Abstract
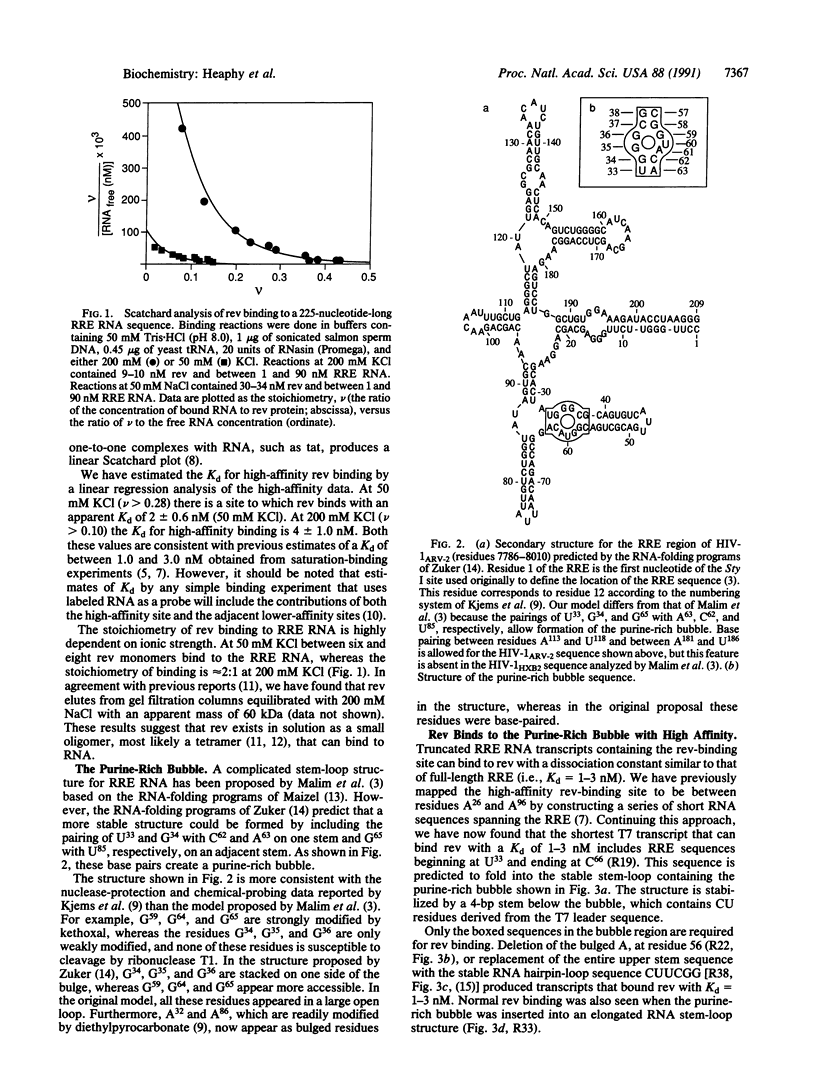
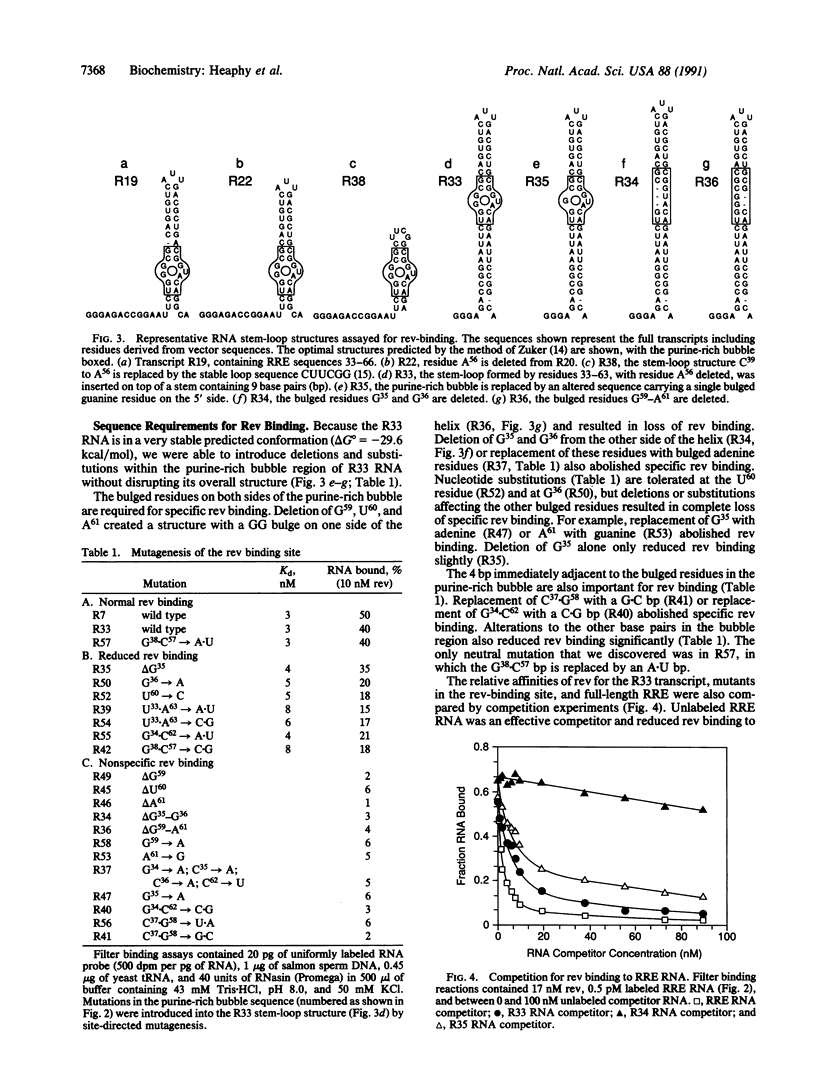
The human immunodeficiency virus type 1 rev protein binds with high affinity (Kd less than 1-3 nM) to a purine-rich "bubble" containing bulged GG and GUA residues on either side of a double-helical RNA stem-loop located toward the 5' end of rev-response element RNA. High-affinity rev binding is maintained when the bubble is placed in heterologous stem-loop structures, but rev binding is reduced when either the bulged residues or flanking base pairs in the stem are altered. Rev binding to the purine-rich bubble nucleates assembly of long filamentous ribonucleoprotein structures containing polymers of rev bound to flanking RNA sequences. It is proposed that rev regulates human immunodeficiency virus RNA expression by selectively packaging viral transcripts carrying the rev-response element sequence into rod-like nucleoprotein complexes that block splicing of the packaged mRNAs.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Chang D. D., Sharp P. A. Regulation by HIV Rev depends upon recognition of splice sites. Cell. 1989 Dec 1;59(5):789–795. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90602-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheong C., Varani G., Tinoco I., Jr Solution structure of an unusually stable RNA hairpin, 5'GGAC(UUCG)GUCC. Nature. 1990 Aug 16;346(6285):680–682. doi: 10.1038/346680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daly T. J., Cook K. S., Gray G. S., Maione T. E., Rusche J. R. Specific binding of HIV-1 recombinant Rev protein to the Rev-responsive element in vitro. Nature. 1989 Dec 14;342(6251):816–819. doi: 10.1038/342816a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dayton E. T., Powell D. M., Dayton A. I. Functional analysis of CAR, the target sequence for the Rev protein of HIV-1. Science. 1989 Dec 22;246(4937):1625–1629. doi: 10.1126/science.2688093. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dingwall C., Ernberg I., Gait M. J., Green S. M., Heaphy S., Karn J., Lowe A. D., Singh M., Skinner M. A. HIV-1 tat protein stimulates transcription by binding to a U-rich bulge in the stem of the TAR RNA structure. EMBO J. 1990 Dec;9(12):4145–4153. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07637.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dreyfuss G. Structure and function of nuclear and cytoplasmic ribonucleoprotein particles. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1986;2:459–498. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.02.110186.002331. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heaphy S., Dingwall C., Ernberg I., Gait M. J., Green S. M., Karn J., Lowe A. D., Singh M., Skinner M. A. HIV-1 regulator of virion expression (Rev) protein binds to an RNA stem-loop structure located within the Rev response element region. Cell. 1990 Feb 23;60(4):685–693. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90671-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holland S. M., Ahmad N., Maitra R. K., Wingfield P., Venkatesan S. Human immunodeficiency virus rev protein recognizes a target sequence in rev-responsive element RNA within the context of RNA secondary structure. J Virol. 1990 Dec;64(12):5966–5975. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.12.5966-5975.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ivey-Hoyle M., Rosenberg M. Rev-dependent expression of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 gp160 in Drosophila melanogaster cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Dec;10(12):6152–6159. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.12.6152. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim S. Y., Byrn R., Groopman J., Baltimore D. Temporal aspects of DNA and RNA synthesis during human immunodeficiency virus infection: evidence for differential gene expression. J Virol. 1989 Sep;63(9):3708–3713. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.9.3708-3713.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kjems J., Brown M., Chang D. D., Sharp P. A. Structural analysis of the interaction between the human immunodeficiency virus Rev protein and the Rev response element. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Feb 1;88(3):683–687. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.3.683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klug A. The assembly of tobacco mosaic virus: structure and specificity. Harvey Lect. 1980;74:141–172. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le S. Y., Malim M. H., Cullen B. R., Maizel J. V. A highly conserved RNA folding region coincident with the Rev response element of primate immunodeficiency viruses. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Mar 25;18(6):1613–1623. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.6.1613. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malim M. H., Hauber J., Le S. Y., Maizel J. V., Cullen B. R. The HIV-1 rev trans-activator acts through a structured target sequence to activate nuclear export of unspliced viral mRNA. Nature. 1989 Mar 16;338(6212):254–257. doi: 10.1038/338254a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malim M. H., Tiley L. S., McCarn D. F., Rusche J. R., Hauber J., Cullen B. R. HIV-1 structural gene expression requires binding of the Rev trans-activator to its RNA target sequence. Cell. 1990 Feb 23;60(4):675–683. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90670-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGhee J. D., von Hippel P. H. Theoretical aspects of DNA-protein interactions: co-operative and non-co-operative binding of large ligands to a one-dimensional homogeneous lattice. J Mol Biol. 1974 Jun 25;86(2):469–489. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90031-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nalin C. M., Purcell R. D., Antelman D., Mueller D., Tomchak L., Wegrzynski B., McCarney E., Toome V., Kramer R., Hsu M. C. Purification and characterization of recombinant Rev protein of human immunodeficiency virus type 1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Oct;87(19):7593–7597. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.19.7593. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olsen H. S., Cochrane A. W., Dillon P. J., Nalin C. M., Rosen C. A. Interaction of the human immunodeficiency virus type 1 Rev protein with a structured region in env mRNA is dependent on multimer formation mediated through a basic stretch of amino acids. Genes Dev. 1990 Aug;4(8):1357–1364. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.8.1357. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olsen H. S., Nelbock P., Cochrane A. W., Rosen C. A. Secondary structure is the major determinant for interaction of HIV rev protein with RNA. Science. 1990 Feb 16;247(4944):845–848. doi: 10.1126/science.2406903. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pomerantz R. J., Trono D., Feinberg M. B., Baltimore D. Cells nonproductively infected with HIV-1 exhibit an aberrant pattern of viral RNA expression: a molecular model for latency. Cell. 1990 Jun 29;61(7):1271–1276. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90691-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosen C. A., Terwilliger E., Dayton A., Sodroski J. G., Haseltine W. A. Intragenic cis-acting art gene-responsive sequences of the human immunodeficiency virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Apr;85(7):2071–2075. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.7.2071. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SantaLucia J., Jr, Kierzek R., Turner D. H. Effects of GA mismatches on the structure and thermodynamics of RNA internal loops. Biochemistry. 1990 Sep 18;29(37):8813–8819. doi: 10.1021/bi00489a044. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trono D., Baltimore D. A human cell factor is essential for HIV-1 Rev action. EMBO J. 1990 Dec;9(12):4155–4160. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07638.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turner D. R., McGuigan C. J., Butler P. J. Assembly of hybrid RNAs with tobacco mosaic virus coat protein. Evidence for incorporation of disks in 5'-elongation along the major RNA tail. J Mol Biol. 1989 Oct 5;209(3):407–422. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(89)90006-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zapp M. L., Green M. R. Sequence-specific RNA binding by the HIV-1 Rev protein. Nature. 1989 Dec 7;342(6250):714–716. doi: 10.1038/342714a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zuker M. On finding all suboptimal foldings of an RNA molecule. Science. 1989 Apr 7;244(4900):48–52. doi: 10.1126/science.2468181. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




