Abstract
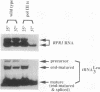
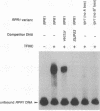
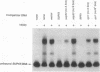
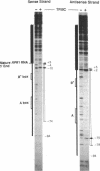
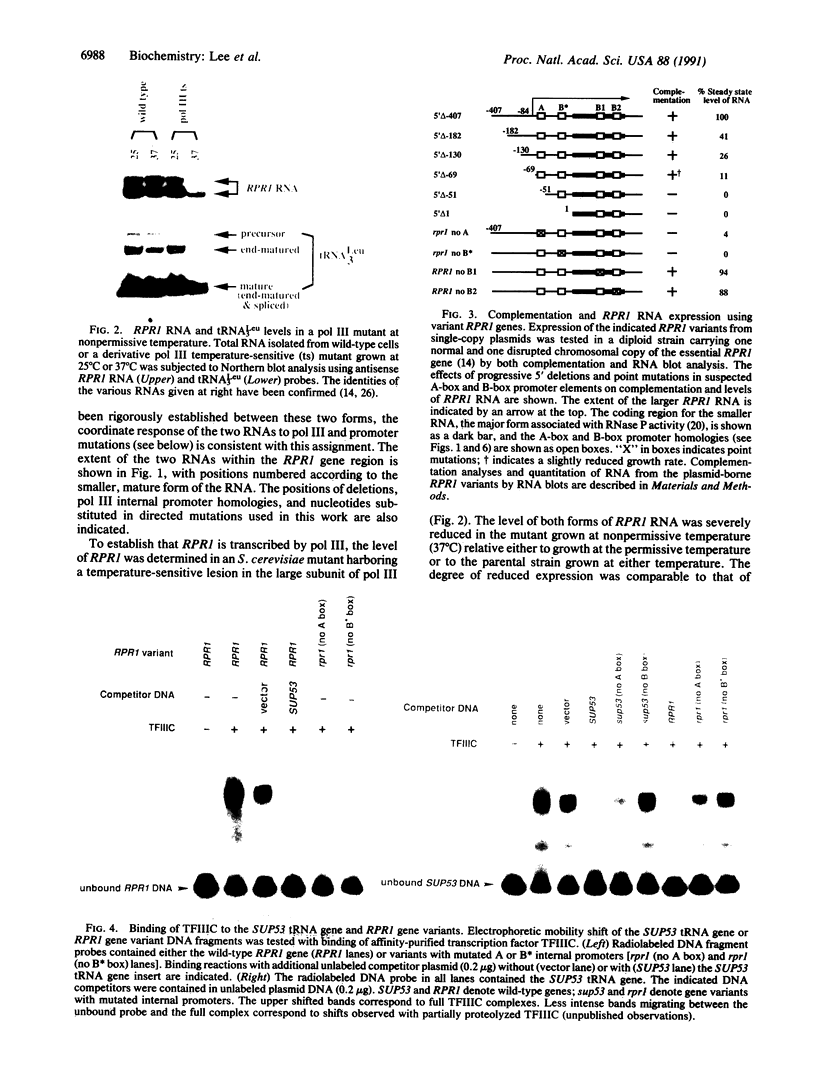
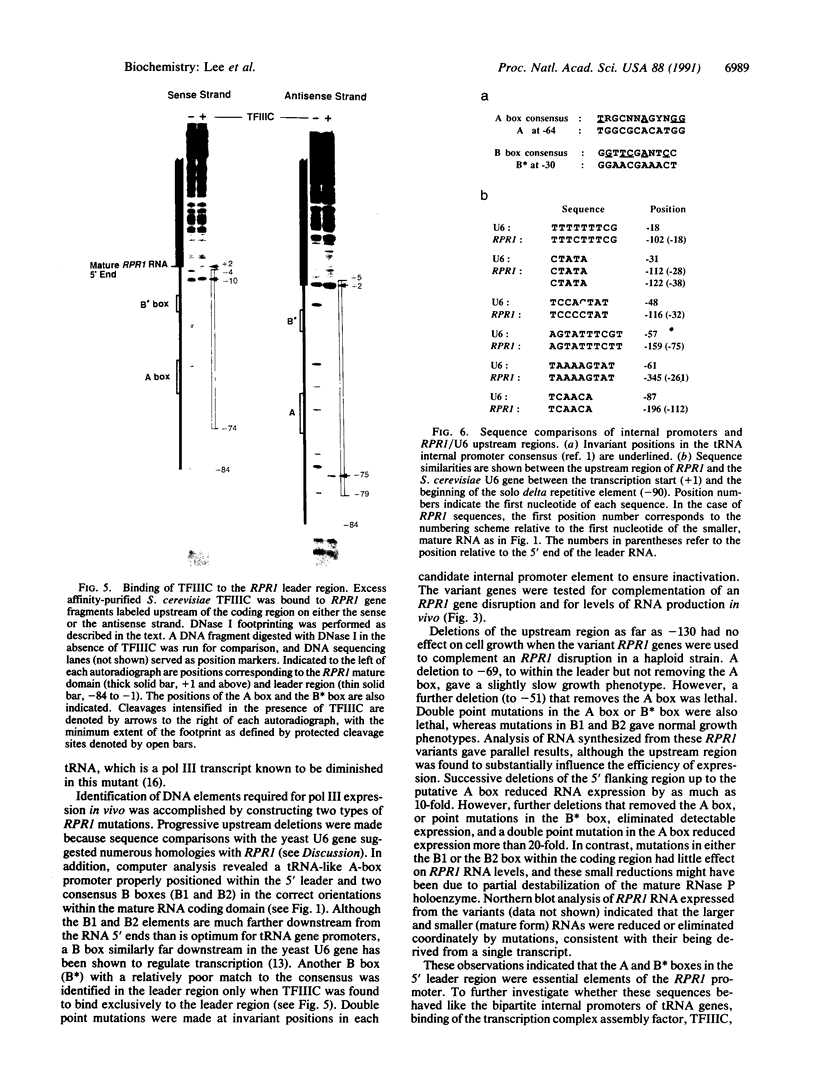
The RNA subunit of Saccharomyces cerevisiae nuclear RNase P is encoded by a single-copy, essential gene, RPR1. The 369-nucleotide mature form of the RNA has an apparent precursor with an 84-nucleotide 5' leader and approximately 33 nucleotides of additional 3' sequence. Analysis of RPR1 transcription in a strain with a temperature-sensitive lesion in RNA polymerase III shows that the gene is transcribed in vivo by RNA polymerase III. Examination of potential promoter regions using both progressive upstream deletions and point mutations indicates that at least two sequences contained within the 5' leader region are essential for expression in vivo, while sequences farther upstream influence efficiency. The required leader elements resemble tRNA gene-like A-box and B-box internal promoters in sequence and spacing. As in the tRNA genes, transcription factor TFIIIC binds to this region in vitro and binding is severely reduced by either A-box or B-box point mutations that impair expression in vivo. It thus appears that the yeast RNase P RNA gene has adopted a promoter strategy that places an RNA polymerase III "internal" promoter upstream of the mature structural domain to help drive transcription.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baer M., Nilsen T. W., Costigan C., Altman S. Structure and transcription of a human gene for H1 RNA, the RNA component of human RNase P. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Jan 11;18(1):97–103. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.1.97. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker R. E., Gabrielsen O., Hall B. D. Effects of tRNATyr point mutations on the binding of yeast RNA polymerase III transcription factor C. J Biol Chem. 1986 Apr 25;261(12):5275–5282. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bark C., Weller P., Zabielski J., Janson L., Pettersson U. A distant enhancer element is required for polymerase III transcription of a U6 RNA gene. Nature. 1987 Jul 23;328(6128):356–359. doi: 10.1038/328356a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brow D. A., Guthrie C. Spliceosomal RNA U6 is remarkably conserved from yeast to mammals. Nature. 1988 Jul 21;334(6179):213–218. doi: 10.1038/334213a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brow D. A., Guthrie C. Transcription of a yeast U6 snRNA gene requires a polymerase III promoter element in a novel position. Genes Dev. 1990 Aug;4(8):1345–1356. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.8.1345. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geiduschek E. P., Tocchini-Valentini G. P. Transcription by RNA polymerase III. Annu Rev Biochem. 1988;57:873–914. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.57.070188.004301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gudenus R., Mariotte S., Moenne A., Ruet A., Memet S., Buhler J. M., Sentenac A., Thuriaux P. Conditional mutants of RPC160, the gene encoding the largest subunit of RNA polymerase C in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Genetics. 1988 Jul;119(3):517–526. doi: 10.1093/genetics/119.3.517. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hannig E. M., Thiele D. J., Leibowitz M. J. Saccharomyces cerevisiae killer virus transcripts contain template-coded polyadenylate tracts. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Jan;4(1):101–109. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.1.101. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huibregtse J. M., Engelke D. R. Direct identification of small sequence changes in chromosomal DNA. Gene. 1986;44(1):151–158. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(86)90056-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huibregtse J. M., Engelke D. R. Genomic footprinting of a yeast tRNA gene reveals stable complexes over the 5'-flanking region. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Aug;9(8):3244–3252. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.8.3244. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito H., Fukuda Y., Murata K., Kimura A. Transformation of intact yeast cells treated with alkali cations. J Bacteriol. 1983 Jan;153(1):163–168. doi: 10.1128/jb.153.1.163-168.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kassavetis G. A., Braun B. R., Nguyen L. H., Geiduschek E. P. S. cerevisiae TFIIIB is the transcription initiation factor proper of RNA polymerase III, while TFIIIA and TFIIIC are assembly factors. Cell. 1990 Jan 26;60(2):235–245. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90739-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kassavetis G. A., Riggs D. L., Negri R., Nguyen L. H., Geiduschek E. P. Transcription factor IIIB generates extended DNA interactions in RNA polymerase III transcription complexes on tRNA genes. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Jun;9(6):2551–2566. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.6.2551. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krol A., Carbon P., Ebel J. P., Appel B. Xenopus tropicalis U6 snRNA genes transcribed by Pol III contain the upstream promoter elements used by Pol II dependent U snRNA genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Mar 25;15(6):2463–2478. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.6.2463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel G. R., Maser R. L., Calvet J. P., Pederson T. U6 small nuclear RNA is transcribed by RNA polymerase III. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Nov;83(22):8575–8579. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.22.8575. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee J. Y., Rohlman C. E., Molony L. A., Engelke D. R. Characterization of RPR1, an essential gene encoding the RNA component of Saccharomyces cerevisiae nuclear RNase P. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Feb;11(2):721–730. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.2.721. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Margottin F., Dujardin G., Gérard M., Egly J. M., Huet J., Sentenac A. Participation of the TATA factor in transcription of the yeast U6 gene by RNA polymerase C. Science. 1991 Jan 25;251(4992):424–426. doi: 10.1126/science.1989075. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moenne A., Camier S., Anderson G., Margottin F., Beggs J., Sentenac A. The U6 gene of Saccharomyces cerevisiae is transcribed by RNA polymerase C (III) in vivo and in vitro. EMBO J. 1990 Jan;9(1):271–277. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08105.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy S., Di Liegro C., Melli M. The in vitro transcription of the 7SK RNA gene by RNA polymerase III is dependent only on the presence of an upstream promoter. Cell. 1987 Oct 9;51(1):81–87. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90012-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy S., Moorefield B., Pieler T. Common mechanisms of promoter recognition by RNA polymerases II and III. Trends Genet. 1989 Apr;5(4):122–126. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(89)90043-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy S., Tripodi M., Melli M. A sequence upstream from the coding region is required for the transcription of the 7SK RNA genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Dec 9;14(23):9243–9260. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.23.9243. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newman A. J., Ogden R. C., Abelson J. tRNA gene transcription in yeast: effects of specified base substitutions in the intragenic promoter. Cell. 1983 Nov;35(1):117–125. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90214-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reddy R., Henning D., Das G., Harless M., Wright D. The capped U6 small nuclear RNA is transcribed by RNA polymerase III. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jan 5;262(1):75–81. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strobel M. C., Abelson J. Intron mutations affect splicing of Saccharomyces cerevisiae SUP53 precursor tRNA. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Jul;6(7):2674–2683. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.7.2674. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waibel F., Filipowicz W. RNA-polymerase specificity of transcription of Arabidopsis U snRNA genes determined by promoter element spacing. Nature. 1990 Jul 12;346(6280):199–202. doi: 10.1038/346199a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]