Abstract
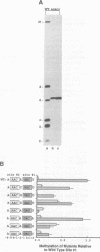
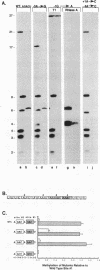
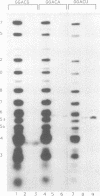
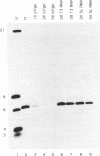
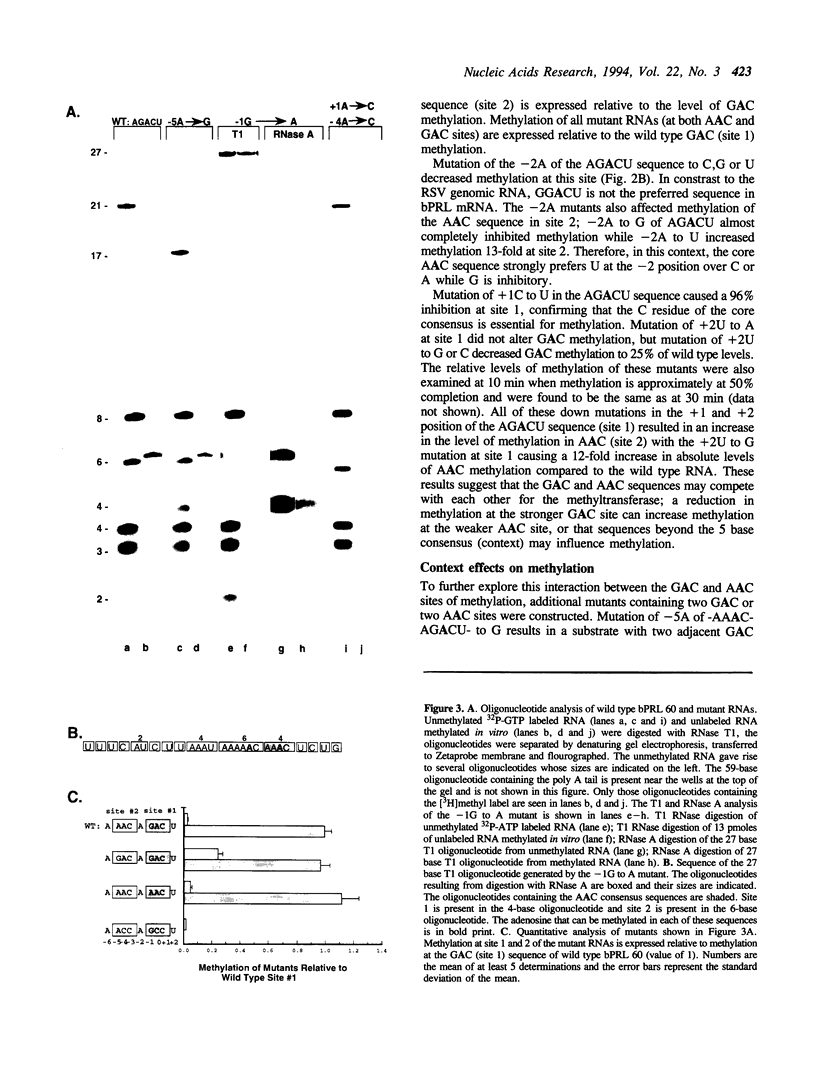
The methylation of internal adenosine residues in mRNA only occurs within GAC or AAC sequences. Although both of these sequence motifs are utilized, a general preference has been noted for the extended sequence RGACU. Not all RGACU sequences in an mRNA are methylated and the mechanisms that govern the selection of methylation sites in mRNA remain unclear. To address this problem we have examined the methylation of transcripts containing sequences of a natural mRNA, namely, bovine prolactin mRNA. In this mRNA, a specific AGACU sequence in the 3' untranslated region is the predominant site of methylation both in vivo and in vitro. The degree to which N6-adenosine methyltransferase recognizes the sequence context of the consensus methylation site was explored by mutational analysis of the nucleotides adjacent to the core sequence as well as the extended regions in which the core element was found. Our results indicate that efficient methylation depends on the extended five nucleotide consensus sequence but is strongly influenced by the context in which the consensus sequence occurs within the overall mRNA molecule. Furthermore, consensus methylation sites present in an RNA duplex are not recognized by the methyltransferase.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bachellerie J. P., Amalric F., Caboche M. Biosynthesis and utilization of extensively undermethylated poly(A)+ RNA in CHO cells during a cycloleucine treatment. Nucleic Acids Res. 1978 Aug;5(8):2927–2943. doi: 10.1093/nar/5.8.2927. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beemon K., Keith J. Localization of N6-methyladenosine in the Rous sarcoma virus genome. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 15;113(1):165–179. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90047-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Camper S. A., Albers R. J., Coward J. K., Rottman F. M. Effect of undermethylation on mRNA cytoplasmic appearance and half-life. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Mar;4(3):538–543. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.3.538. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Canaani D., Kahana C., Lavi S., Groner Y. Identification and mapping of N6-methyladenosine containing sequences in simian virus 40 RNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Jun 25;6(8):2879–2899. doi: 10.1093/nar/6.8.2879. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carroll S. M., Narayan P., Rottman F. M. N6-methyladenosine residues in an intron-specific region of prolactin pre-mRNA. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Sep;10(9):4456–4465. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.9.4456. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Csepany T., Lin A., Baldick C. J., Jr, Beemon K. Sequence specificity of mRNA N6-adenosine methyltransferase. J Biol Chem. 1990 Nov 25;265(33):20117–20122. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finkel D., Groner Y. Methylations of adenosine residues (m6A) in pre-mRNA are important for formation of late simian virus 40 mRNAs. Virology. 1983 Dec;131(2):409–425. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(83)90508-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furdon P. J., Kole R. The length of the downstream exon and the substitution of specific sequences affect pre-mRNA splicing in vitro. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Feb;8(2):860–866. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.2.860. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goguel V., Rosbash M. Splice site choice and splicing efficiency are positively influenced by pre-mRNA intramolecular base pairing in yeast. Cell. 1993 Mar 26;72(6):893–901. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90578-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green M. R. Biochemical mechanisms of constitutive and regulated pre-mRNA splicing. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1991;7:559–599. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.07.110191.003015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harper J. E., Miceli S. M., Roberts R. J., Manley J. L. Sequence specificity of the human mRNA N6-adenosine methylase in vitro. