Abstract
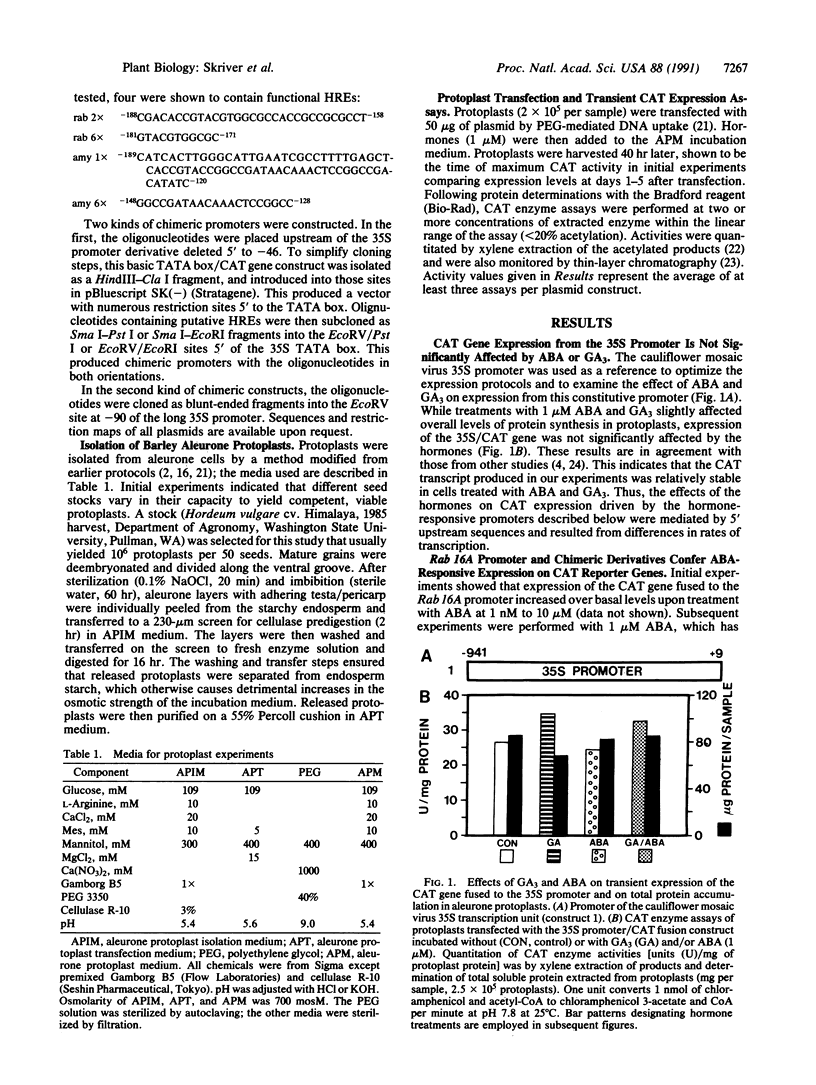
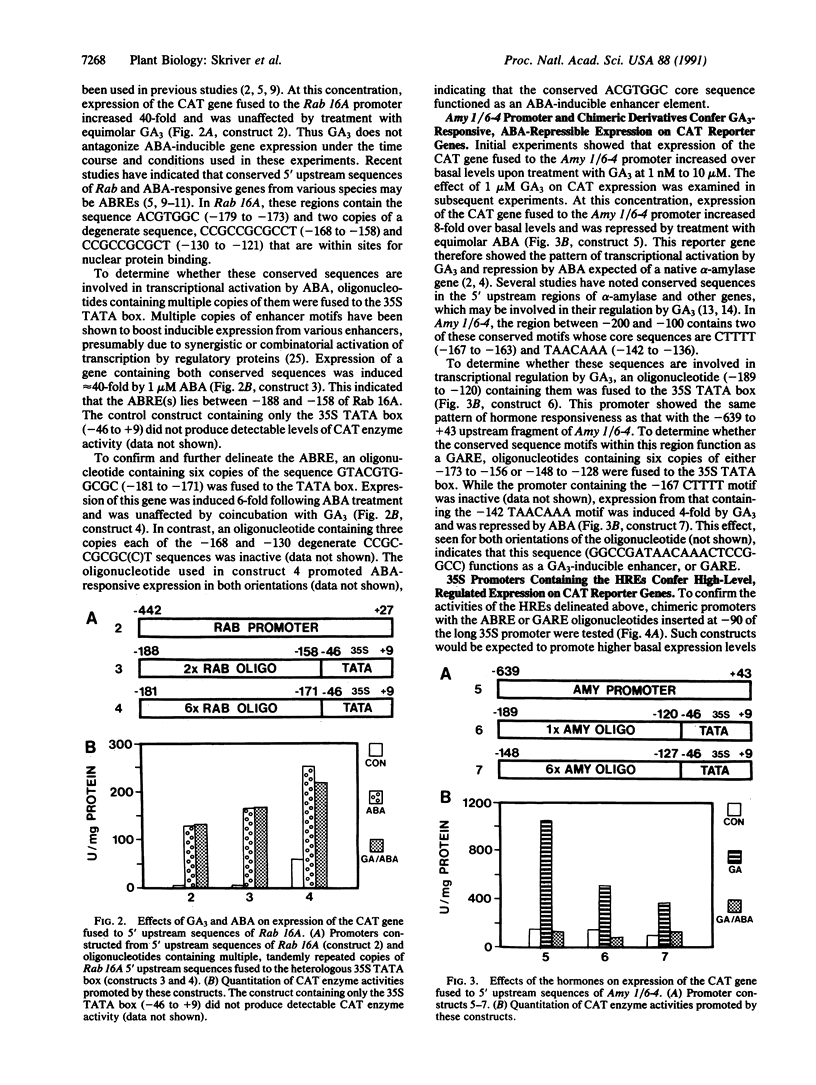
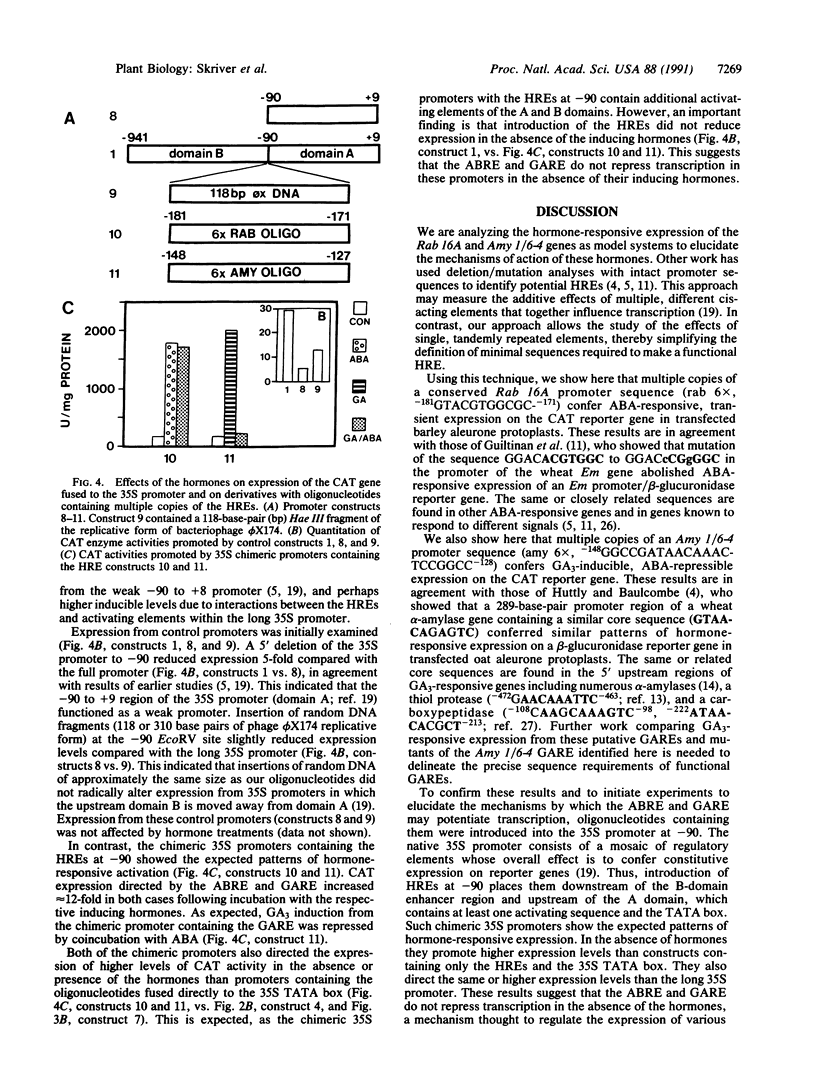
We have used a transient expression assay in aleurone protoplasts of barley to delineate hormone response elements of the abscisic acid (ABA)-responsive rice gene Rab16A and of the gibberellin A3 (GA3)-responsive barley alpha-amylase gene Amy 1/6-4. Our approach used transcriptional fusions between their 5' upstream sequences and a bacterial chloramphenicol acetyltransferase reporter gene. A chimeric promoter containing six copies of the -181 to -171 region of Rab 16A fused to a minimal promoter conferred ABA-responsive expression on the reporter gene. Transcription from this ABA response element (GTACGTGGCGC) was unaffected by GA3. A chimeric promoter containing six copies of the -148 to -128 sequence of Amy 1/6-4 fused to the minimal promoter conferred GA3-responsive expression on the reporter gene. Transcription from this GA3 response element (GGCCGATAACAAACTCCGGCC) was repressed by ABA. The effect on transcription from both hormone response elements was orientation-independent, indicating that they function as inducible enhancers in their native genes.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baulcombe D. C., Barker R. F., Jarvis M. G. A gibberellin responsive wheat gene has homology to yeast carboxypeptidase Y. J Biol Chem. 1987 Oct 5;262(28):13726–13735. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benfey P. N., Ren L., Chua N. H. Combinatorial and synergistic properties of CaMV 35S enhancer subdomains. EMBO J. 1990 Jun;9(6):1685–1696. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08292.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Close T. J., Kortt A. A., Chandler P. M. A cDNA-based comparison of dehydration-induced proteins (dehydrins) in barley and corn. Plant Mol Biol. 1989 Jul;13(1):95–108. doi: 10.1007/BF00027338. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glass C. K., Holloway J. M., Devary O. V., Rosenfeld M. G. The thyroid hormone receptor binds with opposite transcriptional effects to a common sequence motif in thyroid hormone and estrogen response elements. Cell. 1988 Jul 29;54(3):313–323. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90194-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman C. M., Moffat L. F., Howard B. H. Recombinant genomes which express chloramphenicol acetyltransferase in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Sep;2(9):1044–1051. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.9.1044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guiltinan M. J., Marcotte W. R., Jr, Quatrano R. S. A plant leucine zipper protein that recognizes an abscisic acid response element. Science. 