Abstract
The diversity and abundance of retrievable pelagic heterotrophic bacteria in Kongsfjorden, an Arctic fjord, was studied during the summer of 2011 (June, August, and September). Retrievable bacterial load ranged from 103 to 107 CFU L−1 in June, while it was 104–106 CFU L−1 in August and September. Based on 16S rRNA gene sequence similarities, a higher number of phylotypes was observed during August (22 phylotypes) compared to that during June (6 phylotypes) and September (12 phylotypes). The groups were classified into four phyla: Firmicutes, Actinobacteria, Proteobacteria, and Bacteroidetes. Bacteroidetes was represented only by a single member Leewenhoekiella aequorea during the three months and was dominant (40%) in June. However, this dominance changed in August to a well-known phytopathogenic species Rhodococcus fascians (32%), which could be a result of decrease in the phytoplankton biomass following the secondary bloom. It is the first report of Halomonas titanicae isolation from the Arctic waters. It showed an increase in its abundance with the intrusion of Atlantic water into Kongsfjorden. Increased abundance of Psychrobacter species in the late summer months coincided with the presence of cooler waters. Thus, the composition and function of heterotrophic bacterial community was fundamentally different in different months. This could be linked to the changes in the water masses and/or phytoplankton bloom dynamics occurring in Arctic summer.
Keywords: Kongsfjorden, Retrievable heterotrophic bacteria, 16S rRNA, Arctic fjord
Introduction
Arctic marine ecosystems have recently received increased attention, as they are considered to be sensitive to the climate change.1 Kongsfjorden, a glacial fjord in the Svalbard archipelago, Spitsbergen 79° N–12° E, is a key site for the monitoring of Arctic biodiversity and also considered for modeling in climate change studies.1 The marine ecosystem of Kongsfjorden is well explored with regards to hydrography, mesozooplankton, and higher trophic levels, while the knowledge on its bacterial diversity still remains insufficient.2 The information about the bacterial assemblage at a given time-point could convey vital information pertaining to the ecological aspects of the environment. Several factors have been reported to affect the composition of the marine bacterial communities.3 Phytoplankton composition and thereby substrate composition and concentration have been found to play important roles in the dynamics of bacterial communities.4, 5 Heterotrophic bacteria can support the growth of phytoplankton via recycling of nutrients, but at the same time, they also compete with phytoplankton for essential nutrients. Both alive and dead (or dying) phytoplankton release organic compounds that are consumed by heterotrophic bacteria; and these interactions vary with the bacterial species and the physiological status of the phytoplankton.6 Indeed, bacteria sustain at a high level immediately after the collapse of a bloom, as they continue to use the organic matter released from the dying phytoplankton.7 Despite the variation in phytoplankton composition and environmental conditions, a limited number of taxa are consistently found to dominate bloom-associated bacterial communities. The most frequent bacteria, identified by 16S rRNA gene-based analyses, are the members of the classes, Flavobacteria and α-Proteobacteria, and also include Rhodobacteraceae and γ-Proteobacteria.7, 8 An insight, about roles that individual bacterial species play in the formation of blooms and their eventual collapse, will ultimately unravel the forces that control energy flow in the fjord as well as the cycling of compounds, which ultimately influence the climate change.
Culture-dependent and -independent methods using oligonucleotide probes and/or the cloning of environmental DNA have indicated occurrence of exceptionally diverse bacterial communities thriving in Arctic fjord habitats.9, 10 In the recent studies of Piquet et al.11, 12 on the pelagic microbial communities of Kongsfjorden, the diversity of non-culturable communities of bacteria, phytoplankton, and protists was monitored. However, very few attempts have been made to understand the diversity of retrievable heterotrophic bacteria of this ecosystem.13, 14
The present study attempts to understand the taxonomy of retrievable heterotrophic bacteria in Kongsfjorden during the summer of 2011. We carried out an investigation in June–September 2011 to determine the changes in retrievable bacterial community. Observation on phytoplankton blooming pattern using SAMS mooring for the year 2010 (Supplementary Fig. 1) indicated that sampling during these summer months maximized the possibility of high heterotrophic bacterial activity and diversity due to the collapse of the spring bloom (June–July) and the secondary bloom (August–September). In addition, we also address the ecological significance of the various groups of bacteria present in Kongsfjorden.
Materials and methods
Sampling site
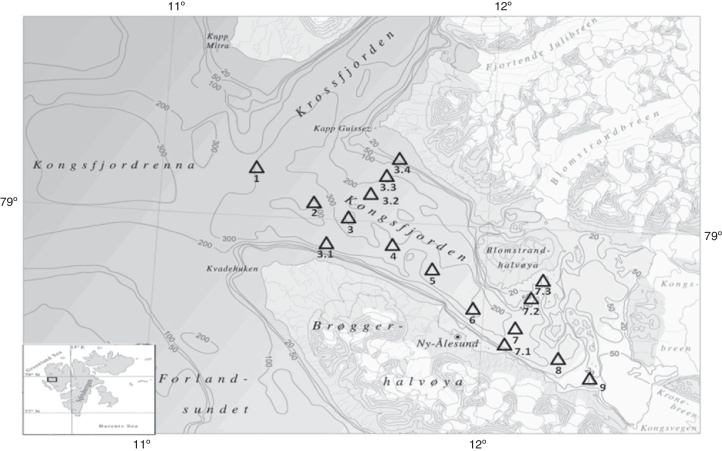
Kongsfjorden (Fig. 1) is a polar fjord located between 78°04′ N–79°05′ N and 11°03′ E–13°03′ E on the west coast of Spitsbergen, Svalbard Archipelago. The fjord is characterized by a weak tidal range (∼2 m) strongly influenced by the topography and adjacent ocean. Western Svalbard coastal waters are influenced by the northernmost extension of the warm North Atlantic Current.15 Kongsfjorden, at its inner end, has three main glaciers, viz., Kongsbreen, Conwaybreen, and Blomstrandbreen, draining into it and providing the major source of fresh water. Thus, Kongsfjorden is under the influence of both meltwater of glacial origin as well as by mild temperatures mediated by the inflow of Atlantic water.
Fig. 1.
Bathymetric map of Kongsfjorden with sampling locations. Samples were collected from 16 stations. Stations 1–9 along the fjord and stations 3.1–3.4 and 7.1–7.3 at the intersection of station 3 and 7, respectively.
