Abstract
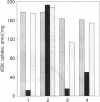
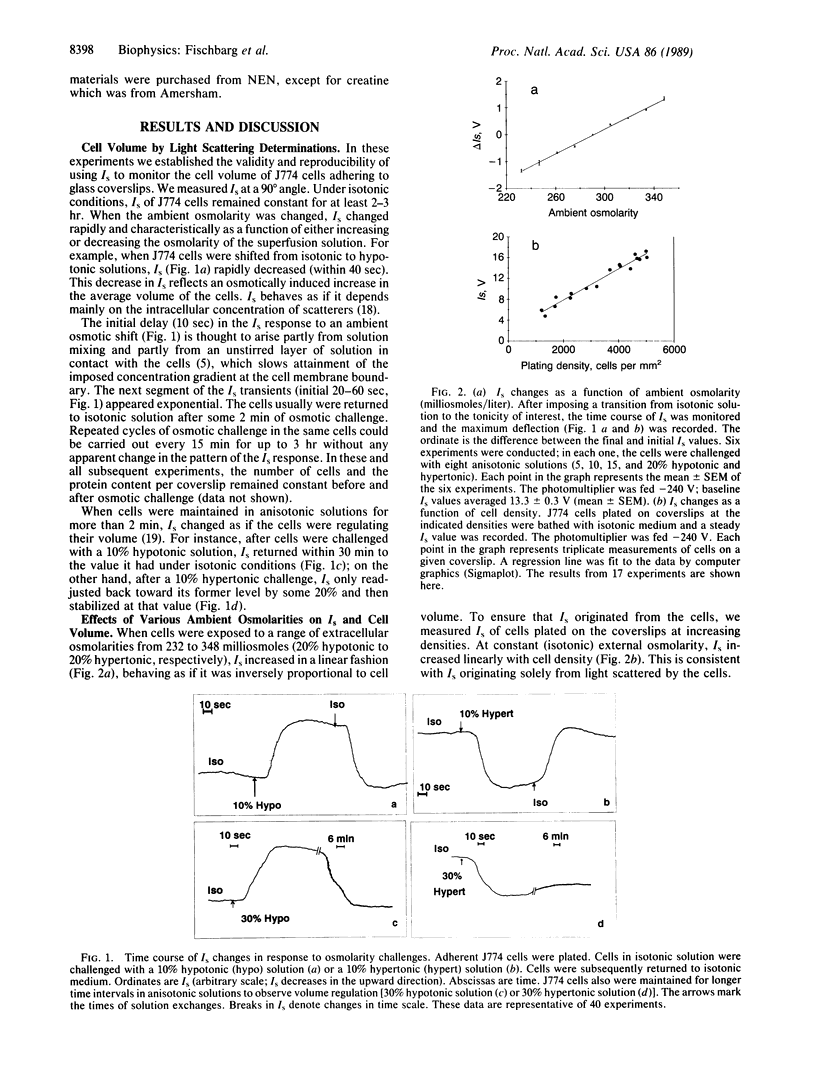
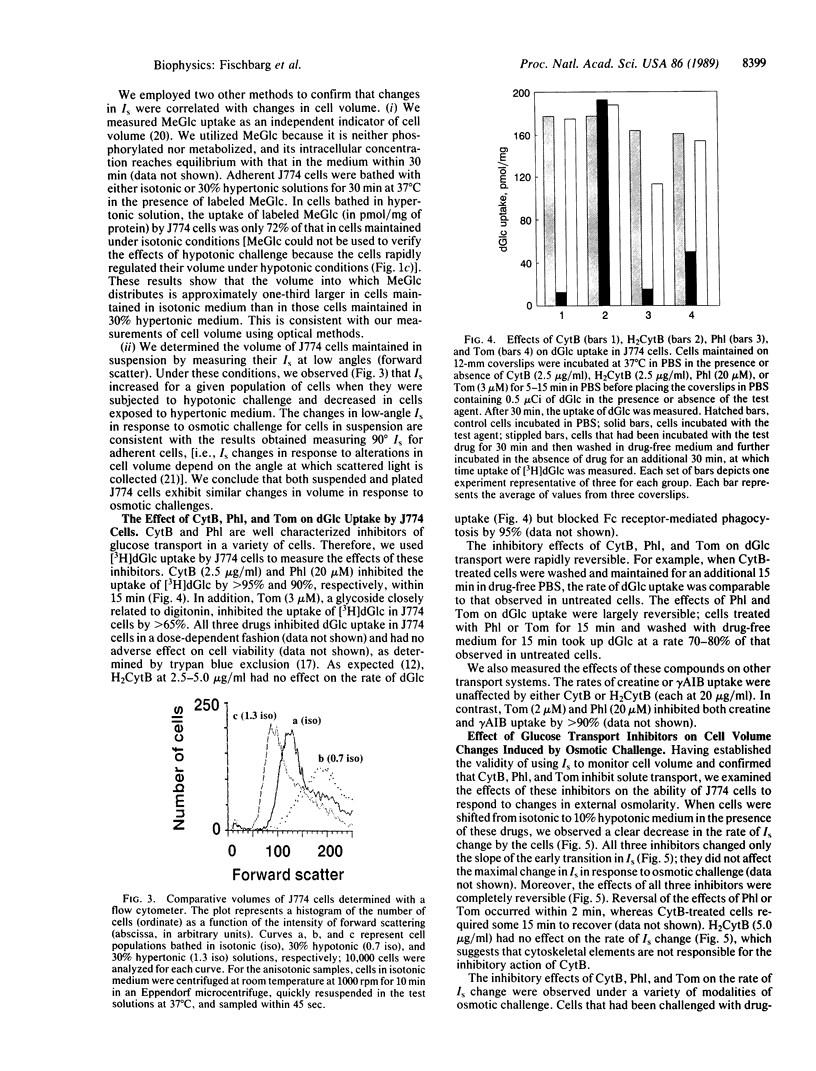
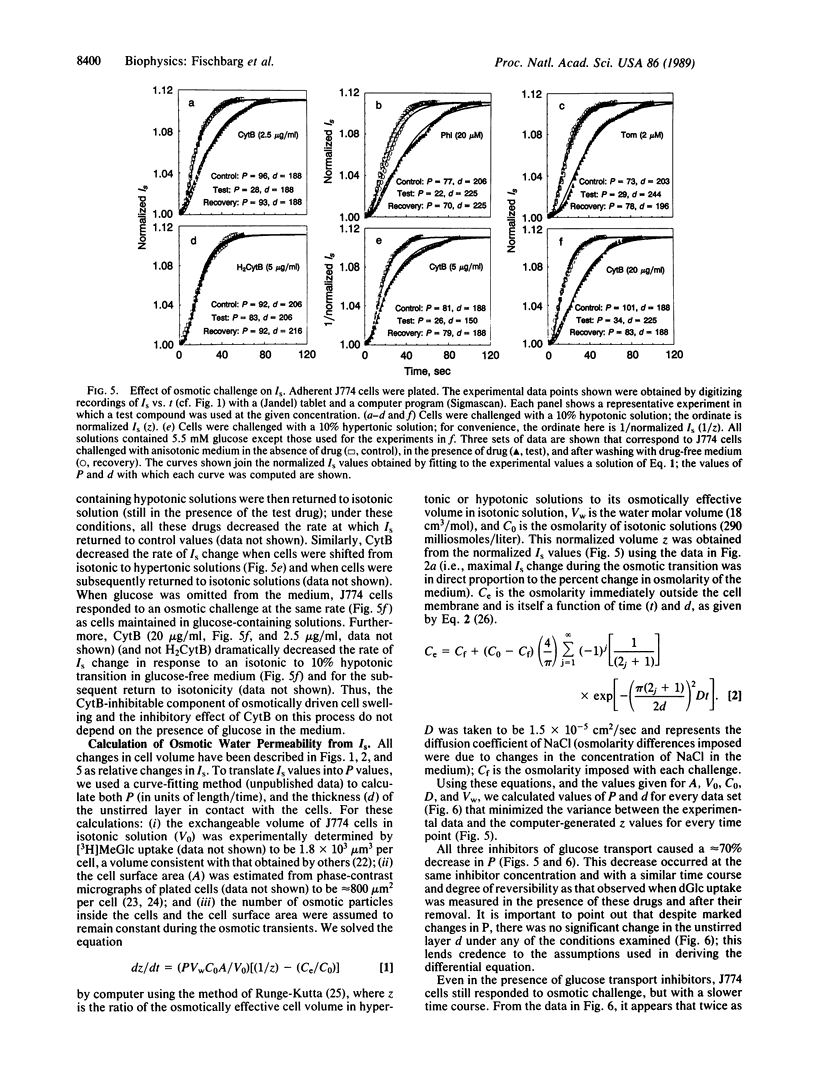
Water transport across plasma membranes is a universal property of cells, but the route of such transport is unclear. In this study, volume changes of cells of the J774 murine macrophage-like cell line were monitored by recording the intensity of light scattered by the cells. We investigated the effects of several inhibitors of glucose transport on cell membrane osmotic water permeability as calculated from the rates of cell volume change. Cytochalasin B (2.5 micrograms/ml), phloretin (20 microM), and tomatine (3 microM) reversibly blocked glucose uptake into these cells. All three inhibitors reversibly decreased the osmotic water permeability of J774 cells from 89.6 +/- 3.2 to 27.2 +/- 1.4 microns/sec. We conclude that a major component of the osmotic water flow across the plasma membranes of these cells is accounted for by water traversing their glucose transporters.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alvarez J., Lee D. C., Baldwin S. A., Chapman D. Fourier transform infrared spectroscopic study of the structure and conformational changes of the human erythrocyte glucose transporter. J Biol Chem. 1987 Mar 15;262(8):3502–3509. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benga G., Pop V. I., Popescu O., Ionescu M., Mihele V. Water exchange through erythrocyte membranes: nuclear magnetic resonance studies on the effects of inhibitors and of chemical modifications of human membranes. J Membr Biol. 1983;76(2):129–137. doi: 10.1007/BF02000613. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benga G., Popescu O., Borza V., Pop V. I., Muresan A., Mocsy I., Brain A., Wrigglesworth J. M. Water permeability in human erythrocytes: identification of membrane proteins involved in water transport. Eur J Cell Biol. 1986 Aug;41(2):252–262. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brahm J. Kinetics of glucose transport in human erythrocytes. J Physiol. 1983 Jun;339:339–354. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1983.sp014720. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chevalier J., Bourguet J., Hugon J. S. Membrane associated particles: distribution in frog urinary bladder epithelium at rest and after oxytocin treatment. Cell Tissue Res. 1974;152(2):129–140. doi: 10.1007/BF00224690. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fettiplace R. The influence of the lipid on the water permeability of artificial membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Oct 19;513(1):1–10. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(78)90106-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischbarg J. On the possible permeation of water across the glucose transporter. Mol Cell Biochem. 1988 Jul-Aug;82(1-2):107–111. doi: 10.1007/BF00242524. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jung E. K., Chin J. J., Jung C. Y. Structural basis of human erythrocyte glucose transporter function in reconstituted system. Hydrogen exchange. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jul 15;261(20):9155–9160. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kletzien R. F., Pariza M. W., Becker J. E., Potter V. R. A method using 3-O-methyl-D-glucose and phloretin for the determination of intracellular water space of cells in monolayer culture. Anal Biochem. 1975 Oct;68(2):537–544. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(75)90649-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LARIS P. C. Permeability and utilization of glucose in mammalian erythrocytes. J Cell Physiol. 1958 Apr;51(2):273–307. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1030510212. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEAF A., HAYS R. M. Permeability of the isolated toad bladder to solutes and its modification by vasopressin. J Gen Physiol. 1962 May;45:921–932. doi: 10.1085/jgp.45.5.921. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Latimer P., Moore D. M., Bryant F. D. Changes in total light scattering and absorption caused by changes in particle conformation. J Theor Biol. 1968 Dec;21(3):348–367. doi: 10.1016/0022-5193(68)90120-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Latimer P., Pyle B. E. Light scattering at various angles. Theoretical predictions of the effects of particle volume changes. Biophys J. 1972 Jul;12(7):764–773. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(72)86120-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loike J. D., Somes M., Silverstein S. C. Creatine uptake, metabolism, and efflux in human monocytes and macrophages. Am J Physiol. 1986 Jul;251(1 Pt 1):C128–C135. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1986.251.1.C128. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macey R. I. Transport of water and urea in red blood cells. Am J Physiol. 1984 Mar;246(3 Pt 1):C195–C203. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1984.246.3.C195. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maness P. F., Walsh R. C., Jr Dihydrocytochalasin B disorganizes actin cytoarchitecture and inhibits initiation of DNA synthesis in 3T3 cells. Cell. 1982 Aug;30(1):253–262. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90031-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mueckler M., Caruso C., Baldwin S. A., Panico M., Blench I., Morris H. R., Allard W. J., Lienhard G. E., Lodish H. F. Sequence and structure of a human glucose transporter. Science. 1985 Sep 6;229(4717):941–945. doi: 10.1126/science.3839598. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owen J. D., Solomon A. K. Control of nonelectrolyte permeability in red cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Dec 1;290(1):414–418. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(72)90087-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phaire-Washington L., Wang E., Silverstein S. C. Phorbol myristate acetate stimulates pinocytosis and membrane spreading in mouse peritoneal macrophages. J Cell Biol. 1980 Aug;86(2):634–640. doi: 10.1083/jcb.86.2.634. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ralph P., Prichard J., Cohn M. Reticulum cell sarcoma: an effector cell in antibody-dependent cell-mediated immunity. J Immunol. 1975 Feb;114(2 Pt 2):898–905. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rich G. T., Sha'afi R. I., Barton T. C., Solomon A. K. Permeability studies on red cell membranes of dog, cat, and beef. J Gen Physiol. 1967 Nov;50(10):2391–2405. doi: 10.1085/jgp.50.10.2391. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Solomon A. K., Chasan B., Dix J. A., Lukacovic M. F., Toon M. R., Verkman A. S. The aqueous pore in the red cell membrane: band 3 as a channel for anions, cations, nonelectrolytes, and water. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1983;414:97–124. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1983.tb31678.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinman R. M., Brodie S. E., Cohn Z. A. Membrane flow during pinocytosis. A stereologic analysis. J Cell Biol. 1976 Mar;68(3):665–687. doi: 10.1083/jcb.68.3.665. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sung S. S., Young J. D., Origlio A. M., Heiple J. M., Kaback H. R., Silverstein S. C. Extracellular ATP perturbs transmembrane ion fluxes, elevates cytosolic [Ca2+], and inhibits phagocytosis in mouse macrophages. J Biol Chem. 1985 Nov 5;260(25):13442–13449. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]