1990 Oct 12;250(4978):267–271. doi: 10.1126/science.2145628. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang N., Sutliff T. D., Litts J. C., Rodriguez R. L. Classification and characterization of the rice alpha-amylase multigene family. Plant Mol Biol. 1990 May;14(5):655–668. doi: 10.1007/BF00016499. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huttly A. K., Baulcombe D. C. A wheat alpha-Amy2 promoter is regulated by gibberellin in transformed oat aleurone protoplasts. EMBO J. 1989 Jul;8(7):1907–1913. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03593.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khursheed B., Rogers J. C. Barley alpha-amylase genes. Quantitative comparison of steady-state mRNA levels from individual members of the two different families expressed in aleurone cells. J Biol Chem. 1988 Dec 15;263(35):18953–18960. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee B., Murdoch K., Topping J., Kreis M., Jones M. G. Transient gene expression in aleurone protoplasts isolated from developing caryopses of barley and wheat. Plant Mol Biol. 1989 Jul;13(1):21–29. doi: 10.1007/BF00027332. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marcotte W. R., Jr, Russell S. H., Quatrano R. S. Abscisic acid-responsive sequences from the em gene of wheat. Plant Cell. 1989 Oct;1(10):969–976. doi: 10.1105/tpc.1.10.969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mundy J., Chua N. H. Abscisic acid and water-stress induce the expression of a novel rice gene. EMBO J. 1988 Aug;7(8):2279–2286. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03070.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mundy J., Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K., Chua N. H. Nuclear proteins bind conserved elements in the abscisic acid-responsive promoter of a rice rab gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Feb;87(4):1406–1410. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.4.1406. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muthukrishnan S., Chandra G. R., Maxwell E. S. Hormone-induced increase in levels of functional mRNA and alpha-amylase mRNA in barley aleurones. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Dec;76(12):6181–6185. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.12.6181. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Odell J. T., Nagy F., Chua N. H. Identification of DNA sequences required for activity of the cauliflower mosaic virus 35S promoter. 1985 Feb 28-Mar 6Nature. 