Sampling method
During the year 2011, water samples were collected from 16 locations (Fig. 1) at various depths from 5 m to a maximum of 100 m in the month of June, August, and September. In order to monitor the effect of phytoplankton assemblage on retrievable heterotrophic bacteria, most of our sampling depths were restricted to upper 40 m with few exceptions in August where weak fluorescence was also observed at higher depths (Supplementary Table 1). The sampling was done following the hydrological observations with a conductivity-temperature-depth (CTD) profiler (SBE 19 plus V2, Sea Bird Electronics, Bellevue, WA, USA) equipped with a fluorescence sensor (Wet Labs, Philomath, USA). The average volume of the transformed Atlantic water inside Kongsfjorden was calculated with the upper boundary (thickness) of the water mass, which was delineated using a combination of its characteristic hydrography values16 with upper limit temperature of 3 °C and salinity of >34.65 psu. Water samples were collected aseptically in sterile glass bottles (Duran Schott, Stafford, UK). The samples were immediately subjected to analysis in the shore laboratory.
Total counts, culture, and isolation of heterotrophic bacteria
Total cells in the water samples (10 mL each) collected from all the discrete depths were stained with 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole (DAPI)17 before counting. Cells stained with DAPI were first fixed with filter sterilized particle free buffered formaldehyde (final concentration, 3.7%) to preserve the cell morphology and improve the staining efficiency. The stained cells were filtered through 0.22 μ black polycarbonate membranes (Nucleopore Track-Etch Membrane, Whatman, Maidstone, UK) and counted under an Olympus epifluorescence microscope (BX 51) with the aid of an Olympus U-MWU2 filter (Excitation 330–385 nm and Emission 420 nm). Counting was done on a Whipple grid with a 100× objective (Olympus UPLNFLN, Tokyo, Japan).
Water samples were spread plated using 100 μL aliquot on pre cooled (4 °C) quarter strength Zobell Marine Agar (ZMA) and incubated at 4 °C for 1–2 weeks. Colonies with unique morphological features were isolated and sub-cultured to obtain pure cultures.
PCR amplification of the 16S rDNA, sequencing and phylogenetic analysis
Cell biomass for DNA extraction was obtained by growing the pure cultures in quarter strength Zobell Marine Broth (ZMB). Total bacterial genomic DNA was extracted using ChargeSwitch gDNA mini bacteria kit (Invitrogen, Carlsbad, CA, USA). The purity of the DNA extracts was verified by gel electrophoresis on 1% agarose. The 16S rRNA gene was amplified using the universal bacterial 16S primers: forward (27f) 5′-AGA GTT TGA TCM TGG CTC AG-3′ and reverse (1492r) 5′-GGT TAC CTT GTT ACG ACT T-3′.18 The DNA amplification in a final reaction volume of 50 μL containing 0.3 pM/μL of each primer, 1.5 mM MgCl2, 200 μM dNTPs and 2.5 U Taq DNA polymerase (Invitrogen, Carlsbad, CA, USA) was carried out in a thermocycler (BioRad CFX 96) with the following conditions: initial denaturation at 94 °C for 2 min followed by 29 cycles of 30 s at 95 °C, 30 s at 45 °C and 2 min at 72 °C, and a final extension of 10 min at 72 °C. Amplification was confirmed by electrophoresis in 1% agarose gel. The amplicons were purified using ChargeSwitch Pro PCR cleanup kit (Invitrogen, Carlsbad, CA, USA). The eluted fragments were sequenced using an automated DNA sequencing system (Applied Biosystems, Carlsbad, CA, USA). The obtained sequences were checked for chimera with the CHIMERA detection program (http://rdp8.cme.msu.edu/cgis/chimera.cgi).19 The 16S rDNA sequences of the isolates (∼1200 bp) were compared with the type strains belonging to the same phylogenetic group, using the Seqmatch tool of Ribosomal Database Project (http://rdp.cme.msu.edu/).19 SINA v1.2.1120 software was used to align the 16S rRNA gene sequences. The phylogenetic trees were constructed using maximum likelihood and neighbor-joining methods using MEGA Version 521 and 1000 subsamples were generated using the bootstrap analysis. The 16S rRNA gene sequences of the isolated strains were deposited with accession number HE800807-HE800839, HE815462-HE815463, HG795014-HG795016, HF569156-HF569159 and HF913434-HF913440 in the EMBL database.
Results
Physical properties of the sampling sites
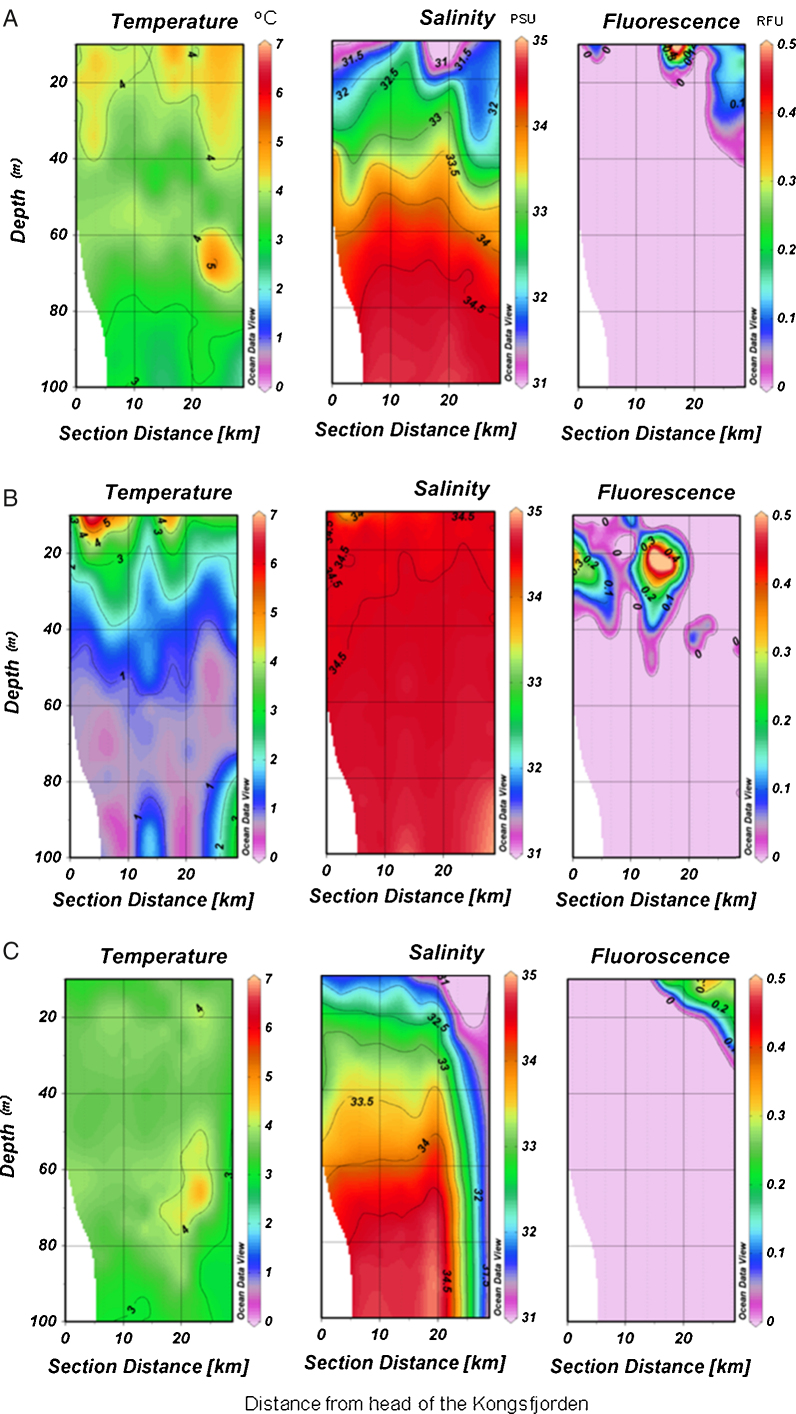
The details about the geographic location of the stations selected for sampling during summer 2011 are given in Fig. 1. The water column was warmer (4 °C) during June compared to that in August, where temperature decreased gradually along with the depth, except at the surface, which was warmer in the vicinity of the glacier as depicted in Fig. 2. Water temperature was uniform (4 °C) throughout the column during September. Salinity ranged from 31 to 35 psu during summer 2011 (Fig. 2). The surface water was less saline during June and September (∼31 psu), while salinity increased along with the depth up to ∼35 psu. Autotrophic biomass (fluorescence) was restricted to shallower depths during September and was higher during June and August as compared to that in September (Fig. 2). The abundance was confined in the vicinity of Kongsbreen glacier during August, whereas during June and September, it was more toward the mouth of Kongsfjorden (Fig. 2). The average volume of the transformed Atlantic water inside Kongsfjorden was 7.9 km3, 27.2 km3 and 12 km3 during June, August, and September, respectively.
Fig. 2.
Physiochemical properties of water samples collected from Kongsfjorden in June (A), August (B), and September (C) 2011.
Total and retrievable bacterial count and phylogenetic identification of bacterial isolates
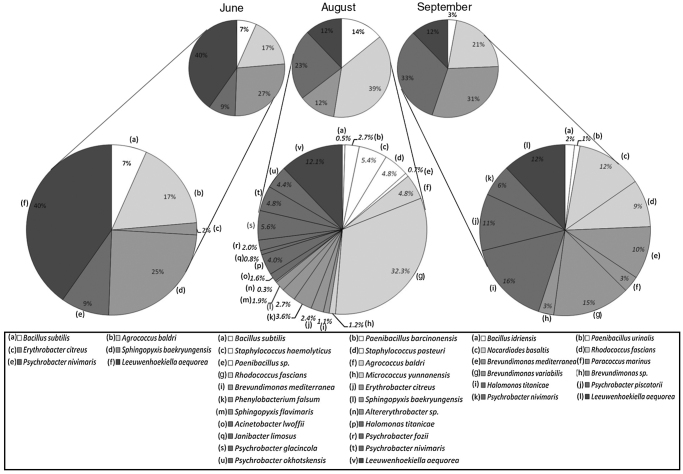
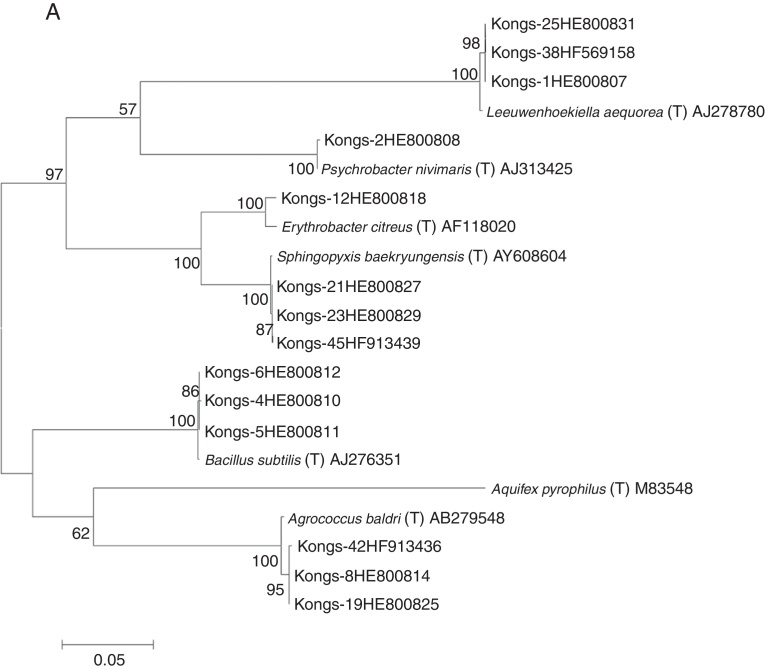
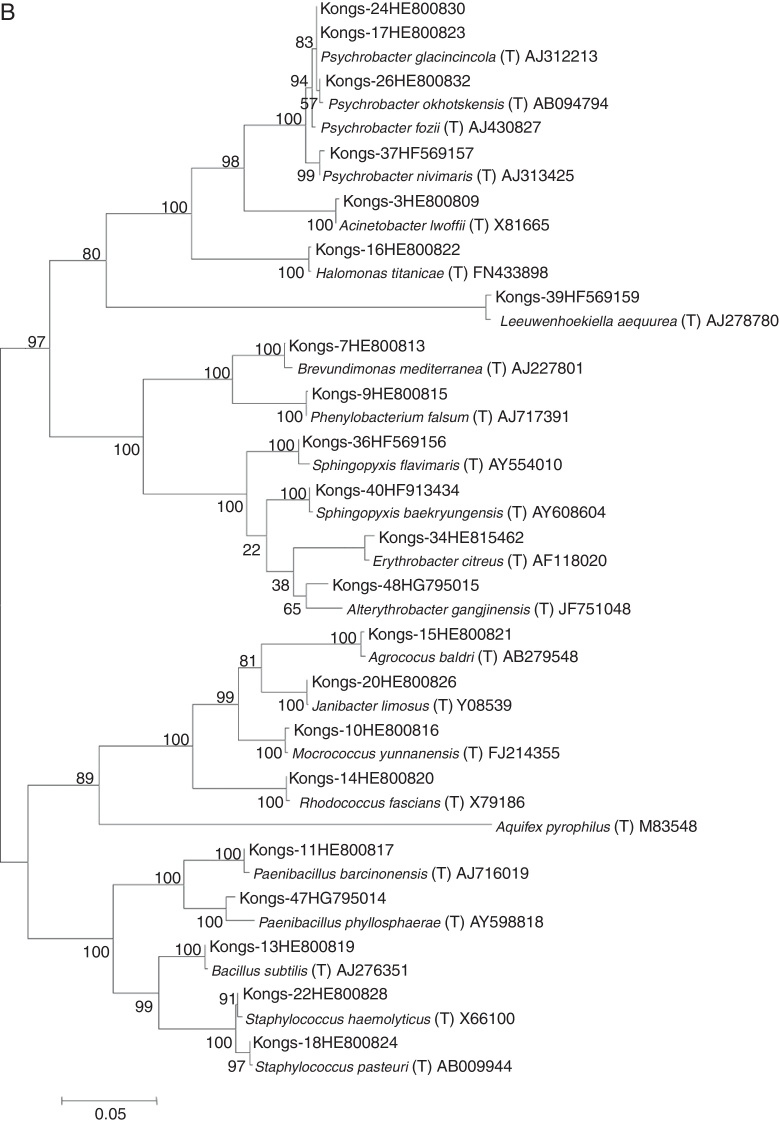
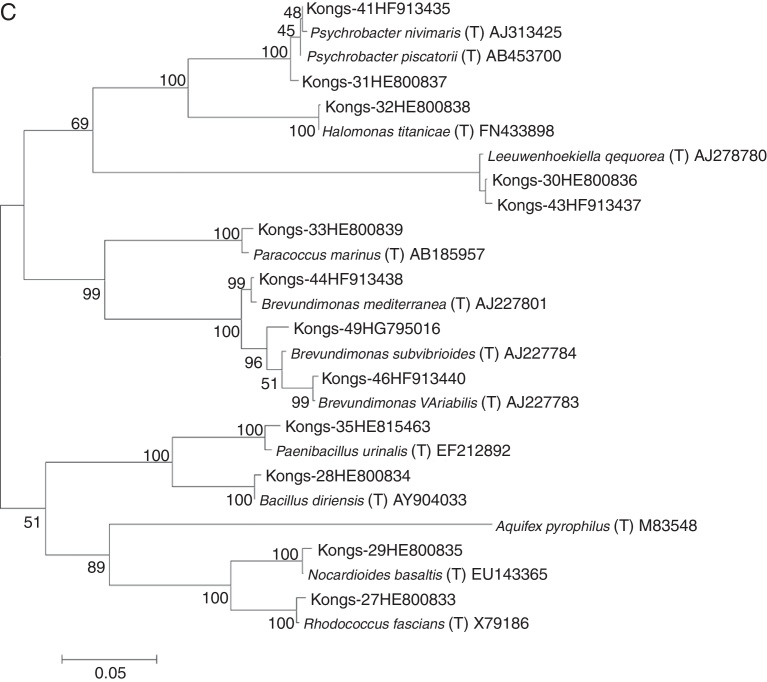
