Abstract
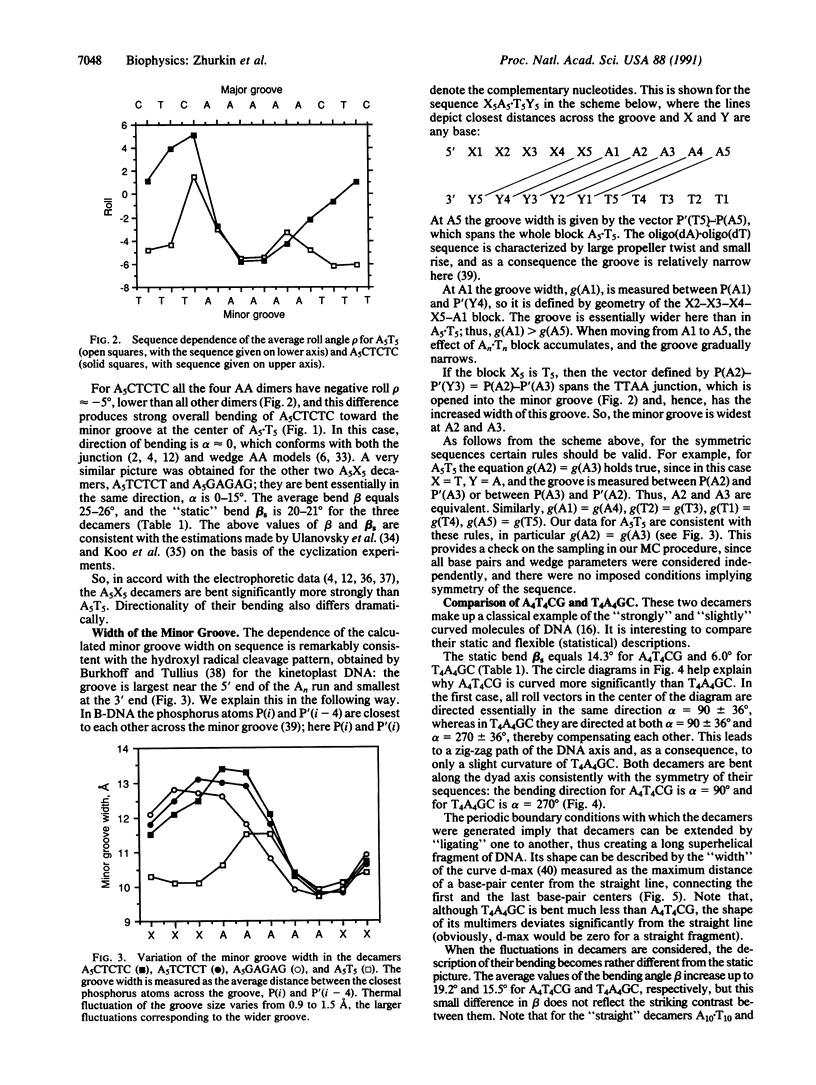
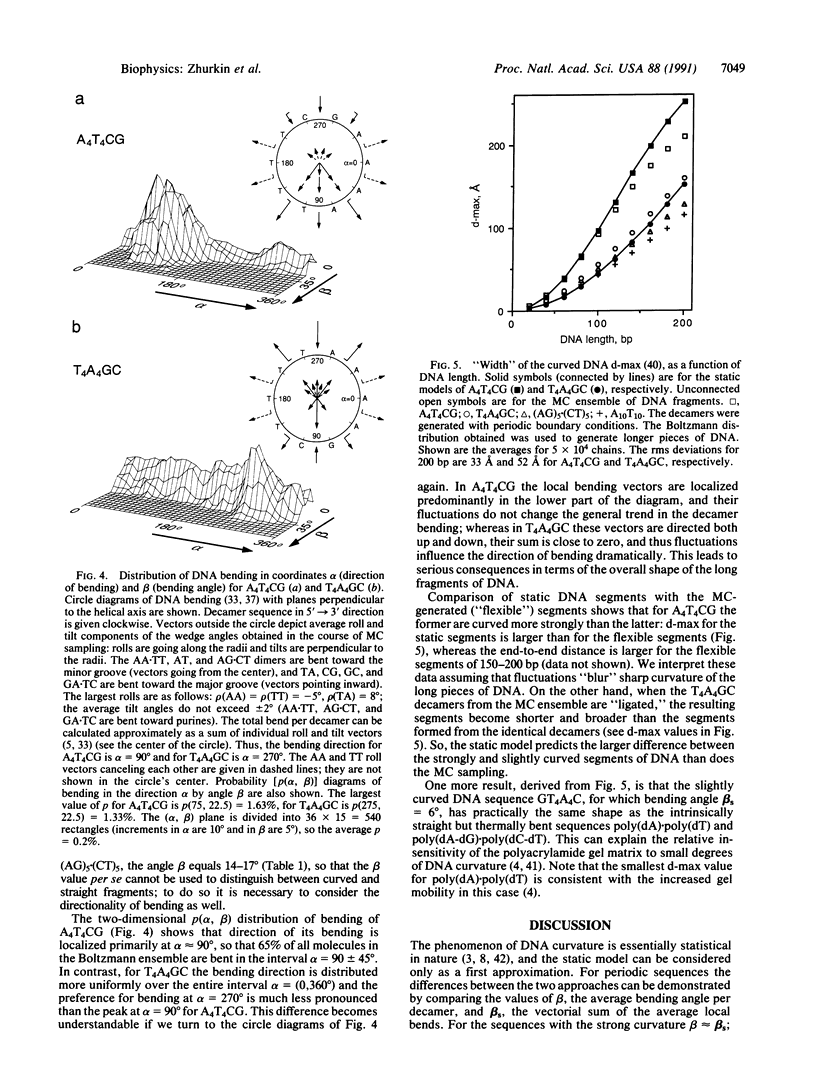
To investigate the influence of thermal fluctuations on DNA curvature the Metropolis procedure at 300 K was applied to B-DNA decamers containing A5.T5 and A4.T4 blocks. Monte Carlo simulations have confirmed the DNA bending anisotropy: B-DNA bends most easily in a groove direction (roll). The A5.T5 block is more rigid than the other sequences; the pyrimidine-purine dimers are found to be the most flexible. For A5TCTCT, A5CTCTC, and A5GAGAG, the average bend angle per decamer is 20-25 degrees in a direction toward the minor groove in the center of the A5.T5 tract, which is consistent with both the "junction" and "wedge AA" models. However, in A5T5, A4T4CG, and T4A4GC, bending is directed into the grooves at the 5' and 3' ends of purine tracts. Thus, directionality of bending caused by An.Tn blocks strongly depends on their neighboring sequences. These calculations demonstrate that the sequence-dependent variation of the minor-groove width mimics the observed hydroxyl radical cleavage pattern. To estimate the effect of fluctuations on the overall shape of curved DNA fragments, longer pieces of DNA (up to 200 base pairs) were generated. For sequences with strong curvature (A5X5 and A4T4CG), the static model and Monte Carlo ensemble give similar results but, for moderately and slightly curved sequences (A5T5 or T4A4GC), the static model predicts a much smaller degree of bending than does the statistical representation. Considering fluctuations is important for quantitative interpretation of the gel electrophoresis measurements of DNA curvature, where both the static and statistical bends are operative.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barber A. M., Zhurkin V. B. CAP binding sites reveal pyrimidine-purine pattern characteristic of DNA bending. J Biomol Struct Dyn. 1990 Oct;8(2):213–232. doi: 10.1080/07391102.1990.10507803. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolshoy A., McNamara P., Harrington R. E., Trifonov E. N. Curved DNA without A-A: experimental estimation of all 16 DNA wedge angles. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Mar 15;88(6):2312–2316. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.6.2312. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burkhoff A. M., Tullius T. D. The unusual conformation adopted by the adenine tracts in kinetoplast DNA. Cell. 1987 Mar 27;48(6):935–943. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90702-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chuprina V. P. Anomalous structure and properties of poly (dA).poly(dT). Computer simulation of the polynucleotide structure with the spine of hydration in the minor groove. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Jan 12;15(1):293–311. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.1.293. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crothers D. M., Haran T. E., Nadeau J. G. Intrinsically bent DNA. J Biol Chem. 1990 May 5;265(13):7093–7096. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Santis P., Palleschi A., Savino M., Scipioni A. Validity of the nearest-neighbor approximation in the evaluation of the electrophoretic manifestations of DNA curvature. Biochemistry. 