Abstract
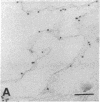
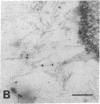
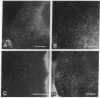
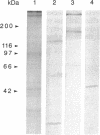
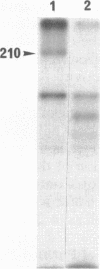
Amiloride-sensitive sodium channels are localized to the microvillar domain of apical membranes in sodium-transporting renal epithelial cells. To elucidate the elements that maintain sodium channel distribution at the apical membrane, we searched for specific proteins associating with the channel. Triton X-100 extraction of A6 epithelial cells reveals that sodium channels are associated with detergent-insoluble and assembled cytoskeleton. Indirect immunofluorescence and confocal microscopy show that sodium channels are segregated to the apical microvillar membrane and colocalize with ankyrin, fodrin, and actin. We document by immunoblot analysis that ankyrin and fodrin remain associated with sodium channels after isolation and purification from bovine renal papillae. 125I-labeled ankyrine can be precipitated by anti-sodium-channel antibodies only in the presence of purified bovine sodium-channel complex. Direct binding of 125I-labeled ankyrin shows ankyrin binds to the 150-kDa subunit of the channel. Fluorescence photobleach lateral-diffusion measurements indicate sodium channels are severely restricted in their lateral mobility. We conclude that ankyrin links the amiloride-sensitive sodium channel to the underlying cytoskeleton and this association may sequester sodium channels at apical microvilli and maintain their polarized distribution in renal epithelial cells.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Angelides K. J., Elmer L. W., Loftus D., Elson E. Distribution and lateral mobility of voltage-dependent sodium channels in neurons. J Cell Biol. 1988 Jun;106(6):1911–1925. doi: 10.1083/jcb.106.6.1911. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett V. Proteins involved in membrane--cytoskeleton association in human erythrocytes: spectrin, ankyrin, and band 3. Methods Enzymol. 1983;96:313–324. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(83)96029-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett V. Spectrin-based membrane skeleton: a multipotential adaptor between plasma membrane and cytoplasm. Physiol Rev. 1990 Oct;70(4):1029–1065. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1990.70.4.1029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett V., Stenbuck P. J. Human erythrocyte ankyrin. Purification and properties. J Biol Chem. 1980 Mar 25;255(6):2540–2548. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benos D. J., Saccomani G., Brenner B. M., Sariban-Sohraby S. Purification and characterization of the amiloride-sensitive sodium channel from A6 cultured cells and bovine renal papilla. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Nov;83(22):8525–8529. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.22.8525. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benos D. J., Saccomani G., Sariban-Sohraby S. The epithelial sodium channel. Subunit number and location of the amiloride binding site. J Biol Chem. 1987 Aug 5;262(22):10613–10618. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown D., Sorscher E. J., Ausiello D. A., Benos D. J. Immunocytochemical localization of Na+ channels in rat kidney medulla. Am J Physiol. 1989 Feb;256(2 Pt 2):F366–F369. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1989.256.2.F366. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coleman T. R., Fishkind D. J., Mooseker M. S., Morrow J. S. Functional diversity among spectrin isoforms. Cell Motil Cytoskeleton. 1989;12(4):225–247. doi: 10.1002/cm.970120405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis J. Q., Bennett V. Brain ankyrin. Purification of a 72,000 Mr spectrin-binding domain. J Biol Chem. 1984 Feb 10;259(3):1874–1881. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis J. Q., Bennett V. The anion exchanger and Na+K(+)-ATPase interact with distinct sites on ankyrin in in vitro assays. J Biol Chem. 1990 Oct 5;265(28):17252–17256. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis J., Davis L., Bennett V. Diversity in membrane binding sites of ankyrins. Brain ankyrin, erythrocyte ankyrin, and processed erythrocyte ankyrin associate with distinct sites in kidney microsomes. J Biol Chem. 1989 Apr 15;264(11):6417–6426. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drenckhahn D., Bennett V. Polarized distribution of Mr 210,000 and 190,000 analogs of erythrocyte ankyrin along the plasma membrane of transporting epithelia, neurons and photoreceptors. Eur J Cell Biol. 1987 Jun;43(3):479–486. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drenckhahn D., Schlüter K., Allen D. P., Bennett V. Colocalization of band 3 with ankyrin and spectrin at the basal membrane of intercalated cells in the rat kidney. Science. 