Total bacterial count during June–September ranged from 107 to 109 cells L−1. During June and August, the cell counts were in the range of 107–108 cells L−1, while in September the bacterial load was higher (107–109 cells L−1). The lowest bacterial count (2.3 × 107 cells L−1) was recorded in the vicinity of Kongsbreen glacier during June, while it was higher (108 cells L−1) in August. The highest bacterial load (2.7 × 109 cells L−1) was observed during September toward the mouth of Kongsfjorden. The retrievable bacterial load during June ranged from 103 to 106 CFU L−1, while during August and September, it was in the range of 104–106 CFU L−1. A total of 117, 332, and 107 bacterial isolates were recovered in June, August, and September, respectively, from the water samples collected at various depths. The isolates having >97% 16S rRNA gene sequence similarity with the type strain were considered as phylotypes. Using the representative phylotypes, all the bacterial isolates recovered from samples collected in June, August, and September 2011 were categorized into 6, 22, and 12 phylotypes, respectively; and the obtained results about abundance of each species are given in Fig. 3. The phylogenetic trees illustrating the evolutionary relationships among the bacterial isolates are presented in Fig. 4A–C. Two bacterial strains, Paenibacillus sp. (Kongs – 47, HG795014) and Altererythrobacter sp. (Kongs – 48, HG795015) recovered from water samples of August and one strain, Brevundimonas sp. (Kongs – 49, HG795016), recovered from September could not be identified as any known species due to low sequence similarity (≤97%) with any type strain, and probably might represent new species. The closest phylogenetic relative of Kongs–47 was type strain of Paenibacillus phyllosphaerae (96%) and those of Kongs–48 and Kongs–49 were Altererythrobacter gangjinensis (96%) and Brevundimonas subvibrioides (97%), respectively (Fig. 4A).
Fig. 3.
Percentage composition and abundance of heterotrophic bacterial species belonging to the phylum Firmicutes ( ), Actinobacteria (
), Actinobacteria ( ), α-Proteobacteria (
), α-Proteobacteria ( ), γ-Proteobacteria (
), γ-Proteobacteria ( ) and Bacteroidetes (
) and Bacteroidetes ( ) isolated from Kongsfjorden water samples during June, August, and September 2011.
) isolated from Kongsfjorden water samples during June, August, and September 2011.
Fig. 4.
Phylogenetic tree constructed on the basis of 16S rRNA gene sequences showing the relationship among the bacterial strains (prefix with Kongs), obtained from the water samples collected during June (A), August (B) and September (C) 2011 from Kongsfjorden, with their nearest phylogenetic type strains. The accession number of 16s rRNA gene sequence of the strains is denoted next to its name. Phylogenetic tree was constructed by maximum likelihood method. Numbers shown at nodes are bootstrap values. The bar represents 0.02 substitutions per alignment position.