1990 Oct 2;29(39):9269–9273. doi: 10.1021/bi00491a023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diekmann S. Sequence specificity of curved DNA. FEBS Lett. 1986 Jan 20;195(1-2):53–56. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(86)80128-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frank-Kamenetskii M. D., Lukashin A. V., Anshelevich V. V., Vologodskii A. V. Torsional and bending rigidity of the double helix from data on small DNA rings. J Biomol Struct Dyn. 1985 Feb;2(5):1005–1012. doi: 10.1080/07391102.1985.10507616. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fratini A. V., Kopka M. L., Drew H. R., Dickerson R. E. Reversible bending and helix geometry in a B-DNA dodecamer: CGCGAATTBrCGCG. J Biol Chem. 1982 Dec 25;257(24):14686–14707. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagerman P. J. Evidence for the existence of stable curvature of DNA in solution. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Aug;81(15):4632–4636. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.15.4632. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagerman P. J. Sequence-directed curvature of DNA. Nature. 1986 May 22;321(6068):449–450. doi: 10.1038/321449a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagerman P. J. Sequence-directed curvature of DNA. Annu Rev Biochem. 1990;59:755–781. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.59.070190.003543. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katahira M., Sugeta H., Kyogoku Y. A new model for the bending of DNAs containing the oligo(dA) tracts based on NMR observations. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Feb 11;18(3):613–618. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.3.613. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koo H. S., Crothers D. M. Calibration of DNA curvature and a unified description of sequence-directed bending. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Mar;85(6):1763–1767. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.6.1763. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koo H. S., Drak J., Rice J. A., Crothers D. M. Determination of the extent of DNA bending by an adenine-thymine tract. Biochemistry. 1990 May 1;29(17):4227–4234. doi: 10.1021/bi00469a027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koo H. S., Wu H. M., Crothers D. M. DNA bending at adenine . thymine tracts. Nature. 1986 Apr 10;320(6062):501–506. doi: 10.1038/320501a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levene S. D., Crothers D. M. Topological distributions and the torsional rigidity of DNA. A Monte Carlo study of DNA circles. J Mol Biol. 1986 May 5;189(1):73–83. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90382-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipanov A. A., Chuprina V. P. The structure of poly(dA):poly(dT) in a condensed state and in solution. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Jul 24;15(14):5833–5844. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.14.5833. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McNamara P. T., Bolshoy A., Trifonov E. N., Harrington R. E. Sequence-dependent kinks induced in curved DNA. J Biomol Struct Dyn. 1990 Dec;8(3):529–538. doi: 10.1080/07391102.1990.10507827. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nadeau J. G., Crothers D. M. Structural basis for DNA bending. