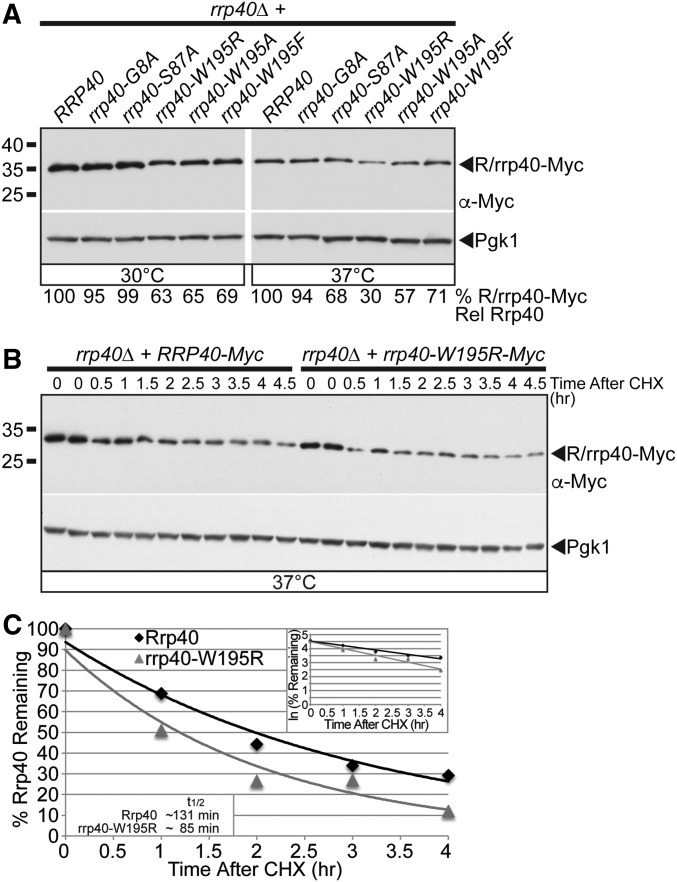
Figure 4.
The rrp40-W195R variant is less stable than wild-type Rrp40 in cells as the only copy of Rrp40. (A) The steady-state level of the rrp40-W195R and rrp40-W195A variant is decreased compared to wild-type Rrp40 in rrp40∆ cells at 37°. Lysates of rrp40∆ cells expressing Myc-tagged wild-type Rrp40 or rrp40 variant (G8A, S87A, W195A, W195R, and W195F) grown at 30 or 37° were analyzed by immunoblotting with anti-Myc antibody to detect Myc-tagged Rrp40 and rrp40 variants (R/rrp40-Myc), and anti-Pgk1 antibody to detect Pgk1 as a loading control. The percentage of Rrp40-Myc or rrp40-Myc variant relative to wild-type Rrp40-Myc (% R/rrp40-Myc Rel Rrp40) is shown below each lane, and was calculated as described in Materials and Methods. (B) The rrp40-W195R variant is unstable in rrp40∆ cells at 37°. The rrp40∆ cells expressing Myc-tagged Rrp40 or rrp40-W195R were treated with the translation inhibitor CHX. Samples were collected over time (0–4.5 hr) and analyzed by immunoblotting with anti-Myc antibody to detect Myc-tagged Rrp40 and rrp40-W195R protein (R/rrp40-Myc), and anti-Pgk1 antibody to detect Pgk1 as a loading control. (C) The immunoblot shown in (B) was quantitated to plot the percentage of Rrp40 and rrp40-W195R protein remaining at each time point relative to inhibition of translation at time 0 in rrp40∆ cells. The inset graph shows the natural logarithm (ln)-transformed percentages of Rrp40 and rrp40-W195R at time points 0–4 hr fitted with linear least-squares fit lines to determine the decay rate constant (k) for each protein. The inset half-lives (t1/2) of Rrp40 and rrp40-W195R in rrp40∆ cells at 37° were calculated from each decay rate constant using the equation t1/2 = ln(2)/k (Belle et al. 2006). Further details on the measurement of the percentages of protein using protein band intensities and calculation of the protein half-lives are described in Materials and Methods. Quantitation is for the specific experiment shown, but is representative of multiple experiments.