Bacterial diversity at Kongsfjorden
The bacterial isolates retrieved from the water samples belonged to five phyla: Firmicutes, Actinobacteria, α-Proteobacteria, γ-Proteobacteria and Bacteroidetes (Fig. 3). The phylum Bacteroidetes was the most dominant (40%) during June and was entirely represented by the species Leeuwenhoekiella aequorea. It was followed by α-Proteobacteria (27%), Actinobacteria (17%), γ-Proteobacteria (9%) and Firmicutes (7%). Sphingopyxis baekryungensis (25%) and Erythrobacter citreus (2%) constituted α-Proteobacterial population while Agrococcus baldri, Psychrobacter nivimaris, and Bacillus subtilis represented the phyla Actinobacteria, γ-Proteobacteria, and Firmicutes, respectively.
The retrievable bacterial diversity was higher during August; it was represented by 22 phylotypes including two unclassified sequences (Paenibacillus sp. and Altererythrobacter sp.). The population was dominated by Actinobacteria (39%) and γ-Proteobacteria (23%), while Firmicutes (14%), α-Proteobacteria (12%), and Bacteroidetes (12%) shared similar abundance. The abundance of Firmicutes was almost twice of that in June, and was mainly constituted by the genus Staphylococcus, which was represented by Staphylococcus haemolyticus and Staphylococcus pasteuri (5% of each). A well-known phytopathogenic bacterium Rhodococcus fascians constituted to the most (32%) of the Actinobacterial population, which increased by 22% as compared to that in June. A total of five genera (Brevundimonas, Erythrobacter, Phenylobacterium, Sphingopyxis, and Altererythrobacter) were recovered within the class α-Proteobacteria, where Phenylobacterium falsum was major contributor (4%). However, the total abundance of this phylum decreased by 15% as compared to June. γ-Proteobacteria was represented by four genera and seven species. The major fraction was constituted by the genus Psychrobacter (17%), which was represented by Psychrobacter fozii (2%), Psychrobacter glacincola (6%), P. nivimaris (4%), and Psychrobacter okhotskensis (4%). Other genera included Acinetobacter (2%), Halomonas (4%), and Janibacter (1%). In June, L. aequorea was the only species recovered under the phylum Bacteroidetes; however, its abundance decreased by 28% during August.
During September, Proteobacteria was the major phylum with α-Proteobacteria (31%) and γ-Proteobacteria (33%) being dominant, followed by Actinobacteria (21%), Bacteroidetes (12%), and Firmicutes (3%). Halomonas titanicae (16%) represented the major fraction of γ-Proteobacteria, while Brevundimonas variabilis (15%) was dominant γ-Proteobacteria. Firmicutes was represented by two bacterial species, Bacillus idriensis (2%) and Paenibacillus urinalis (1%). The population of Actinobacteria was reduced by 18% in September as compared to that in August and it was represented by Nocardioides basaltis (12%) and R. fascians (9%). L. aequorea was the only species representing Bacteroidetes even in September with an almost equal abundance as in August.
Discussion
The physico-chemical conditions in the Kongsfjorden water column are highly dynamic, especially in the summer, when there is a large scale flux of cold Arctic water from the eastern side and intrusion of warm Atlantic water (AW) on the western side.1 Kongsfjorden is one of the western fjords those receive AW. According to the moored observatories, the fjord normally receives the maximum content of AW in late summer, while through the fall and winter, the fjord water masses are gradually replaced by fresher and cold Arctic water.16 In the present study, the fjord was found to receive highest volume of transformed Atlantic water (27.2 km3) during August as compared to June (7.9 km3) and September (12 km3). The complex dynamics of the fjord water masses may be regarded as the major driving force for the variability in phytoplankton assemblages. During June and September, the autotrophic biomass was confined toward the mouth of the fjord, while during August it was higher in the proximity of glacier. During June and September, the glacial melt water input could be higher as evident by the lower salinity values in the upper water column. High sediment concentrations derived from the input of melted glacial water can limit the light availability for phytoplankton growth near the glaciers.12 The euphotic zone can be restricted to the upper 0.3 m close to the glaciers,22 leading to highly unfavorable conditions for phytoplankton growth.23
The bacteria–phytoplankton interactions during bloom events are complex and change throughout the lifetime of the bloom. An earlier study by Jankowska et al.,24 conducted during summer 1999, reported bacterioplankton abundance in the range of 108–109 cells L−1 in Kongsfjorden and the adjacent Krossfjorden, while in our study the total cell count varied from 107 to 109 cells L−1. This variable distribution of the bacteria during the observation period could be primarily attributed to the variation in the water masses and/or phytoplankton distribution. During August, the higher bacterial cell count toward head of the fjord coincided with a higher phytoplankton density. The localized and transient increase in the abundance of phytoplankton could alter the levels of dissolved organic matter, particularly during the collapse of the phytoplankton bloom.3 As phytoplankton blooms are often seasonal events and transient in nature, the abundance and activity of heterotrophic bacteria vary accordingly. These processes are partly balanced by a subsequent increase in the activity of heterotrophic bacteria, which transform phytoplankton-derived organic matter.3 The heterotrophic retrievable counts in Kongsfjorden water were markedly dynamic ranging from 103 to 107 CFU L−1 during summer 2011. Previous studies from Kongsfjorden have reported similar findings13, 14 with low counts, that can be attributed to the culture-dependent approach using only one medium (ZMA).14 The use of different media and/or culture conditions can perhaps improve the viable heterotrophic bacterial counts.