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Apr;86(8):2622–2626. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.8.2622. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poltev V. I., Shulyupina N. V. Simulation of interactions between nucleic acid bases by refined atom-atom potential functions. J Biomol Struct Dyn. 1986 Feb;3(4):739–765. doi: 10.1080/07391102.1986.10508459. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarai A., Mazur J., Nussinov R., Jernigan R. L. Sequence dependence of DNA conformational flexibility. Biochemistry. 1989 Sep 19;28(19):7842–7849. doi: 10.1021/bi00445a046. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schellman J. A. Flexibility of DNA. Biopolymers. 1974 Jan;13(1):217–226. doi: 10.1002/bip.1974.360130115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singh U. C., Weiner S. J., Kollman P. Molecular dynamics simulations of d(C-G-C-G-A) X d(T-C-G-C-G) with and without "hydrated" counterions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Feb;82(3):755–759. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.3.755. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Srinivasan A. R., Torres R., Clark W., Olson W. K. Base sequence effects in double helical DNA. I. Potential energy estimates of local base morphology. J Biomol Struct Dyn. 1987 Dec;5(3):459–496. doi: 10.1080/07391102.1987.10506409. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steitz T. A. Structural studies of protein-nucleic acid interaction: the sources of sequence-specific binding. Q Rev Biophys. 1990 Aug;23(3):205–280. doi: 10.1017/s0033583500005552. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trifonov E. N. Curved DNA. CRC Crit Rev Biochem. 1985;19(2):89–106. doi: 10.3109/10409238509082540. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tung C. S., Burks C. A quantitative measure of DNA curvature enabling the comparison of predicted structures. J Biomol Struct Dyn. 1987 Feb;4(4):553–559. doi: 10.1080/07391102.1987.10507659. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ulanovsky L. E., Trifonov E. N. Estimation of wedge components in curved DNA. Nature. 1987 Apr 16;326(6114):720–722. doi: 10.1038/326720a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ulanovsky L., Bodner M., Trifonov E. N., Choder M. Curved DNA: design, synthesis, and circularization. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Feb;83(4):862–866. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.4.862. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ulyanov N. B., Zhurkin V. B. Sequence-dependent anisotropic flexibility of B-DNA. A conformational study. J Biomol Struct Dyn. 1984 Oct;2(2):361–385. doi: 10.1080/07391102.1984.10507573. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhurkin V. B., Lysov Y. P., Florentiev V. L., Ivanov V. I. Torsional flexibility of B-DNA as revealed by conformational analysis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Mar 11;10(5):1811–1830. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.5.1811. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhurkin V. B., Lysov Y. P., Ivanov V. I. Anisotropic flexibility of DNA and the nucleosomal structure. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Mar;6(3):1081–1096. doi: 10.1093/nar/6.3.1081. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



