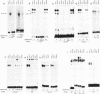
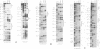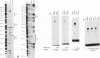Abstract
To analyse the 5'-flanking sequences required for the tissue specific transcription of the human erythropoietin receptor (hEpo-R) gene, a DNA region spanning nucleotides -1050 to +135 relative to the transcription initiation site (+1) was explored. Our studies indicate that a minimum promoter (-76/+33) containing GATA and SP1 binding sites at positions -45 and -20 is not sufficient to confer erythroid specific expression to a reporter gene. Erythroid specificity of the promoter was observed either with the (-1050/+33 construct) which contains a cluster of Alu repetitive elements or with the addition of the 135 bp down to the transcription initiation site (-76/+135 construct) which exert a negative control on the promoter activity with a major effect in non erythroid tissues. The latter region can be subdivided on two distinct domains: the +1/+78 region that exerts a positive effect and the +79/+135 region that has a negative effect on the Epo-R promoter activity measured by CAT assays. The first region contains three CANNTG motifs, whereas the second contains an SP1/CACCC motif at position +85. These findings reveal a complex regulation of the hEpo-R gene and provide a working model useful to explain how the minimal promoter, containing GATA/SP1, can be positively and negatively regulated during erythroid differentiation.
Full text
PDF


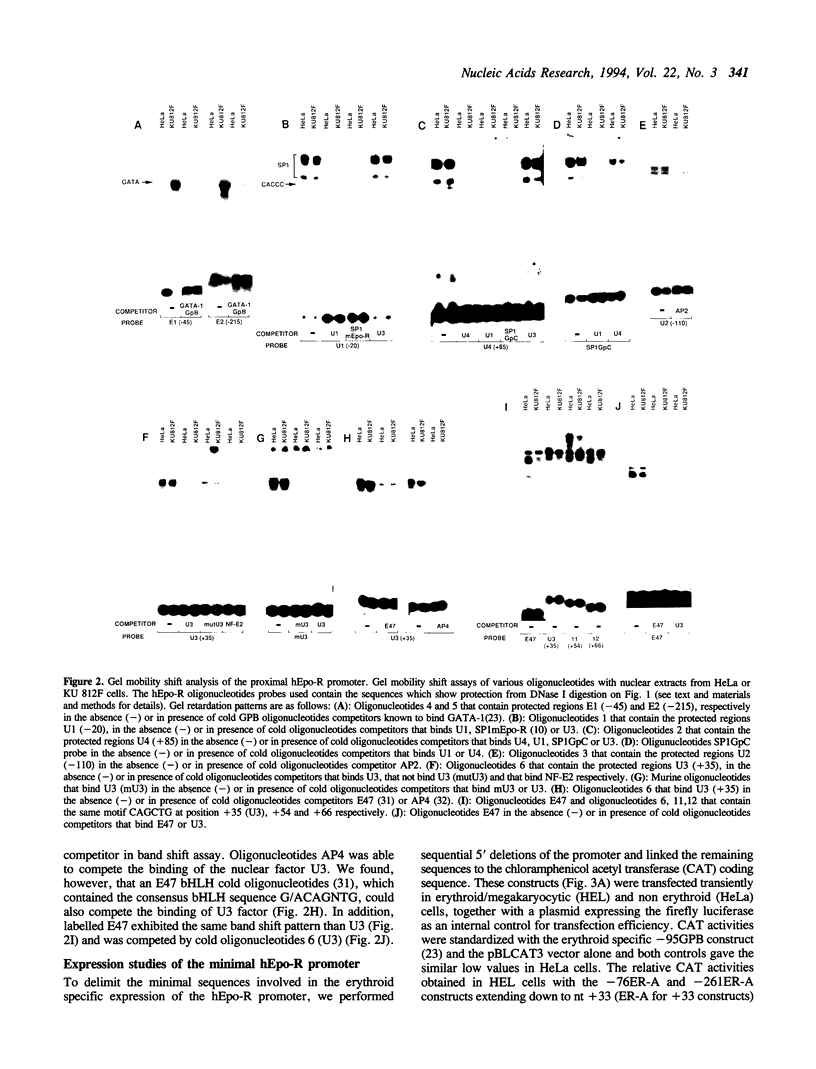




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adeniyi-Jones S., Zasloff M. Transcription, processing and nuclear transport of a B1 Alu RNA species complementary to an intron of the murine alpha-fetoprotein gene. Nature. 1985 Sep 5;317(6032):81–84. doi: 10.1038/317081a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bazan J. F. Structural design and molecular evolution of a cytokine receptor superfamily. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Sep;87(18):6934–6938. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.18.6934. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackwell T. K., Weintraub H. Differences and similarities in DNA-binding preferences of MyoD and E2A protein complexes revealed by binding site selection. Science. 1990 Nov 23;250(4984):1104–1110. doi: 10.1126/science.2174572. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackwood E. M., Eisenman R. N. Max: a helix-loop-helix zipper protein that forms a sequence-specific DNA-binding complex with Myc. Science. 1991 Mar 8;251(4998):1211–1217. doi: 10.1126/science.2006410. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiba T., Ikawa Y., Todokoro K. GATA-1 transactivates erythropoietin receptor gene, and erythropoietin receptor-mediated signals enhance GATA-1 gene expression. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Jul 25;19(14):3843–3848. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.14.3843. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colin Y., Joulin V., Le Van Kim C., Roméo P. H., Cartron J. P. Characterization of a new erythroid/megakaryocyte-specific nuclear factor that binds the promoter of the housekeeping human glycophorin C gene. J Biol Chem. 1990 Oct 5;265(28):16729–16732. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- D'Andrea A. D., Lodish H. F., Wong G. G. Expression cloning of the murine erythropoietin receptor. Cell. 1989 Apr 21;57(2):277–285. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90965-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis R. L., Weintraub H., Lassar A. B. Expression of a single transfected cDNA converts fibroblasts to myoblasts. Cell. 1987 Dec 24;51(6):987–1000. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90585-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dignam J. D., Lebovitz R. M., Roeder R. G. Accurate transcription initiation by RNA polymerase II in a soluble extract from isolated mammalian nuclei. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Mar 11;11(5):1475–1489. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.5.1475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dynan W. S., Tjian R. The promoter-specific transcription factor Sp1 binds to upstream sequences in the SV40 early promoter. Cell. 1983 Nov;35(1):79–87. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90210-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eleouet J. F., Roméo P. H. CCACC-binding or simian-virus-40-protein-1-binding proteins cooperate with human GATA-1 to direct erythroid-specific transcription and to mediate 5' hypersensitive site 2 sensitivity of a TATA-less promoter. Eur J Biochem. 1993 Mar 15;212(3):763–770. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1993.tb17716.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frampton J., Walker M., Plumb M., Harrison P. R. Synergy between the NF-E1 erythroid-specific transcription factor and the CACCC factor in the erythroid-specific promoter of the human porphobilinogen deaminase gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Jul;10(7):3838–3842. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.7.3838. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman C. M., Moffat L. F., Howard B. H. Recombinant genomes which express chloramphenicol acetyltransferase in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Sep;2(9):1044–1051. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.9.1044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gregor P. D., Sawadogo M., Roeder R. G. The adenovirus major late transcription factor USF is a member of the helix-loop-helix group of regulatory proteins and binds to DNA as a dimer. Genes Dev. 1990 Oct;4(10):1730–1740. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.10.1730. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heberlein C., Fischer K. D., Stoffel M., Nowock J., Ford A., Tessmer U., Stocking C. The gene for erythropoietin receptor is expressed in multipotential hematopoietic and embryonal stem cells: evidence for differentiation stage-specific regulation. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Apr;12(4):1815–1826. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.4.1815. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsu H. L., Cheng J. T., Chen Q., Baer R. Enhancer-binding activity of the tal-1 oncoprotein in association with the E47/E12 helix-loop-helix proteins. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Jun;11(6):3037–3042. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.6.3037. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hu Y. F., Lüscher B., Admon A., Mermod N., Tjian R. Transcription factor AP-4 contains multiple dimerization domains that regulate dimer specificity. Genes Dev. 1990 Oct;4(10):1741–1752. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.10.1741. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kishi K. A new leukemia cell line with Philadelphia chromosome characterized as basophil precursors. Leuk Res. 1985;9(3):381–390. doi: 10.1016/0145-2126(85)90060-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleinert H., Gladen A., Geisler M., Benecke B. J. Differential regulation of transcription of human 7 S K and 7 S L RNA genes. J Biol Chem. 1988 Aug 15;263(23):11511–11515. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koury M. J., Bondurant M. C. The molecular mechanism of erythropoietin action. Eur J Biochem. 1992 Dec 15;210(3):649–663. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1992.tb17466.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuramochi S., Ikawa Y., Todokoro K. Characterization of murine erythropoietin receptor genes. J Mol Biol. 1990 Dec 5;216(3):567–575. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(90)90384-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luckow B., Schütz G. CAT constructions with multiple unique restriction sites for the functional analysis of eukaryotic promoters and regulatory elements. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Jul 10;15(13):5490–5490. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.13.5490. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maouche L., Tournamille C., Hattab C., Boffa G., Cartron J. P., Chrétien S. Cloning of the gene encoding the human erythropoietin receptor. Blood. 1991 Nov 15;78(10):2557–2563. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin D. I., Zon L. I., Mutter G., Orkin S. H. Expression of an erythroid transcription factor in megakaryocytic and mast cell lineages. Nature. 1990 Mar 29;344(6265):444–447. doi: 10.1038/344444a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Max-Audit I., Eleouet J. F., Roméo P. H. Transcriptional regulation of the pyruvate kinase erythroid-specific promoter. J Biol Chem. 1993 Mar 15;268(8):5431–5437. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller I. J., Bieker J. J. A novel, erythroid cell-specific murine transcription factor that binds to the CACCC element and is related to the Krüppel family of nuclear proteins. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 May;13(5):2776–2786. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.5.2776. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murre C., McCaw P. S., Baltimore D. A new DNA binding and dimerization motif in immunoglobulin enhancer binding, daughterless, MyoD, and myc proteins. Cell. 1989 Mar 10;56(5):777–783. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90682-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murre C., McCaw P. S., Vaessin H., Caudy M., Jan L. Y., Jan Y. N., Cabrera C. V., Buskin J. N., Hauschka S. D., Lassar A. B. Interactions between heterologous helix-loop-helix proteins generate complexes that bind specifically to a common DNA sequence. Cell. 1989 Aug 11;58(3):537–544. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90434-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noguchi C. T., Bae K. S., Chin K., Wada Y., Schechter A. N., Hankins W. D. Cloning of the human erythropoietin receptor gene. Blood. 1991 Nov 15;78(10):2548–2556. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orkin S. H. GATA-binding transcription factors in hematopoietic cells. Blood. 1992 Aug 1;80(3):575–581. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Penny L. A., Forget B. G. Genomic organization of the human erythropoietin receptor gene. Genomics. 1991 Dec;11(4):974–980. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(91)90022-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pugh B. F., Tjian R. Mechanism of transcriptional activation by Sp1: evidence for coactivators. Cell. 1990 Jun 29;61(7):1187–1197. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90683-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rahuel C., Vinit M. A., Lemarchandel V., Cartron J. P., Roméo P. H. Erythroid-specific activity of the glycophorin B promoter requires GATA-1 mediated displacement of a repressor. EMBO J. 1992 Nov;11(11):4095–4102. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05502.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Romeo P. H., Prandini M. H., Joulin V., Mignotte V., Prenant M., Vainchenker W., Marguerie G., Uzan G. Megakaryocytic and erythrocytic lineages share specific transcription factors. Nature. 1990 Mar 29;344(6265):447–449. doi: 10.1038/344447a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spivak J. L. The mechanism of action of erythropoietin. Int J Cell Cloning. 1986 May;4(3):139–166. doi: 10.1002/stem.5530040302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsai S. F., Strauss E., Orkin S. H. Functional analysis and in vivo footprinting implicate the erythroid transcription factor GATA-1 as a positive regulator of its own promoter. Genes Dev. 1991 Jun;5(6):919–931. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.6.919. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vidal F., Mougneau E., Glaichenhaus N., Vaigot P., Darmon M., Cuzin F. Coordinated posttranscriptional control of gene expression by modular elements including Alu-like repetitive sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jan 1;90(1):208–212. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.1.208. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walters M., Martin D. I. Functional erythroid promoters created by interaction of the transcription factor GATA-1 with CACCC and AP-1/NFE-2 elements. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Nov 1;89(21):10444–10448. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.21.10444. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wickrema A., Krantz S. B., Winkelmann J. C., Bondurant M. C. Differentiation and erythropoietin receptor gene expression in human erythroid progenitor cells. Blood. 1992 Oct 15;80(8):1940–1949. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams T., Tjian R. Analysis of the DNA-binding and activation properties of the human transcription factor AP-2. Genes Dev. 1991 Apr;5(4):670–682. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.4.670. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu J., Grindlay G. J., Bushel P., Mendelsohn L., Allan M. Negative regulation of the human epsilon-globin gene by transcriptional interference: role of an Alu repetitive element. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Mar;10(3):1209–1216. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.3.1209. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xiao J. H., Davidson I., Macchi M., Rosales R., Vigneron M., Staub A., Chambon P. In vitro binding of several cell-specific and ubiquitous nuclear proteins to the GT-I motif of the SV40 enhancer. Genes Dev. 1987 Oct;1(8):794–807. doi: 10.1101/gad.1.8.794. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Youssoufian H., Lodish H. F. Transcriptional inhibition of the murine erythropoietin receptor gene by an upstream repetitive element. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Jan;13(1):98–104. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.1.98. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Youssoufian H., Longmore G., Neumann D., Yoshimura A., Lodish H. F. Structure, function, and activation of the erythropoietin receptor. Blood. 1993 May 1;81(9):2223–2236. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Youssoufian H., Zon L. I., Orkin S. H., D'Andrea A. D., Lodish H. F. Structure and transcription of the mouse erythropoietin receptor gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Jul;10(7):3675–3682. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.7.3675. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhou Q., Lieberman P. M., Boyer T. G., Berk A. J. Holo-TFIID supports transcriptional stimulation by diverse activators and from a TATA-less promoter. Genes Dev. 1992 Oct;6(10):1964–1974. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.10.1964. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zon L. I., Youssoufian H., Mather C., Lodish H. F., Orkin S. H. Activation of the erythropoietin receptor promoter by transcription factor GATA-1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Dec 1;88(23):10638–10641. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.23.10638. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de la Chapelle A., Sistonen P., Lehväslaiho H., Ikkala E., Juvonen E. Familial erythrocytosis genetically linked to erythropoietin receptor gene. Lancet. 1993 Jan 9;341(8837):82–84. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(93)92558-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- deBoer E., Antoniou M., Mignotte V., Wall L., Grosveld F. The human beta-globin promoter; nuclear protein factors and erythroid specific induction of transcription. EMBO J. 1988 Dec 20;7(13):4203–4212. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03317.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]