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Oct 11;18(19):5735–5741. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.19.5735. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horowitz S., Horowitz A., Nilsen T. W., Munns T. W., Rottman F. M. Mapping of N6-methyladenosine residues in bovine prolactin mRNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Sep;81(18):5667–5671. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.18.5667. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kane S. E., Beemon K. Inhibition of methylation at two internal N6-methyladenosine sites caused by GAC to GAU mutations. J Biol Chem. 1987 Mar 5;262(7):3422–3427. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kane S. E., Beemon K. Precise localization of m6A in Rous sarcoma virus RNA reveals clustering of methylation sites: implications for RNA processing. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Sep;5(9):2298–2306. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.9.2298. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Narayan P., Ayers D. F., Rottman F. M., Maroney P. A., Nilsen T. W. Unequal distribution of N6-methyladenosine in influenza virus mRNAs. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Apr;7(4):1572–1575. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.4.1572. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Narayan P., Rottman F. M. An in vitro system for accurate methylation of internal adenosine residues in messenger RNA. Science. 1988 Nov 25;242(4882):1159–1162. doi: 10.1126/science.3187541. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Narayan P., Rottman F. M. Methylation of mRNA. Adv Enzymol Relat Areas Mol Biol. 1992;65:255–285. doi: 10.1002/9780470123119.ch7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson K. K., Green M. R. Splice site selection and ribonucleoprotein complex assembly during in vitro pre-mRNA splicing. Genes Dev. 1988 Mar;2(3):319–329. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.3.319. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pikielny C. W., Rosbash M. mRNA splicing efficiency in yeast and the contribution of nonconserved sequences. Cell. 1985 May;41(1):119–126. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90066-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rajkovic A., Davis R. E., Simonsen J. N., Rottman F. M. A spliced leader is present on a subset of mRNAs from the human parasite Schistosoma mansoni. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Nov;87(22):8879–8883. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.22.8879. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rana A. P., Tuck M. T. Analysis and in vitro localization of internal methylated adenine residues in dihydrofolate reductase mRNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Aug 25;18(16):4803–4808. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.16.4803. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed R., Maniatis T. A role for exon sequences and splice-site proximity in splice-site selection. Cell. 1986 Aug 29;46(5):681–690. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90343-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schibler U., Kelley D. E., Perry R. P. Comparison of methylated sequences in messenger RNA and heterogeneous nuclear RNA from mouse L cells. J Mol Biol. 1977 Oct 5;115(4):695–714. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90110-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Setzer D. R., Hmiel R. M., Liao S. Y. A simple vector modification to facilitate oligonucleotide-directed mutagenesis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Jul 25;18(14):4175–4178. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.14.4175. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sommer S., Salditt-Georgieff M., Bachenheimer S., Darnell J. E., Furuichi Y., Morgan M., Shatkin A. J. The methylation of adenovirus-specific nuclear and cytoplasmic RNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1976 Mar;3(3):749–765. doi: 10.1093/nar/3.3.749. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoltzfus C. M., Dane R. W. Accumulation of spliced avian retrovirus mRNA is inhibited in S-adenosylmethionine-depleted chicken embryo fibroblasts. J Virol. 1982 Jun;42(3):918–931. doi: 10.1128/jvi.42.3.918-931.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]