Although the phytoplankton composition varies with the environmental conditions, a limited number of taxa are consistently found to dominate bloom-associated bacterial communities. The 16S rRNA gene sequences corresponding to α-Proteobacteria, Firmicutes and γ-Proteobacteria were earlier reported from freshwater as well as marine water samples of the Kongsfjorden.11 In the current study, the phyla, Bacteroidetes and Actinobacteria, were also retrieved along with α-Proteobacteria, Firmicutes, and γ-Proteobacteria. The predominance of Actinobacteria, Proteobacteria, and Bacteroidetes has already been reported in Arctic water, ice, and sediments.11, 14, 25, 26 During June a remarkable dominance of Bacteroidetes represented entirely by L. aequorea was seen. The second most abundant species, during June, was S. baekryungensis – a yellow-pigmented α-Proteobacteria. Specific associations between phytoplankton and certain species of Bacteroidetes and α-Proteobacteria have been found in laboratory conditions.7, 8, 27 The metabolic properties of these bacteria enable them to respond promptly to the transient nutrient pulses, which are a hallmark of phytoplankton blooms.3
Culture-independent studies have shown that Arctic waters harbor diverse taxa including Acidobacteria, Planctomycetes, Lentisphaerae, and Verrucomicrobiae9, 10, 28, 29 which could be due to the recalcitrance of these bacterial groups on culture media. In contrast to several other major marine bacterial lineages, such as the SAR86 and SAR116 clades, which are either difficult to culture or have not yet been brought into culture, the cultivable representatives are available for several important groups including Bacteroidetes and α-Proteobacteria.30 Indeed, cultivated representatives of these two groups have frequently been isolated from blooms and in vitro enrichment cultures of different phytoplankton31, 32, 33 and have even been found to be directly attached to the phytoplankton cells during a bloom.34 In fact, the nature of these bacterial–phytoplankton interactions ranges from mutualistic to parasitic. Some bacteria provide their hosts with essential vitamins and nutrients and bestow resistance against toxic metabolic byproducts, whereas others compete with their hosts for nutrients or produce algicidal compounds.3
The shift of bacterial community from June to August 2011 could be attributed to change in the environmental conditions and differences in the depth of isolation of bacterial species (Supplementary Table 1), at least in part as the effects of physicochemical properties. For instance, the increased phytoplankton abundance in August could promote the growth of R. fascians (an Actinobacteria), a well-known phytopathogen, which constituted 32% of the total retrievable bacterial diversity during this period. However, its association has only been reported with higher plants35, 36 and the same needs to be examined in this context. Mergaert et al.37 observed that a large proportion of facultative and psychrotrophic strains isolated from Arctic and Antarctic seawaters can be grouped into the R. fascians cluster. The studies based on stable carbon isotope probing have demonstrated that in addition to the members of α-Proteobacteria and Bacteroidetes, Actinobacteria and γ-Proteobacteria assimilate algal extracts quickly; these phyla can express a broad range of hydrolases in immediate response to the availability of phytoplankton detritus.38 Thus, oscillations in the bacterial diversity perhaps provide a clue for biochemical process and related changes functioning in the ecosystem.
In September 2011, the most abundant species recovered from the water sample was H. titanicae. This is the first report on the occurrence of H. titanicae in Kongsfjorden water. The type strain of this species has been isolated from the samples of rusticles collected from the RMS Titanic wreck site at a depth of ∼3000 m in Atlantic Ocean and was found to be associated with corrosion of iron wrecks.39 A rapid and overwhelming intrusion of Atlantic water across the shelf and into the fjord occurs during mid-summer, and the fjord water switches from being Arctic dominant to Atlantic dominant.16 Similar observations were recorded during our study where the volume of the transformed Atlantic water was found to increase during late summer (August and September). A recent study from North Atlantic Ocean shows that distinct water bodies host different bacterial populations, which may serve as biological markers for oceanic provinces.40 Similarly, Fu et al.41 found water mass to be the most important factor for the distribution of marine Rhodobacterales communities in the Arctic marine system. Thus, the increased population of H. titanicae could be due to the increased intrusion of Atlantic water into Kongsfjorden during this period.
During the seasonal shift, along with the phytoplankton bloom dynamics, temperature could be one of the most important parameters that determine the distribution of the bacterial communities and affect cell structure and function. Low temperatures reduce biochemical reaction rates and substrate transport. Not surprisingly, an organism's compatibility with the temperature of its habitat is ultimately determined by its underlying genetic structure. The genus Psychrobacter, under γ-Proteobacteria, includes a group of Gram-negative, heterotrophic bacteria, and among them, many Psychrobacter species are capable to grow at low temperatures. The members of this genus can even grow at temperatures as low as −20 °C and they have frequently been isolated from various cold environments, including Antarctic and Arctic sea ice.42, 43, 44, 45, 46 In the present study, we observed a high occurrence of Psychrobacter species with a decrease in temperature from June to September. During August and September, the water column was colder than that in June, which coincides with the maximum retrieval of Psychrobacter species in these months. P. glacincola, P. fozii, and P. nivimaris retrieved from Kongsfjorden belong to the same type strains reported earlier from Antarctic regimes.44, 47, 48 Several similarities exist between the marine regimes of Arctic and Antarctica; however, there are also fundamental differences in water masses and water currents. Whether these differences influence the distribution and development of bacterial community is still an open question. In a study by Brinkmeyer et al.,42 the analysis of 16S rRNA gene clone libraries from multiple Arctic and Antarctic samples revealed a high occurrence of closely overlapping 16S rRNA gene clone and the isolates’ sequences. Approximately 50 and 36% sequences were identified as γ-Proteobacteria in Arctic and Antarctic samples, respectively. The general similarity of bacterial phylotypes in Arctic and Antarctic samples implies that probably similar selective mechanisms occur at both the poles. However, the analysis at the conservative gene level of 16S rRNA is not sufficient to determine if the same species are present at both poles. Other analytical methods, e.g., DNA–DNA hybridization, might elucidate the diversity that goes undetectable by 16S rRNA gene sequencing.
Conclusion
The heterotrophic retrievable counts in Kongsfjorden water were markedly dynamic ranging from 103 to 107 CFU L−1 during summer 2011. The variable distribution of the retrievable heterotrophic bacteria during the observation period could primarily be attributed to the variation in the water masses and/or phytoplankton distribution. Increased phytoplankton concentration during August could promote the growth of R. fascians, a well-known phytopathogen. The occurrence of H. titanicae from Kongsfjorden water has been reported first time. The increased population of H. titanicae during August and September could be due to the higher intrusion of Atlantic water into Kongsfjorden during this period. Similarly, an increased occurrence of the member of the genus Psychrobacter in the late summer indicates a shift in the heterotrophic bacterial community toward the one that is more capable to thrive at lower temperatures. Thus, changes in the environmental parameters could strongly alter the species composition; therefore, it is worthwhile to monitor the fjord ecosystem for a long term to get a deeper insight of this sensitive ecosystem.
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Acknowledgements
The authors wish to express their gratitude to Dr. S. Rajan, Director, National Centre for Antarctic and Ocean Research (ESSO-NCAOR). Thanks are due to Dr. Finlo Cottier, Head of Physics, Sea Ice and Technology Department, Scottish Association of Marine Sciences, for facilitating the SAMS mooring data collection for the period 2010. This work was undertaken as a part of the project ‘Long term monitoring of Kongsfjorden system of Arctic region for climate change studies’. This is ESSO-NCAOR contribution number 32/2016.
