Abstract
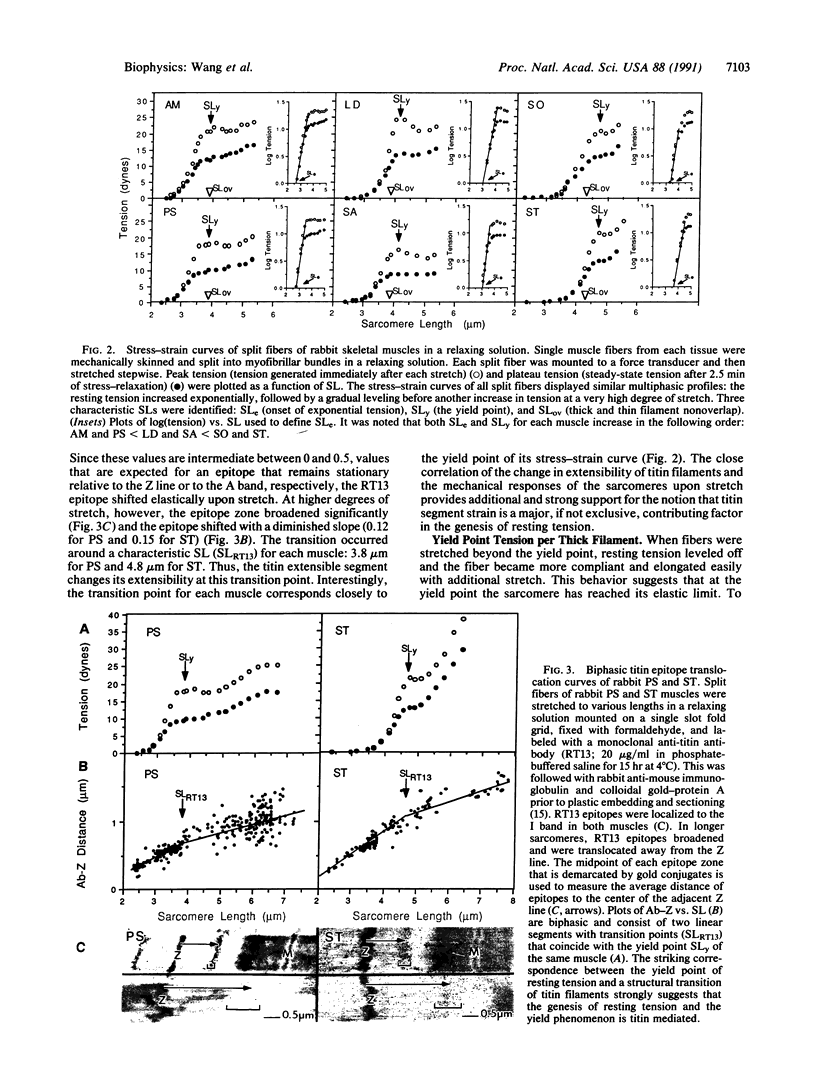
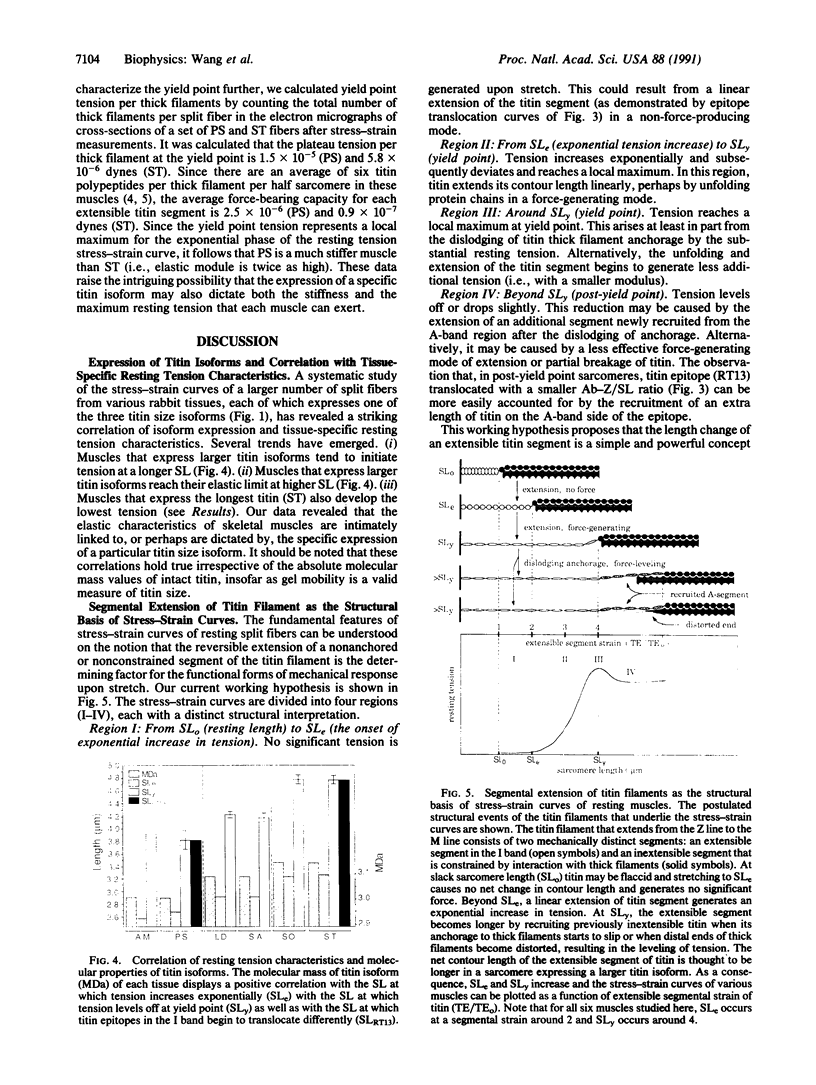
To explore the role of titin filaments in muscle elasticity, we measured the resting tension-sarcomere length curves of six rabbit skeletal muscles that express three size classes of titin isoform. The stress-strain curves of the split fibers of these muscles displayed a similar multiphasic shape, with an exponential increase in tension at low sarcomere strain followed by a leveling of tension and a decrease in stiffness at and beyond an elastic limit (yield point) at higher sarcomere strain. Significantly, positive correlations exist between the size of the expressed titin isoform, the sarcomere length at the onset of exponential resting tension, and the yield point of each muscle. Immunoelectron microscopic studies of an epitope in the extensible segment of titin revealed a transition in the elastic behavior of the titin filaments near the yield point sarcomere length of these muscles, providing direct evidence of titin's involvement in the genesis of resting tension. Our data led to the formulation of a segmental extension model of resting tension that recognizes the interplay of three major factors in shaping the stress-strain curves: the net contour length of an extensible segment of titin filaments (between the Z line and the ends of the thick filaments), the intrinsic molecular elasticity of titin, and the strength of titin thick filament anchorage. Our data further suggest that skeletal muscle cells may control and modulate stiffness and elastic limit coordinately by selective expression of specific titin isoforms.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cooke R. The mechanism of muscle contraction. CRC Crit Rev Biochem. 1986;21(1):53–118. doi: 10.3109/10409238609113609. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fürst D. O., Osborn M., Nave R., Weber K. The organization of titin filaments in the half-sarcomere revealed by monoclonal antibodies in immunoelectron microscopy: a map of ten nonrepetitive epitopes starting at the Z line extends close to the M line. J Cell Biol. 1988 May;106(5):1563–1572. doi: 10.1083/jcb.106.5.1563. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hainfeld J. F., Wall J. S., Wang K. Titin: quantitative mass measurements by scanning transmission electron microscopy and structural implications for the sarcomere matrix of skeletal muscle. FEBS Lett. 1988 Jul 4;234(1):145–148. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(88)81321-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higuchi H., Umazume Y. Localization of the parallel elastic components in frog skinned muscle fibers studied by the dissociation of the A- and I-bands. Biophys J. 1985 Jul;48(1):137–147. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(85)83767-X. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horowits R., Kempner E. S., Bisher M. E., Podolsky R. J. A physiological role for titin and nebulin in skeletal muscle. Nature. 1986 Sep 11;323(6084):160–164. doi: 10.1038/323160a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horowits R., Podolsky R. J. Thick filament movement and isometric tension in activated skeletal muscle. Biophys J. 1988 Jul;54(1):165–171. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(88)82941-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hu D. H., Kimura S., Maruyama K. Sodium dodecyl sulfate gel electrophoresis studies of connectin-like high molecular weight proteins of various types of vertebrate and invertebrate muscles. J Biochem. 1986 May;99(5):1485–1492. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a135618. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Itoh Y., Suzuki T., Kimura S., Ohashi K., Higuchi H., Sawada H., Shimizu T., Shibata M., Maruyama K. Extensible and less-extensible domains of connectin filaments in stretched vertebrate skeletal muscle sarcomeres as detected by immunofluorescence and immunoelectron microscopy using monoclonal antibodies. J Biochem. 1988 Oct;104(4):504–508. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a122499. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurzban G. P., Wang K. Giant polypeptides of skeletal muscle titin: sedimentation equilibrium in guanidine hydrochloride. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 Feb 15;150(3):1155–1161. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(88)90750-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magid A., Law D. J. Myofibrils bear most of the resting tension in frog skeletal muscle. Science. 1985 Dec 13;230(4731):1280–1282. doi: 10.1126/science.4071053. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maruyama K. Connectin, an elastic filamentous protein of striated muscle. Int Rev Cytol. 1986;104:81–114. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7696(08)61924-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang K. Sarcomere-associated cytoskeletal lattices in striated muscle. Review and hypothesis. Cell Muscle Motil. 1985;6:315–369. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4757-4723-2_10. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang K., Wright J. Architecture of the sarcomere matrix of skeletal muscle: immunoelectron microscopic evidence that suggests a set of parallel inextensible nebulin filaments anchored at the Z line. J Cell Biol. 1988 Dec;107(6 Pt 1):2199–2212. doi: 10.1083/jcb.107.6.2199. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whiting A., Wardale J., Trinick J. Does titin regulate the length of muscle thick filaments? J Mol Biol. 1989 Jan 5;205(1):263–268. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(89)90381-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]