1985 Dec 13;230(4731):1287–1289. doi: 10.1126/science.2933809. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fey E. G., Wan K. M., Penman S. Epithelial cytoskeletal framework and nuclear matrix-intermediate filament scaffold: three-dimensional organization and protein composition. J Cell Biol. 1984 Jun;98(6):1973–1984. doi: 10.1083/jcb.98.6.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujimoto T., Ogawa K. Immunoelectron microscopy of fodrin in the rat uriniferous and collecting tubular epithelium. J Histochem Cytochem. 1989 Sep;37(9):1345–1352. doi: 10.1177/37.9.2671151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gumbiner B. Structure, biochemistry, and assembly of epithelial tight junctions. Am J Physiol. 1987 Dec;253(6 Pt 1):C749–C758. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1987.253.6.C749. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris A. S., Green L. A., Ainger K. J., Morrow J. S. Mechanism of cytoskeletal regulation (I): functional differences correlate with antigenic dissimilarity in human brain and erythrocyte spectrin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1985 Aug 8;830(2):147–158. doi: 10.1016/0167-4838(85)90022-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lisanti M. P., Sargiacomo M., Graeve L., Saltiel A. R., Rodriguez-Boulan E. Polarized apical distribution of glycosyl-phosphatidylinositol-anchored proteins in a renal epithelial cell line. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Dec;85(24):9557–9561. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.24.9557. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lux S. E., John K. M., Bennett V. Analysis of cDNA for human erythrocyte ankyrin indicates a repeated structure with homology to tissue-differentiation and cell-cycle control proteins. Nature. 1990 Mar 1;344(6261):36–42. doi: 10.1038/344036a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCloskey M., Poo M. M. Protein diffusion in cell membranes: some biological implications. Int Rev Cytol. 1984;87:19–81. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7696(08)62439-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrow J. S., Cianci C. D., Ardito T., Mann A. S., Kashgarian M. Ankyrin links fodrin to the alpha subunit of Na,K-ATPase in Madin-Darby canine kidney cells and in intact renal tubule cells. J Cell Biol. 1989 Feb;108(2):455–465. doi: 10.1083/jcb.108.2.455. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson W. J., Veshnock P. J. Dynamics of membrane-skeleton (fodrin) organization during development of polarity in Madin-Darby canine kidney epithelial cells. J Cell Biol. 1986 Nov;103(5):1751–1765. doi: 10.1083/jcb.103.5.1751. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ojakian G. K., Schwimmer R. The polarized distribution of an apical cell surface glycoprotein is maintained by interactions with the cytoskeleton of Madin-Darby canine kidney cells. J Cell Biol. 1988 Dec;107(6 Pt 1):2377–2387. doi: 10.1083/jcb.107.6.2377. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodman J. S., Mooseker M., Farquhar M. G. Cytoskeletal proteins of the rat kidney proximal tubule brush border. Eur J Cell Biol. 1986 Dec;42(2):319–327. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodriguez-Boulan E., Nelson W. J. Morphogenesis of the polarized epithelial cell phenotype. Science. 1989 Aug 18;245(4919):718–725. doi: 10.1126/science.2672330. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salas P. J., Vega-Salas D. E., Hochman J., Rodriguez-Boulan E., Edidin M. Selective anchoring in the specific plasma membrane domain: a role in epithelial cell polarity. J Cell Biol. 1988 Dec;107(6 Pt 1):2363–2376. doi: 10.1083/jcb.107.6.2363. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sariban-Sohraby S., Benos D. J. Detergent solubilization, functional reconstitution, and partial purification of epithelial amiloride-binding protein. Biochemistry. 1986 Aug 12;25(16):4639–4646. doi: 10.1021/bi00364a028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sorscher E. J., Accavitti M. A., Keeton D., Steadman E., Frizzell R. A., Benos D. J. Antibodies against purified epithelial sodium channel protein from bovine renal papilla. Am J Physiol. 1988 Dec;255(6 Pt 1):C835–C843. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1988.255.6.C835. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Srinivasan Y., Elmer L., Davis J., Bennett V., Angelides K. Ankyrin and spectrin associate with voltage-dependent sodium channels in brain. Nature. 1988 May 12;333(6169):177–180. doi: 10.1038/333177a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tousson A., Alley C. D., Sorscher E. J., Brinkley B. R., Benos D. J. Immunochemical localization of amiloride-sensitive sodium channels in sodium-transporting epithelia. J Cell Sci. 1989 Jun;93(Pt 2):349–362. doi: 10.1242/jcs.93.2.349. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]