Associate Editor: Valeria Maia de Oliveira
Footnotes
Supplementary data associated with this article can be found, in the online version, at doi:10.1016/j.bjm.2016.09.011.
Appendix A. Supplementary data
The following are the supplementary data to this article:
References
- 1.Hop H., Pearson T., Hegseth E.N. The marine ecosystem of Kongsfjorden. Svalbard Polar Res. 2002;21:167–208. [Google Scholar]
- 2.Iversen K.R., Seuthe L. Seasonal microbial processes in a high-latitude fjord (Kongsfjorden, Svalbard): I. Heterotrophic bacteria, picoplankton and nanoflagellates. Polar Biol. 2011;34:731–749. [Google Scholar]
- 3.Buchan A., LeCleir G.R., Gulvik C.A., González J.M. Master recyclers: features and functions of bacteria associated with phytoplankton blooms. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2014;12:686–698. doi: 10.1038/nrmicro3326. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.González J.M., Simó R., Massana R. Bacterial community structure associated with a dimethylsulfoniopropionate producing North Atlantic algal bloom. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2000;66:4237–4246. doi: 10.1128/aem.66.10.4237-4246.2000. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Ray J.L., Töpper B., An S. Effect of increased pCO2 on bacterial assemblage shifts in response to glucose addition in Fram Strait seawater mesocosms. FEMS Microbiol Ecol. 2012;82:713–723. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6941.2012.01443.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Biddanda B., Benner R. Carbon, nitrogen, and carbohydrate fluxes during the production of particulate and dissolved organic matter by marine phytoplankton. Limnol Oceanogr. 1997;42:506–518. [Google Scholar]
- 7.Buchan A., Gonzalez J.M., Moran M.A. Overview of the marine Roseobacter lineage. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2005;71:5665–5677. doi: 10.1128/AEM.71.10.5665-5677.2005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Kirchman D.L. The ecology of Cytophaga–Flavobacteria in aquatic environments. FEMS Microbiol Ecol. 2002;39:91–100. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6941.2002.tb00910.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Teske A., Durbin A., Ziervogel K., Cox C., Arnosti C. Microbial community composition and function in permanently cold seawater and sediments from an Arctic Fjord of Svalbard. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2011;77(6):2008–2018. doi: 10.1128/AEM.01507-10. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Zeng Y., Zheng T., Li H. Community composition of the marine bacterioplankton in Kongsfjorden (Spitsbergen) as revealed by 16S rRNA gene analysis. Polar Biol. 2009;32:1447–1460. [Google Scholar]
- 11.Piquet A.M.-T., Scheepens J.F., Bolhuis H., Wiencke C., Buma A.G.J. Variability of protistan and bacterial communities in two Arctic fjords (Spitsbergen) Polar Biol. 2010;33:1521–1536. [Google Scholar]
- 12.Piquet A.M.-T., van de Poll W.H., Visser R.J.W., Wiencke C., Bolhuis H., Buma A.G.J. Springtime phytoplankton dynamics in Arctic Krossfjorden and Kongsfjorden (Spitsbergen) as a function of glacier proximity. Biogeosciences. 2014;11:2263–2279. [Google Scholar]
- 13.Prasad S., Manasa P., Buddhi S. Diversity and bioprospective potential (cold-active enzymes) of cultivable marine bacteria from the subarctic glacial Fjord, Kongsfjorden. Curr Microbiol. 2014;68:233–238. doi: 10.1007/s00284-013-0467-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Srinivas T.N.R., Nageswara Rao S.S.S., Reddy P.V.V. Bacterial diversity and bioprospecting for cold-active lipases, amylases and proteases, from culturable bacteria of Kongsfjorden and Ny-Alesund, Svalbard, Arctic. Curr Microbiol. 2009;59:537–547. doi: 10.1007/s00284-009-9473-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Svendsen H., Beszczynska-Møller A., Hagen J.O. The physical environment of Kongsfjorden–Krossfjorden, an Arctic fjord system in Svalbard. Polar Res. 2002;21(1):133–166. [Google Scholar]
- 16.Cottier F., Tverberg V., Inall M., Svendsen H., Nilsen F., Griffiths C. Water mass modification in an Arctic fjord through cross-shelf exchange: the seasonal hydrography of Kongsfjorden. Svalbard J Geophys Res. 2005;110 [Google Scholar]
- 17.Hicks R.E., Amann R.I., Stahl D.A. Dual staining of natural bacterioplankton with 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole and fluorescent oligo nucleotide probes targeting kingdom-level 16S rRNA sequences. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1992;58:2158–2163. doi: 10.1128/aem.58.7.2158-2163.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Weisburg W.G., Barns S.M., Pelletier D.A., Lane D.J. 16S ribosomal DNA amplification for phylogenetic study. J Bacteriol. 1991;173(2):697–703. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.2.697-703.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Cole J.R., Wang Q., Cardenas E. The Ribosomal Database Project: improved alignments and new tools for rRNA analysis. Nucl Acids Res. 2009;37:D141–D145. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkn879. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Pruesse E., Peplies J., Glöckner F.O. SINA: accurate high-throughput multiple sequence alignment of ribosomal RNA genes. Bioinformatics. 2012;28:1823–1829. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/bts252. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Tamura K., Peterson D., Peterson N., Stecher G., Nei M., Kumar S. MEGA5: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis using maximum likelihood, evolutionary distance, and maximum parsimony methods. Mol Biol Evol. 2011;28(10):2731–2739. doi: 10.1093/molbev/msr121. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Keck A., Wiktor J., Hapter R., Nilsen R. Phytoplankton assemblages related to physical gradients in an Arctic, glacier-fed fjord in summer. ICES J Mar Sci. 1999;56:203–214. [Google Scholar]
- 23.Hop H., Falk-Peterson S., Svendsen H. Physical and biological characteristics of the pelagic system across Fram Strait to Kongsfjorden. Prog Oceanogr. 2006;71:182–231. [Google Scholar]
- 24.Jankowska K., Włodarska-Kowalczuk M., Wieczorek P. Abundance and biomass of bacteria in two Arctic glacial fjords. Polish Polar Res. 2006;26:77–84. [Google Scholar]
