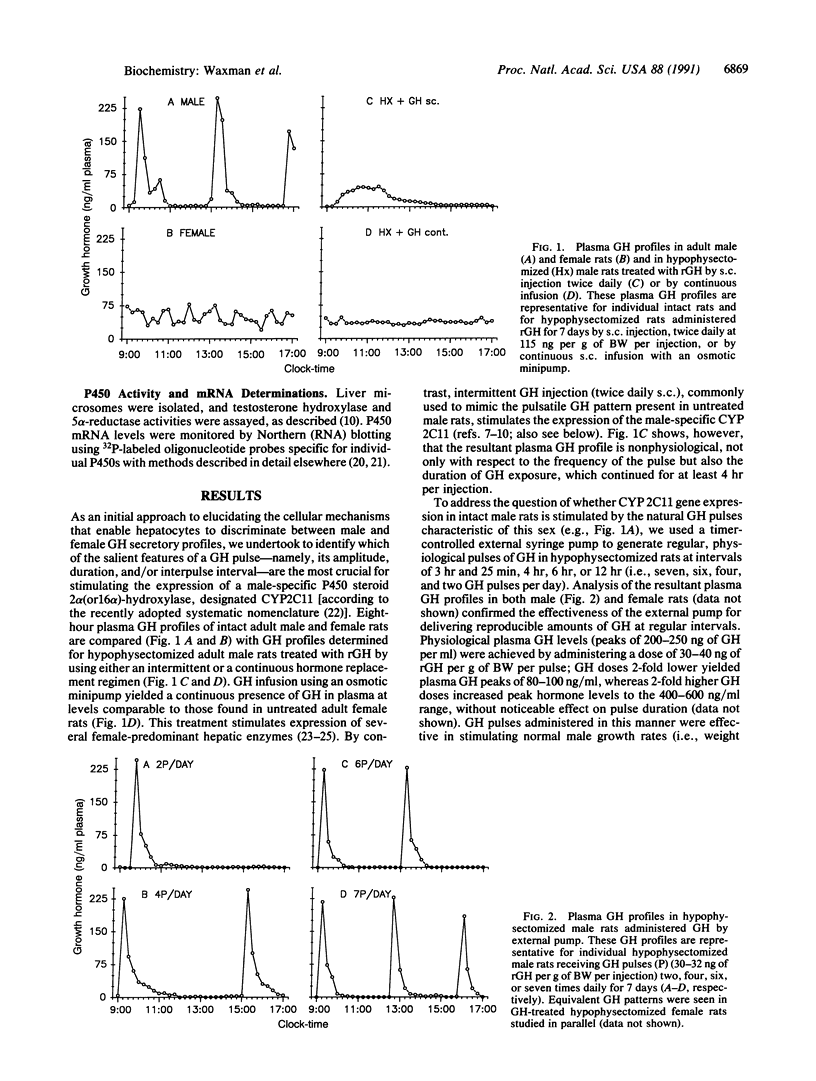
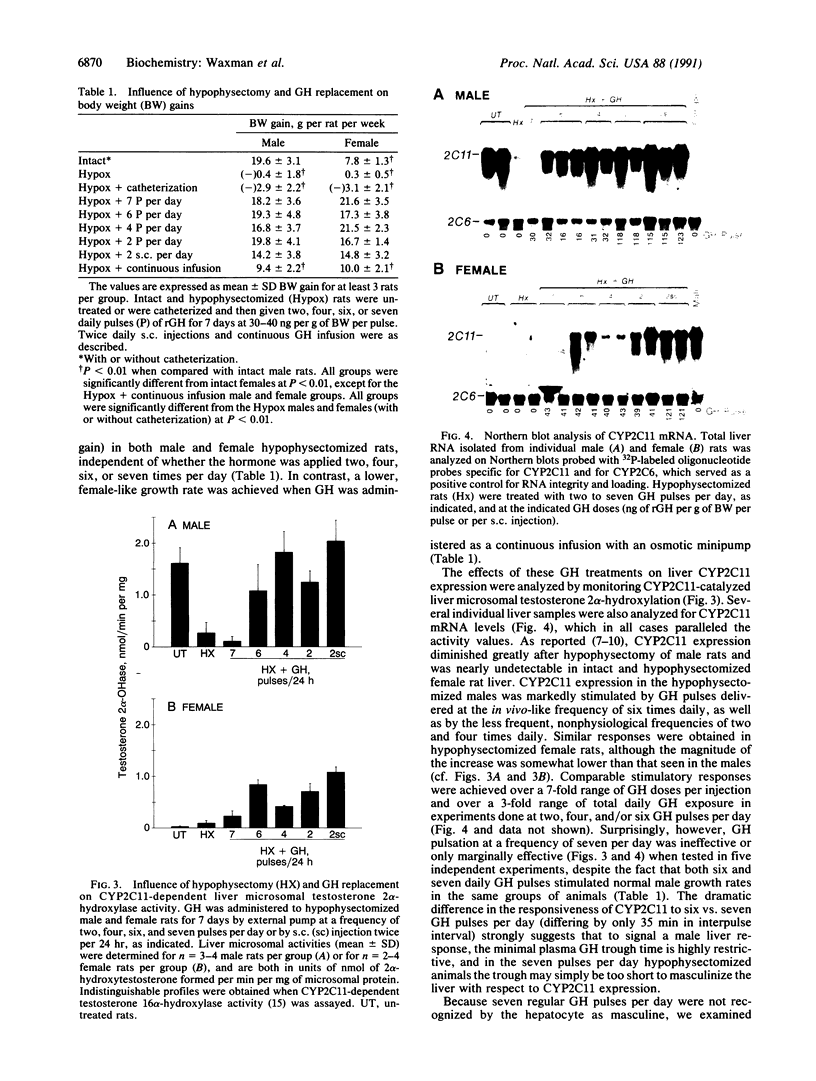
Plasma growth hormone (GH) profiles are sexually differentiated in many species and regulate the sex-dependence of peripubescent growth rates and liver function, including steroid hydroxylase cytochrome P450 expression, by mechanisms that are poorly understood. By use of an external pump to deliver to hypophysectomized rats pulses of rat GH of varying frequency and amplitude, a critical element for liver discrimination between male and female GH patterns was identified. Liver expression of the male-specific steroid 2 alpha (or 16 alpha)-hydroxylase P450, designated CYP2C11, was stimulated by GH at both physiological and nonphysiological pulse amplitudes, durations, and frequencies, provided that an interpulse interval of no detectable GH was maintained for at least 2.5 hr. This finding suggests that hepatocytes undergo an obligatory recovery period after stimulation by a GH pulse. This period may be required to reset a GH-activated intracellular signaling pathway or may relate to the short-term absence of GH receptors at the hepatocyte surface after a cycle of GH binding and receptor internalization. These requirements were distinguished from those necessary for the stimulation by GH of normal male growth rates in hypophysectomized rats, indicating that different GH responses and, perhaps, different GH-responsive tissues recognize distinct signaling elements in the sexually dimorphic patterns of circulating GH.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Asplin C. M., Faria A. C., Carlsen E. C., Vaccaro V. A., Barr R. E., Iranmanesh A., Lee M. M., Veldhuis J. D., Evans W. S. Alterations in the pulsatile mode of growth hormone release in men and women with insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1989 Aug;69(2):239–245. doi: 10.1210/jcem-69-2-239. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bick T., Youdim M. B., Hochberg Z. Adaptation of liver membrane somatogenic and lactogenic growth hormone (GH) binding to the spontaneous pulsation of GH secretion in the male rat. Endocrinology. 1989 Sep;125(3):1711–1717. doi: 10.1210/endo-125-3-1711. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bick T., Youdim M. B., Hochberg Z. The dynamics of somatogenic and lactogenic growth hormone binding: internalization to Golgi fractions in the male rat. Endocrinology. 1989 Sep;125(3):1718–1722. doi: 10.1210/endo-125-3-1718. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bullock P., Gemzik B., Johnson D., Thomas P., Parkinson A. Evidence from dwarf rats that growth hormone may not regulate the sexual differentiation of liver cytochrome P450 enzymes and steroid 5 alpha-reductase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jun 15;88(12):5227–5231. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.12.5227. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Charlton H. M., Clark R. G., Robinson I. C., Goff A. E., Cox B. S., Bugnon C., Bloch B. A. Growth hormone-deficient dwarfism in the rat: a new mutation. J Endocrinol. 1988 Oct;119(1):51–58. doi: 10.1677/joe.0.1190051. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doglio A., Dani C., Grimaldi P., Ailhaud G. Growth hormone stimulates c-fos gene expression by means of protein kinase C without increasing inositol lipid turnover. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Feb;86(4):1148–1152. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.4.1148. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goble F. C. Sex as a factor in metabolism, toxicity, and efficacy of pharmacodynamic and chemotherapeutic agents. Adv Pharmacol Chemother. 1975;13:173–252. doi: 10.1016/s1054-3589(08)60232-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gustafsson J. A., Mode A., Norstedt G., Skett P. Sex steroid induced changes in hepatic enzymes. Annu Rev Physiol. 1983;45:51–60. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.45.030183.000411. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janeczko R., Waxman D. J., Le Blanc G. A., Morville A., Adesnik M. Hormonal regulation of levels of the messenger RNA encoding hepatic P450 2c (IIC11), a constitutive male-specific form of cytochrome P450. Mol Endocrinol. 1990 Feb;4(2):295–303. doi: 10.1210/mend-4-2-295. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jansson J. O., Albertsson-Wikland K., Edén S., Thorngren K. G., Isaksson O. Effect of frequency of growth hormone administration on longitudinal bone growth and body weight in hypophysectomized rats. Acta Physiol Scand. 1982 Feb;114(2):261–265. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1982.tb06980.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jansson J. O., Edén S., Isaksson O. Sexual dimorphism in the control of growth hormone secretion. Endocr Rev. 1985 Spring;6(2):128–150. doi: 10.1210/edrv-6-2-128. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jansson J. O., Frohman L. A. Differential effects of neonatal and adult androgen exposure on the growth hormone secretory pattern in male rats. Endocrinology. 1987 Apr;120(4):1551–1557. doi: 10.1210/endo-120-4-1551. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson R. J. Diminution of pulsatile growth hormone secretion in the domestic fowl (Gallus domesticus): evidence of sexual dimorphism. J Endocrinol. 1988 Oct;119(1):101–109. doi: 10.1677/joe.0.1190101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kato R. Sex-related differences in drug metabolism. Drug Metab Rev. 1974;3(1):1–32. doi: 10.3109/03602537408993737. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kato R., Yamazoe Y., Shimada M., Murayama N., Kamataki T. Effect of growth hormone and ectopic transplantation of pituitary gland on sex-specific forms of cytochrome P-450 and testosterone and drug oxidations in rat liver. J Biochem. 1986 Oct;100(4):895–902. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a121802. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leung D. W., Spencer S. A., Cachianes G., Hammonds R. G., Collins C., Henzel W. J., Barnard R., Waters M. J., Wood W. I. Growth hormone receptor and serum binding protein: purification, cloning and expression. Nature. 1987 Dec 10;330(6148):537–543. doi: 10.1038/330537a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacGeoch C., Morgan E. T., Gustafsson J. A. Hypothalamo-pituitary regulation of cytochrome P-450(15) beta apoprotein levels in rat liver. Endocrinology. 1985 Nov;117(5):2085–2092. doi: 10.1210/endo-117-5-2085. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacLeod J. N., Shapiro B. H. Growth hormone regulation of hepatic drug-metabolizing enzymes in the mouse. Biochem Pharmacol. 