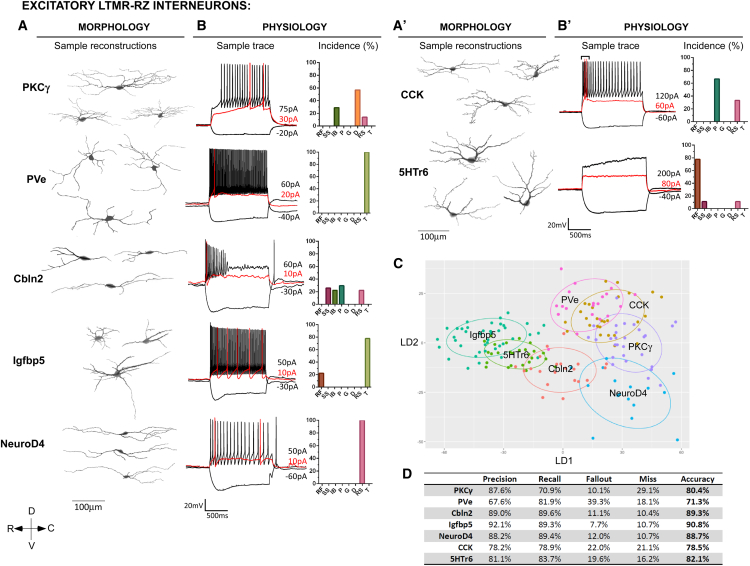
Figure 3.
Morphological and Physiological Characterization of Excitatory LTMR-RZ Interneurons
(A and A′) Sample Neurolucida reconstructions from the seven excitatory LTMR-RZ interneuron lines.
(B and B′) Sample action potential discharge patterns (left) during somatic injection of hyperpolarizing and depolarizing current steps of increasing magnitude (black traces, rheobase trace in red, current step magnitude noted in pA). Percentage of quantification of firing properties (right).
(C) Representative plot of an excitatory interneuron training set chosen at random for linear discriminant analysis, demonstrating grouping of excitatory interneuron classes when described by the first two linear discriminants. Ellipses demarcate significant 95% confidence intervals for each interneuron subtype.
(D) Performance of an excitatory interneuron classifier generated using linear discriminant analysis. Classifier predictive performance is quantified by precision (positive predictive value), recall (true positive value), fallout (false positive rate), miss (false negative rate), and accuracy (true positive and true negative rate).
For further details, see STAR Methods. See also Figure S4.