Abstract
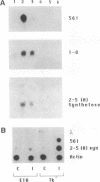
Infection with wild-type adenovirus 5, but not with a mutant lacking the E1A gene, prevented the induction by interferon (IFN) alpha of chloramphenicol acetyltransferase (CAT) activity in HeLaM cell lines that had been permanently transfected with chimeric CAT reporter genes driven by the transcriptional regulatory regions of the IFN-responsive genes 561 and 6-16. Similar inhibition of IFN-inducible CAT activity was observed in cells that were cotransfected with the same reporter genes and plasmids expressing either the E1A 289- or 243-amino acid protein. These proteins also prevented the induction of CAT activity by IFN-gamma from a cotransfected HLA-DR alpha-CAT gene. Experiments with E1A mutants mapped the inhibitory activity to amino acid residues 38-65 of these proteins. In a HeLa cell line permanently expressing the E1A 289-amino acid protein, the replication of vesicular stomatitis virus and encephalomyocarditis virus was not inhibited by IFN-alpha, suggesting a global blockade of IFN responses. In accord with this theory, induction of 561, 1-8, and (2'-5')oligoadenylate synthetase mRNAs by IFN was blocked in these cells at the transcriptional level. The observed transcriptional inhibition could be attributed to the lack of formation of the crucial IFN-stimulated gene factor 3 (ISGF3) transcriptional complex. As shown by mobility shift assays, this complex was not formed in the nuclear extracts of IFN-treated adenovirus-infected cells or IFN-treated E1A-producing cells. These nuclear extracts were deficient in both ISGF3 alpha and ISGF3 gamma subunits. However, they did not block the formation of ISGF3 complex from exogenously added components.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson K. P., Fennie E. H. Adenovirus early region 1A modulation of interferon antiviral activity. J Virol. 1987 Mar;61(3):787–795. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.3.787-795.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bagchi S., Raychaudhuri P., Nevins J. R. Adenovirus E1A proteins can dissociate heteromeric complexes involving the E2F transcription factor: a novel mechanism for E1A trans-activation. Cell. 1990 Aug 24;62(4):659–669. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90112-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bandyopadhyay S. K., Kalvakolanu D. V., Sen G. C. Gene induction by interferons: functional complementation between trans-acting factors induced by alpha interferon and gamma interferon. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Oct;10(10):5055–5063. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.10.5055. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dale T. C., Imam A. M., Kerr I. M., Stark G. R. Rapid activation by interferon alpha of a latent DNA-binding protein present in the cytoplasm of untreated cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Feb;86(4):1203–1207. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.4.1203. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalvakolanu D. V., Bandyopadhyay S. K., Tiwari R. K., Sen G. C. Enhancement of expression of exogenous genes by 2-aminopurine. Regulation at the post-transcriptional level. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jan 15;266(2):873–879. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitajewski J., Schneider R. J., Safer B., Munemitsu S. M., Samuel C. E., Thimmappaya B., Shenk T. Adenovirus VAI RNA antagonizes the antiviral action of interferon by preventing activation of the interferon-induced eIF-2 alpha kinase. Cell. 1986 Apr 25;45(2):195–200. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90383-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kusari J., Tiwari R. K., Kumar R., Sen G. C. Expression of interferon-inducible genes in RD-114 cells. J Virol. 1987 May;61(5):1524–1531. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.5.1524-1531.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lengyel P. Biochemistry of interferons and their actions. Annu Rev Biochem. 1982;51:251–282. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.51.070182.001343. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy D. E., Kessler D. S., Pine R., Darnell J. E., Jr Cytoplasmic activation of ISGF3, the positive regulator of interferon-alpha-stimulated transcription, reconstituted in vitro. Genes Dev. 1989 Sep;3(9):1362–1371. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.9.1362. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy D. E., Kessler D. S., Pine R., Reich N., Darnell J. E., Jr Interferon-induced nuclear factors that bind a shared promoter element correlate with positive and negative transcriptional control. Genes Dev. 1988 Apr;2(4):383–393. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.4.383. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy D. E., Lew D. J., Decker T., Kessler D. S., Darnell J. E., Jr Synergistic interaction between interferon-alpha and interferon-gamma through induced synthesis of one subunit of the transcription factor ISGF3. EMBO J. 1990 Apr;9(4):1105–1111. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08216.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lillie J. W., Loewenstein P. M., Green M. R., Green M. Functional domains of adenovirus type 5 E1a proteins. Cell. 1987 Sep 25;50(7):1091–1100. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90175-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moran E., Grodzicker T., Roberts R. J., Mathews M. B., Zerler B. Lytic and transforming functions of individual products of the adenovirus E1A gene. J Virol. 1986 Mar;57(3):765–775. doi: 10.1128/jvi.57.3.765-775.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nevins J. R. Mechanisms of viral-mediated trans-activation of transcription. Adv Virus Res. 1989;37:35–83. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3527(08)60832-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Malley R. P., Duncan R. F., Hershey J. W., Mathews M. B. Modification of protein synthesis initiation factors and the shut-off of host protein synthesis in adenovirus-infected cells. Virology. 1989 Jan;168(1):112–118. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(89)90409-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Offringa R., Gebel S., van Dam H., Timmers M., Smits A., Zwart R., Stein B., Bos J. L., van der Eb A., Herrlich P. A novel function of the transforming domain of E1a: repression of AP-1 activity. Cell. 1990 Aug 10;62(3):527–538. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90017-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porter A. C., Chernajovsky Y., Dale T. C., Gilbert C. S., Stark G. R., Kerr I. M. Interferon response element of the human gene 6-16. EMBO J. 1988 Jan;7(1):85–92. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02786.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reich N., Pine R., Levy D., Darnell J. E., Jr Transcription of interferon-stimulated genes is induced by adenovirus particles but is suppressed by E1A gene products. J Virol. 1988 Jan;62(1):114–119. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.1.114-119.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rochette-Egly C., Fromental C., Chambon P. General repression of enhanson activity by the adenovirus-2 E1A proteins. Genes Dev. 1990 Jan;4(1):137–150. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.1.137. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samuel C. E. Mechanisms of the antiviral action of interferons. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 1988;35:27–72. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6603(08)60609-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Webster K. A., Muscat G. E., Kedes L. Adenovirus E1A products suppress myogenic differentiation and inhibit transcription from muscle-specific promoters. Nature. 1988 Apr 7;332(6164):553–557. doi: 10.1038/332553a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weigel R. J., Devoto S. H., Nevins J. R. Adenovirus 12S E1A gene represses differentiation of F9 teratocarcinoma cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Dec;87(24):9878–9882. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.24.9878. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whyte P., Williamson N. M., Harlow E. Cellular targets for transformation by the adenovirus E1A proteins. Cell. 1989 Jan 13;56(1):67–75. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90984-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu D., Suen T. C., Yan D. H., Chang L. S., Hung M. C. Transcriptional repression of the neu protooncogene by the adenovirus 5 E1A gene products. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jun;87(12):4499–4503. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.12.4499. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]