313(6005):810–812. doi: 10.1038/313810a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ou-Lee T. M., Turgeon R., Wu R. Interaction of a gibberellin-induced factor with the upstream region of an alpha-amylase gene in rice aleurone tissue. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Sep;85(17):6366–6369. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.17.6366. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ponglikitmongkol M., White J. H., Chambon P. Synergistic activation of transcription by the human estrogen receptor bound to tandem responsive elements. EMBO J. 1990 Jul;9(7):2221–2231. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07392.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Renkawitz R. Transcriptional repression in eukaryotes. Trends Genet. 1990 Jun;6(6):192–197. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(90)90176-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schulze-Lefert P., Dangl J. L., Becker-André M., Hahlbrock K., Schulz W. Inducible in vivo DNA footprints define sequences necessary for UV light activation of the parsley chalcone synthase gene. EMBO J. 1989 Mar;8(3):651–656. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03422.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seed B., Sheen J. Y. A simple phase-extraction assay for chloramphenicol acyltransferase activity. Gene. 1988 Jul 30;67(2):271–277. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90403-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skriver K., Mundy J. Gene expression in response to abscisic acid and osmotic stress. Plant Cell. 1990 Jun;2(6):503–512. doi: 10.1105/tpc.2.6.503. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vilardell J., Goday A., Freire M. A., Torrent M., Martínez M. C., Torné J. M., Pagès M. Gene sequence, developmental expression, and protein phosphorylation of RAB-17 in maize. Plant Mol Biol. 1990 Mar;14(3):423–432. doi: 10.1007/BF00028778. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whittier R. F., Dean D. A., Rogers J. C. Nucleotide sequence analysis of alpha-amylase and thiol protease genes that are hormonally regulated in barley aleurone cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Mar 25;15(6):2515–2535. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.6.2515. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K., Mundy J., Chua N. H. Four tightly linked rab genes are differentially expressed in rice. Plant Mol Biol. 1990 Jan;14(1):29–39. doi: 10.1007/BF00015652. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zwar J. A., Hooley R. Hormonal Regulation of alpha-Amylase Gene Transcription in Wild Oat (Avena fatua L.) Aleurone Protoplasts. Plant Physiol. 1986 Feb;80(2):459–463. doi: 10.1104/pp.80.2.459. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



