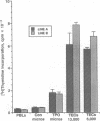
Abstract
Graves disease is a common form of human autoimmune thyroiditis. It shares many pathological features and HLA associations with other, less easily studied, organ-specific autoimmune conditions such as insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus, and hence it is also a useful model for understanding these other diseases. We have previously shown that thyroid-infiltrating T cells in Graves disease that have been recently activated in vivo specifically recognize autologous thyroid epithelial cells. However, the autoantigens involved were not defined. In this study, we have made use of antigen-independent T-cell cloning techniques to show that at least three different thyroid antigens, three different epitopes on a single antigen, and two HLA class II elements are involved in this recognition process in a single individual. This demonstrates that T cells that are present and activated at the site of a human autoimmune disease may show considerable heterogeneity in their recognition of autoantigen on the target tissue. This contrasts with the limited heterogeneity recently reported in some animal models and has potentially important implications for both our understanding of the autoimmune process in humans and the design of immunotherapies to reverse it.
Full text
PDF
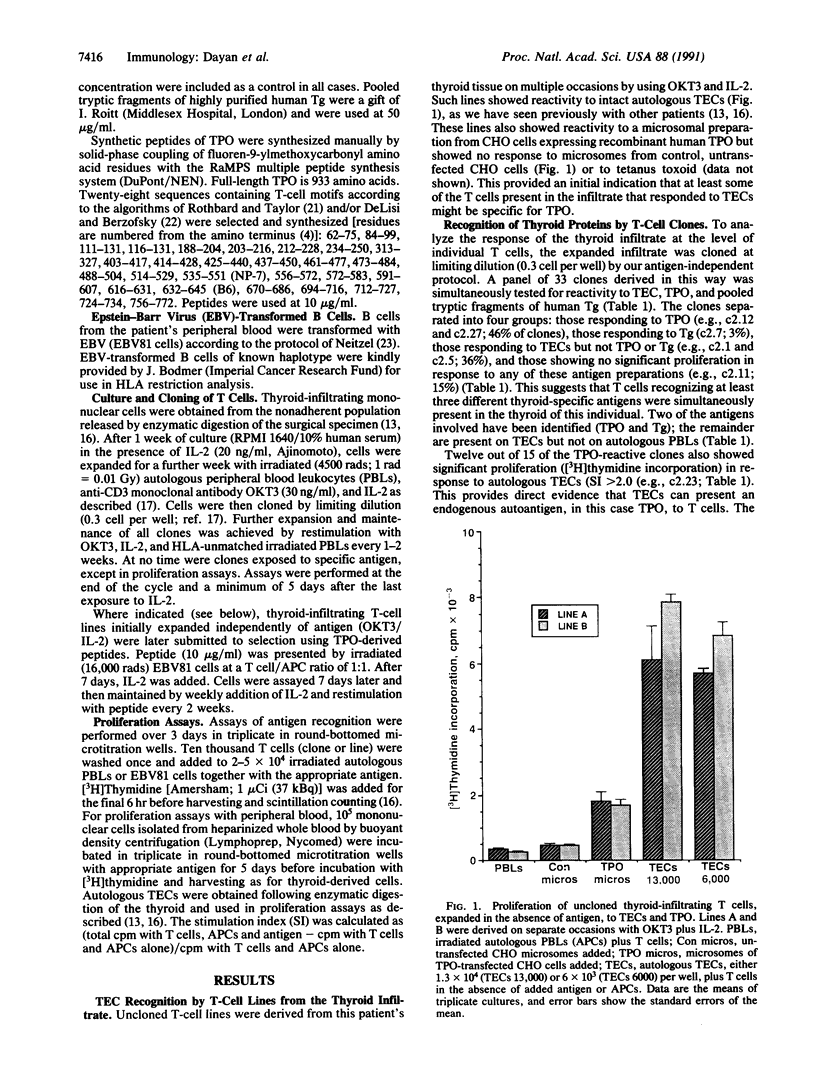
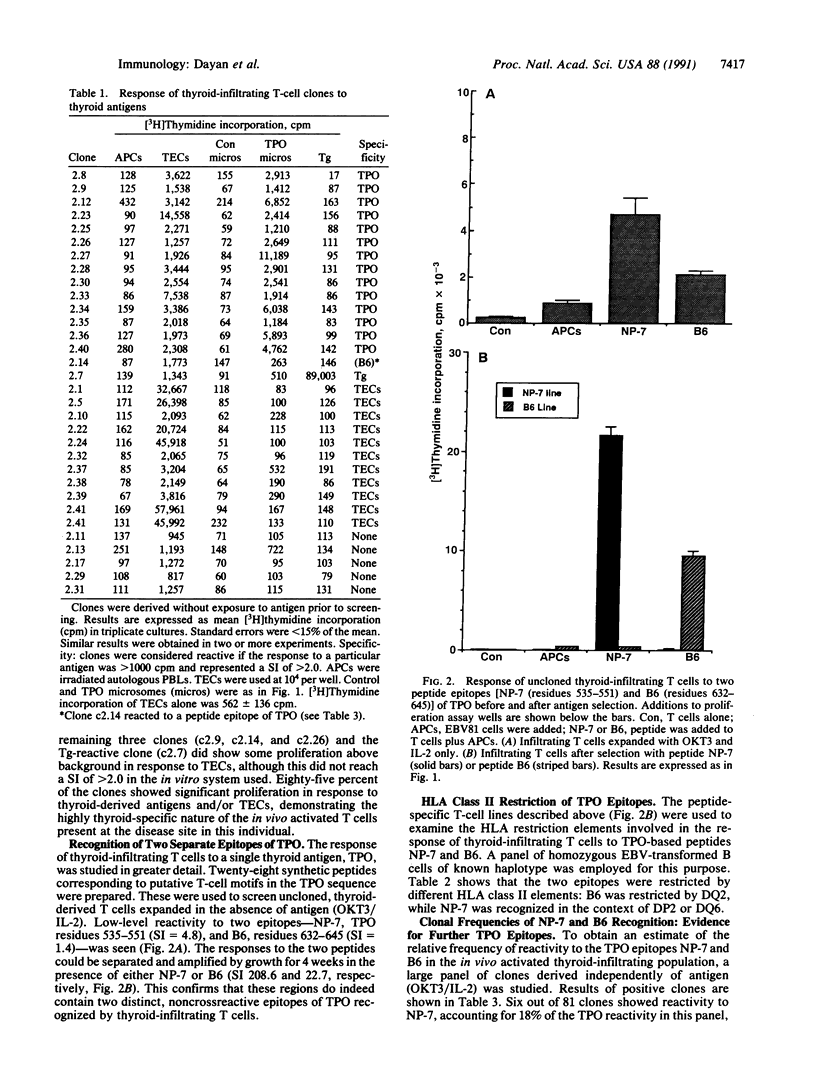
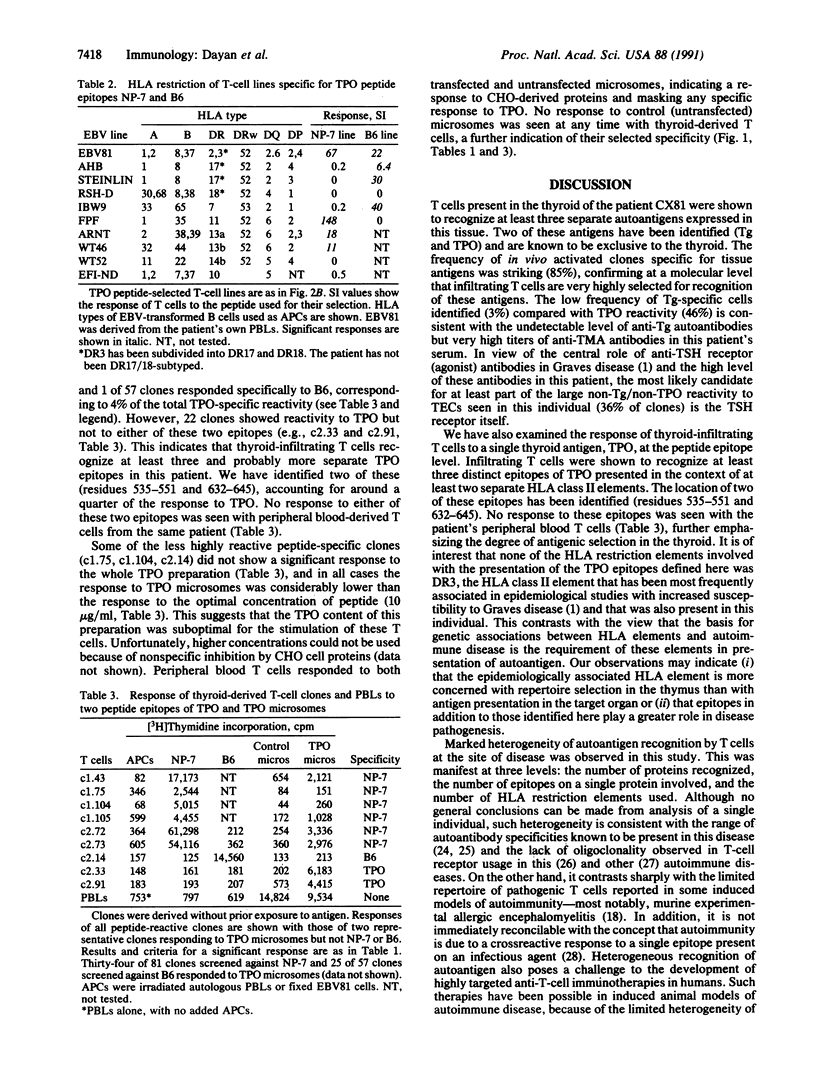

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Banga J. P., Barnett P. S., Ewins D. L., Page M. J., McGregor A. M. Mapping of autoantigenic epitopes on recombinant thyroid peroxidase fragments using the polymerase chain reaction. Autoimmunity. 1990;6(4):257–268. doi: 10.3109/08916939008998418. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bresler H. S., Burek C. L., Hoffman W. H., Rose N. R. Autoantigenic determinants on human thyroglobulin. II. Determinants recognized by autoantibodies from patients with chronic autoimmune thyroiditis compared to autoantibodies from healthy subjects. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1990 Jan;54(1):76–86. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(90)90007-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooke A. Is there restricted T cell receptor usage in autoimmune disease? Clin Exp Immunol. 1991 Mar;83(3):345–346. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.1991.tb05640.