Abstract
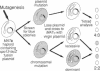
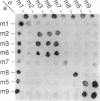
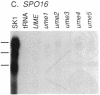
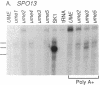
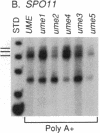
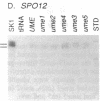
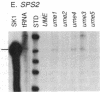
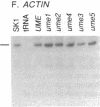
Mutations in Saccharomyces cerevisiae have been identified that derepress early meiotic genes functioning in separable pathways required for normal meiotic development. The phenotypes of these ume (unscheduled meiotic gene expression) mutations suggest that their wild-type alleles encode negative regulators acting downstream of both the cell-type and nutritional controls of meiosis. These newly defined loci do not affect either general transcription or transcription of meiotic genes expressed later in meiosis and spore formation.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Atcheson C. L., DiDomenico B., Frackman S., Esposito R. E., Elder R. T. Isolation, DNA sequence, and regulation of a meiosis-specific eukaryotic recombination gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Nov;84(22):8035–8039. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.22.8035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elder R. T., Loh E. Y., Davis R. W. RNA from the yeast transposable element Ty1 has both ends in the direct repeats, a structure similar to retrovirus RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 May;80(9):2432–2436. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.9.2432. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guarente L., Ptashne M. Fusion of Escherichia coli lacZ to the cytochrome c gene of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Apr;78(4):2199–2203. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.4.2199. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guarente L. Yeast promoters: positive and negative elements. Cell. 1984 Apr;36(4):799–800. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90028-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hyman B. C., Cramer J. H., Rownd R. H. Properties of a Saccharomyces cerevisiae mtDNA segment conferring high-frequency yeast transformation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Mar;79(5):1578–1582. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.5.1578. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito H., Fukuda Y., Murata K., Kimura A. Transformation of intact yeast cells treated with alkali cations. J Bacteriol. 1983 Jan;153(1):163–168. doi: 10.1128/jb.153.1.163-168.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kassir Y., Granot D., Simchen G. IME1, a positive regulator gene of meiosis in S. cerevisiae. Cell. 1988 Mar 25;52(6):853–862. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90427-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kassir Y., Simchen G. Regulation of mating and meiosis in yeast by the mating-type region. Genetics. 1976 Feb;82(2):187–206. doi: 10.1093/genetics/82.2.187. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klapholz S., Esposito R. E. A new mapping method employing a meiotic rec-mutant of yeast. Genetics. 1982 Mar;100(3):387–412. doi: 10.1093/genetics/100.3.387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klapholz S., Esposito R. E. Recombination and chromosome segregation during the single division meiosis in SPO12-1 and SPO13-1 diploids. Genetics. 1980 Nov;96(3):589–611. doi: 10.1093/genetics/96.3.589. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsumoto K., Uno I., Ishikawa T. Initiation of meiosis in yeast mutants defective in adenylate cyclase and cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase. Cell. 1983 Feb;32(2):417–423. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90461-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller A. M., MacKay V. L., Nasmyth K. A. Identification and comparison of two sequence elements that confer cell-type specific transcription in yeast. Nature. 1985 Apr 18;314(6012):598–603. doi: 10.1038/314598a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell A. P., Herskowitz I. Activation of meiosis and sporulation by repression of the RME1 product in yeast. 1986 Feb 27-Mar 5Nature. 319(6056):738–742. doi: 10.1038/319738a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nasmyth K., Stillman D., Kipling D. Both positive and negative regulators of HO transcription are required for mother-cell-specific mating-type switching in yeast. Cell. 1987 Feb 27;48(4):579–587. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90236-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Percival-Smith A., Segall J. Characterization and mutational analysis of a cluster of three genes expressed preferentially during sporulation of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Jul;6(7):2443–2451. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.7.2443. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Percival-Smith A., Segall J. Isolation of DNA sequences preferentially expressed during sporulation in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Jan;4(1):142–150. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.1.142. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slater M. R., Craig E. A. Transcriptional regulation of an hsp70 heat shock gene in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 May;7(5):1906–1916. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.5.1906. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith H. E., Mitchell A. P. A transcriptional cascade governs entry into meiosis in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 May;9(5):2142–2152. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.5.2142. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strathern J., Hicks J., Herskowitz I. Control of cell type in yeast by the mating type locus. The alpha 1-alpha 2 hypothesis. J Mol Biol. 1981 Apr 15;147(3):357–372. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90488-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tatchell K. RAS genes and growth control in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Bacteriol. 1986 May;166(2):364–367. doi: 10.1128/jb.166.2.364-367.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tatchell K., Robinson L. C., Breitenbach M. RAS2 of Saccharomyces cerevisiae is required for gluconeogenic growth and proper response to nutrient limitation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jun;82(11):3785–3789. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.11.3785. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toda T., Uno I., Ishikawa T., Powers S., Kataoka T., Broek D., Cameron S., Broach J., Matsumoto K., Wigler M. In yeast, RAS proteins are controlling elements of adenylate cyclase. Cell. 1985 Jan;40(1):27–36. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90305-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang H. T., Frackman S., Kowalisyn J., Esposito R. E., Elder R. Developmental regulation of SPO13, a gene required for separation of homologous chromosomes at meiosis I. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Apr;7(4):1425–1435. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.4.1425. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whiteway M., Szostak J. W. The ARD1 gene of yeast functions in the switch between the mitotic cell cycle and alternative developmental pathways. Cell. 1985 Dec;43(2 Pt 1):483–492. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90178-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]