- 25.Groudieva T., Kambourova M., Yusef H. Diversity and cold-active hydrolytic enzymes of culturable bacteria associated with Arctic sea ice, Spitzbergen. Extremophiles. 2004;8:475–488. doi: 10.1007/s00792-004-0409-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Reddy P.V.V., Nageswara Rao S.S.S., Pratibha M.S. Bacterial diversity and bioprospecting for cold-active enzymes from culturable bacteria associated with sediment from a meltwater stream of Midtre Lovenbreen glacier, an Arctic glacier. Res Microbiol. 2009;160:538–546. doi: 10.1016/j.resmic.2009.08.008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Teeling H., Fuchs B.M., Becher D. Substrate-controlled succession of marine bacterioplankton populations induced by a phytoplankton bloom. Science. 2012;336:608–611. doi: 10.1126/science.1218344. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Guo C.Y., He J.F., Zhang F., Cai M.H., Wang G.Z. Spatial heterogeneity of a microbial community in Kongsfjorden, Svalbard during late summer 2006 and its relationship to biotic and abiotic factors. Adv Polar Sci. 2011;22(1):55–66. [Google Scholar]
- 29.Ravenschlag K., Sahm K., Pernthaler J., Amann R. High bacterial diversity in permanently cold marine sediments. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1999;65(9):3982–3989. doi: 10.1128/aem.65.9.3982-3989.1999. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Giovannoni S.J., Rappe M. Evolution, diversity and molecular ecology of marine prokaryotes. In: Kirchman D.L., editor. Microbial Ecology of the Oceans. John Wiley & Sons, Inc.; New York: 2000. pp. 47–84. [Google Scholar]
- 31.Grossart H.P., Levold F., Allgaier M., Simon M., Brinkhoff T. Marine diatom species harbour distinct bacterial communities. Environ Microbiol. 2005;7:860–873. doi: 10.1111/j.1462-2920.2005.00759.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Goecke F., Thiel V., Wiese J., Labes A., Imhoff J.F. Algae as an important environment for bacteria–phylogenetic relationships among new bacterial species isolated from algae. Phycologia. 2013;52:14–24. [Google Scholar]
- 33.Wagner-Döbler I., Ballhausen B., Berger M. The complete genome sequence of the algal symbiont Dinoroseobacter shibae: a hitchhiker's guide to life in the sea. ISME J. 2010;4:61–77. doi: 10.1038/ismej.2009.94. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Mayali X., Franks P.J.S., Burton R.S. Temporal attachment dynamics by distinct bacterial taxa during a dinoflagellate bloom. Aquat Microb Ecol. 2011;63:111–122. [Google Scholar]
- 35.Goethals K., Vereecke D., Jaziri M., Van Montagu M., Holsters M. Leafy gall formation by Rhodococcus fascians. Ann Rev Phytopathol. 2001;39:27–52. doi: 10.1146/annurev.phyto.39.1.27. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Vandeputte O., Oden S., Mol A. Biosynthesis of auxin by the gram-positive phytopathogen Rhodococcus fascians is controlled by compounds specific to infected plant tissues. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2005;71(3):1169–1177. doi: 10.1128/AEM.71.3.1169-1177.2005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Mergaert J., Verhelst A.N., Cnockaert M.C., Tan T.-L., Swings J. Characterization of facultative oligotrophic bacteria from polar seas by analysis of their fatty acids and 16S rDNA sequences. Syst Appl Microbiol. 2001;24(1):98–107. doi: 10.1078/0723-2020-00012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Gihring T.M., Humphrys M., Mills H.J., Huettel M., Kostka J.E. Identification of phytodetritus-degrading microbial communities in sublittoral Gulf of Mexico sands. Limnol Oceanogr. 2009;54(4):1073–1083. [Google Scholar]
- 39.Sánchez-Porro C., Kaur B., Mann H., Ventosa A. Halomonas titanicae sp. nov., a halophilic bacterium isolated from the RMS Titanic. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol. 2009;60:2768–2774. doi: 10.1099/ijs.0.020628-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Hahnke R.L., Probian C., Fuch B.M., Harder J. Variations in pelagic bacterial communities in the North Atlantic Ocean coincide with water bodies. Aquat Microb Ecol. 2013;71:131–140. [Google Scholar]
- 41.Fu Y., Keats K.F., Rivkin R.B., Lang A.S. Water mass and depth determine the distribution and diversity of Rhodobacterales in an Arctic marine system. FEMS Microbiol Ecol. 2013;84:564–576. doi: 10.1111/1574-6941.12085. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Brinkmeyer R., Knittel K., Jürgens J., Weyland H., Amann R., Helmke E. Diversity and structure of bacterial communities in Arctic versus Antarctic pack ice. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2003;69(11):6610–6619. doi: 10.1128/AEM.69.11.6610-6619.2003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Ayala-del-Río H.L., Chain P.S., Grzymski J.J. The genome sequence of Psychrobacter arcticus 273–4, a psychroactive Siberian permafrost bacterium, reveals mechanisms for adaptation to low-temperature growth. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2010;76(7):2304–2312. doi: 10.1128/AEM.02101-09. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Bowman J., Nichols D., McMeekin T. Psychrobacter glacincola sp. nov., a halotolerant, psychrophilic bacterium isolated from Antarctic sea ice. Syst Appl Microbiol. 1997;20:209–215. [Google Scholar]
- 45.Maruyama A., Honda D., Yamamoto H., Kitamura K., Higashihara T. Phylogenetic analysis of psychrophilic bacteria isolated from the Japan Trench, including a description of the deep-sea species Psychrobacter pacificensis sp. nov. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol. 2000;50:835–846. doi: 10.1099/00207713-50-2-835. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Romanenko L.A., Schumann P., Rohde M., Lysenko A.M., Mikhailov V.V., Stackebrandt E. Psychrobacter submarinus sp. nov. and Psychrobacter marincola sp. nov., psychrophilic halophiles from marine environments. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol. 2002;52:1291–1297. doi: 10.1099/00207713-52-4-1291. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Bozal N., Montes M.J., Tudela E., Guinea J. Characterization of several Psychrobacter strains isolated from Antarctic environments and description of Psychrobacter luti sp. nov. and Psychrobacter fozii sp. nov. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol. 2003;53(4):1093–1100. doi: 10.1099/ijs.0.02457-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Heuchert A., Glöckner F.O., Amann R., Fischer U. Psychrobacter nivimaris sp. nov., a heterotrophic bacterium attached to organic particles isolated from the South Atlantic (Antarctica) Syst Appl Microbiol. 2004;27(4):399–406. doi: 10.1078/0723202041438455. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.