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeLisi C., Berzofsky J. A. T-cell antigenic sites tend to be amphipathic structures. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Oct;82(20):7048–7052. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.20.7048. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Del Prete G. F., Mariotti S., Tiri A., Ricci M., Pinchera A., Romagnani S. Characterization of thyroid infiltrating lymphocytes in Hashimoto's thyroiditis: detection of B and T cells specific for thyroid antigens. Acta Endocrinol Suppl (Copenh) 1987;281:111–114. doi: 10.1530/acta.0.114s111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gossage A. A., Munro D. S. The pathogenesis of Graves' disease. Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1985 May;14(2):299–330. doi: 10.1016/s0300-595x(85)80036-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grubeck-Loebenstein B., Buchan G., Chantry D., Kassal H., Londei M., Pirich K., Barrett K., Turner M., Waldhausl W., Feldmann M. Analysis of intrathyroidal cytokine production in thyroid autoimmune disease: thyroid follicular cells produce interleukin-1 alpha and interleukin-6. Clin Exp Immunol. 1989 Sep;77(3):324–330. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grubeck-Loebenstein B., Londei M., Greenall C., Pirich K., Kassal H., Waldhäusl W., Feldmann M. Pathogenetic relevance of HLA class II expressing thyroid follicular cells in nontoxic Goiter and in Graves' disease. J Clin Invest. 1988 May;81(5):1608–1614. doi: 10.1172/JCI113495. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grubeck-Loebenstein B., Turner M., Pirich K., Kassal H., Londei M., Waldhäusl W., Feldmann M. CD4+ T-cell clones from autoimmune thyroid tissue cannot be classified according to their lymphokine production. Scand J Immunol. 1990 Nov;32(5):433–440. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1990.tb03183.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanafusa T., Pujol-Borrell R., Chiovato L., Russell R. C., Doniach D., Bottazzo G. F. Aberrant expression of HLA-DR antigen on thyrocytes in Graves' disease: relevance for autoimmunity. Lancet. 1983 Nov 12;2(8359):1111–1115. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(83)90628-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaufman K. D., Rapoport B., Seto P., Chazenbalk G. D., Magnusson R. P. Generation of recombinant, enzymatically active human thyroid peroxidase and its recognition by antibodies in the sera of patients with Hashimoto's thyroiditis. J Clin Invest. 