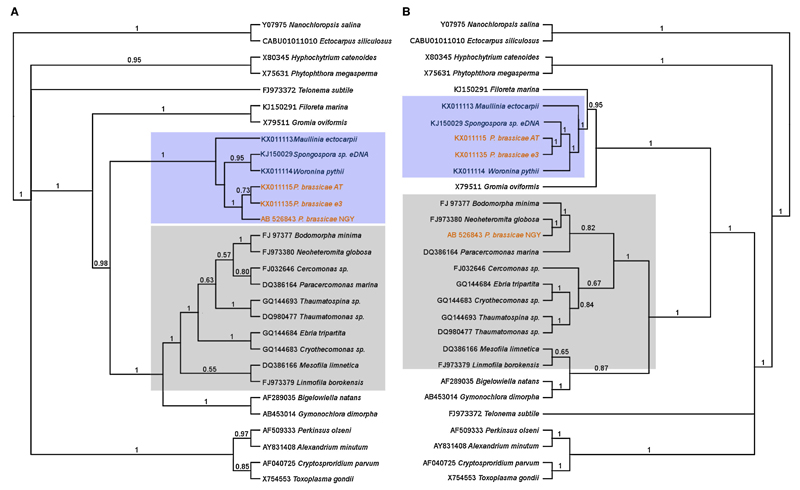
Figure 1.
Cladogram of trees generated from the posterior output tree from Bayesian analyses of the 5′ end (Fig. 1A left) and the 3′ end (Fig. 1B right) of the LSU rDNA. This shows that sequence P. brassicae NGY (AB526843) is a chimeric sequence of P. brassicae and a glissmonad sequence similar to Neoheteromita globosa. Fig. 1A was generated using an alignment of LSU sequences up to position 4400 of sequence (AB526843), the right tree was generated starting from position 4500. Cercozoan sequences are shaded in grey, phytomyxid sequences are shaded in light blue. Trees were generated using phytomyxid sequences plus a selection of Rhizaria, alveolates and stramenopiles from GenBank using .29 sequences, A: 5999 positions, B: 4358 positions. Trees showing distances are given in the Supplementary Material Figures S3 and S4.