1989 May 15;38(10):1673–1677. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(89)90316-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacLeod J. N., Shapiro B. H. Repetitive blood sampling in unrestrained and unstressed mice using a chronic indwelling right atrial catheterization apparatus. Lab Anim Sci. 1988 Oct;38(5):603–608. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mode A., Gustafsson J. A., Jansson J. O., Edén S., Isaksson O. Association between plasma level of growth hormone and sex differentiation of hepatic steroid metabolism in the rat. Endocrinology. 1982 Nov;111(5):1692–1697. doi: 10.1210/endo-111-5-1692. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan E. T., MacGeoch C., Gustafsson J. A. Hormonal and developmental regulation of expression of the hepatic microsomal steroid 16 alpha-hydroxylase cytochrome P-450 apoprotein in the rat. J Biol Chem. 1985 Oct 5;260(22):11895–11898. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nebert D. W., Nelson D. R., Coon M. J., Estabrook R. W., Feyereisen R., Fujii-Kuriyama Y., Gonzalez F. J., Guengerich F. P., Gunsalus I. C., Johnson E. F. The P450 superfamily: update on new sequences, gene mapping, and recommended nomenclature. DNA Cell Biol. 1991 Jan-Feb;10(1):1–14. doi: 10.1089/dna.1991.10.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norstedt G., Palmiter R. Secretory rhythm of growth hormone regulates sexual differentiation of mouse liver. Cell. 1984 Apr;36(4):805–812. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90030-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noshiro M., Negishi M. Pretranslational regulation of sex-dependent testosterone hydroxylases by growth hormone in mouse liver. J Biol Chem. 1986 Dec 5;261(34):15923–15927. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pampori N. A., Agrawal A. K., Shapiro B. H. Renaturalizing the sexually dimorphic profiles of circulating growth hormone in hypophysectomized rats. Acta Endocrinol (Copenh) 1991 Mar;124(3):283–289. doi: 10.1530/acta.0.1240283. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ram P. A., Waxman D. J. Hepatic P450 expression in hypothyroid rats: differential responsiveness of male-specific P450 forms 2a (IIIA2), 2c (IIC11), and RLM2 (IIA2) to thyroid hormone. Mol Endocrinol. 1991 Jan;5(1):13–20. doi: 10.1210/mend-5-1-13. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ram P. A., Waxman D. J. Pretranslational control by thyroid hormone of rat liver steroid 5 alpha-reductase and comparison to the thyroid dependence of two growth hormone-regulated CYP2C mRNAs. J Biol Chem. 1990 Nov 5;265(31):19223–19229. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogers S. A., Hammerman M. R. Growth hormone activates phospholipase C in proximal tubular basolateral membranes from canine kidney. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Aug;86(16):6363–6366. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.16.6363. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roupas P., Herington A. C. Cellular mechanisms in the processing of growth hormone and its receptor. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 1989 Jan;61(1):1–12. doi: 10.1016/0303-7207(89)90184-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro B. H., MacLeod J. N., Pampori N. A., Morrissey J. J., Lapenson D. P., Waxman D. J. Signalling elements in the ultradian rhythm of circulating growth hormone regulating expression of sex-dependent forms of hepatic cytochrome P450. Endocrinology. 1989 Dec;125(6):2935–2944. doi: 10.1210/endo-125-6-2935. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stred S. E., Stubbart J. R., Argetsinger L. S., Shafer J. A., Carter-Su C. Demonstration of growth hormone (GH) receptor-associated tyrosine kinase activity in multiple GH-responsive cell types. Endocrinology. 1990 Nov;127(5):2506–2516. doi: 10.1210/endo-127-5-2506. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tannenbaum G. S., Martin J. B. Evidence for an endogenous ultradian rhythm governing growth hormone secretion in the rat. Endocrinology. 1976 Mar;98(3):562–570. doi: 10.1210/endo-98-3-562. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waxman D. J. Interactions of hepatic cytochromes P-450 with steroid hormones. Regioselectivity and stereospecificity of steroid metabolism and hormonal regulation of rat P-450 enzyme expression. Biochem Pharmacol. 1988 Jan 1;37(1):71–84. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(88)90756-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waxman D. J., LeBlanc G. A., Morrissey J. J., Staunton J., Lapenson D. P. Adult male-specific and neonatally programmed rat hepatic P-450 forms RLM2 and 2a are not dependent on pulsatile plasma growth hormone for expression. J Biol Chem. 1988 Aug 15;263(23):11396–11406. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waxman D. J., Morrissey J. J., LeBlanc G. A. Female-predominant rat hepatic P-450 forms j (IIE1) and 3 (IIA1) are under hormonal regulatory controls distinct from those of the sex-specific P-450 forms. Endocrinology. 1989 Jun;124(6):2954–2966. doi: 10.1210/endo-124-6-2954. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waxman D. J., Morrissey J. J., MacLeod J. N., Shapiro B. H. Depletion of serum growth hormone in adult female rats by neonatal monosodium glutamate treatment without loss of female-specific hepatic enzymes P450 2d (IIC12) and steroid 5 alpha-reductase. Endocrinology. 1990 Feb;126(2):712–720. doi: 10.1210/endo-126-2-712. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waxman D. J., Ram P. A., Notani G., LeBlanc G. A., Alberta J. A., Morrissey J. J., Sundseth S. S. Pituitary regulation of the male-specific steroid 6 beta-hydroxylase P-450 2a (gene product IIIA2) in adult rat liver. Suppressive influence of growth hormone and thyroxine acting at a pretranslational leve;. Mol Endocrinol. 1990 Mar;4(3):447–454. doi: 10.1210/mend-4-3-447. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waxman D. J. Rat hepatic P450IIA and P450IIC subfamily expression using catalytic, immunochemical, and molecular probes. Methods Enzymol. 1991;206:249–267. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(91)06095-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winer L. M., Shaw M. A., Baumann G. Basal plasma growth hormone levels in man: new evidence for rhythmicity of growth hormone secretion. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1990 Jun;70(6):1678–1686. doi: 10.1210/jcem-70-6-1678. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