1989 Aug;84(2):394–403. doi: 10.1172/JCI114179. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimura S., Kotani T., McBride O. W., Umeki K., Hirai K., Nakayama T., Ohtaki S. Human thyroid peroxidase: complete cDNA and protein sequence, chromosome mapping, and identification of two alternately spliced mRNAs. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Aug;84(16):5555–5559. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.16.5555. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipoldova M., Londei M., Grubeck-Loebenstein B., Feldmann M., Owen M. J. Analysis of T-cell receptor usage in activated T-cell clones from Hashimoto's thyroiditis and Graves' disease. J Autoimmun. 1989 Feb;2(1):1–13. doi: 10.1016/0896-8411(89)90103-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Londei M., Bottazzo G. F., Feldmann M. Human T-cell clones from autoimmune thyroid glands: specific recognition of autologous thyroid cells. Science. 1985 Apr 5;228(4695):85–89. doi: 10.1126/science.3871967. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malthiéry Y., Lissitzky S. Primary structure of human thyroglobulin deduced from the sequence of its 8448-base complementary DNA. Eur J Biochem. 1987 Jun 15;165(3):491–498. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1987.tb11466.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller J. F. Lymphocyte interactions in antibody responses. Int Rev Cytol. 1972;33:77–130. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7696(08)61449-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagayama Y., Kaufman K. D., Seto P., Rapoport B. Molecular cloning, sequence and functional expression of the cDNA for the human thyrotropin receptor. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1989 Dec 29;165(3):1184–1190. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(89)92727-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neitzel H. A routine method for the establishment of permanent growing lymphoblastoid cell lines. Hum Genet. 1986 Aug;73(4):320–326. doi: 10.1007/BF00279094. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oldstone M. B. Molecular mimicry and autoimmune disease. Cell. 1987 Sep 11;50(6):819–820. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90507-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothbard J. B., Taylor W. R. A sequence pattern common to T cell epitopes. EMBO J. 1988 Jan;7(1):93–100. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02787.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seto P., Hirayu H., Magnusson R. P., Gestautas J., Portmann L., DeGroot L. J., Rapoport B. Isolation of a complementary DNA clone for thyroid microsomal antigen. Homology with the gene for thyroid peroxidase. J Clin Invest. 1987 Oct;80(4):1205–1208. doi: 10.1172/JCI113181. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Urban J. L., Kumar V., Kono D. H., Gomez C., Horvath S. J., Clayton J., Ando D. G., Sercarz E. E., Hood L. Restricted use of T cell receptor V genes in murine autoimmune encephalomyelitis raises possibilities for antibody therapy. Cell. 1988 Aug 12;54(4):577–592. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90079-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warford A., McLachlan S. M., Malcolm A. J., Young E. T., Farndon J. R., Rees Smith B. Characterization of lymphoid cells in the thyroid of patients with Graves' disease. Clin Exp Immunol. 1984 Sep;57(3):626–632. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weetman A. P., McGregor A. M., Lazarus J. H., Hall R. Thyroid antibodies are produced by thyroid-derived lymphocytes. Clin Exp Immunol. 1982 Apr;48(1):196–200. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weetman A. P., Volkman D. J., Burman K. D., Margolick J. B., Petrick P., Weintraub B. D., Fauci A. S. The production and characterization of thyroid-derived T-cell lines in Graves' disease and Hashimoto's thyroiditis. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1986 Apr;39(1):139–150. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(86)90213-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wraith D. C., Smilek D. E., Mitchell D. J., Steinman L., McDevitt H. O. Antigen recognition in autoimmune encephalomyelitis and the potential for peptide-mediated immunotherapy. Cell. 1989 Oct 20;59(2):247–255. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90287-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zheng R. Q., Abney E. R., Grubeck-Loebenstein B., Dayan C., Maini R. N., Feldmann M. Expression of intercellular adhesion molecule-1 and lymphocyte function-associated antigen-3 on human thyroid epithelial cells in Graves' and Hashimoto's diseases. J Autoimmun. 1990 Dec;3(6):727–736. doi: 10.1016/s0896-8411(05)80039-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]