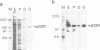Abstract
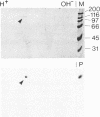
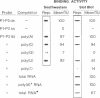
We have previously identified two proteins from chicken oviduct nuclei that specifically bind to matrix/scaffold attachment regions (MARs/SARs). Here one of these proteins, named p120 due to its apparent molecular weight, is purified to near homogeneity and shown to be identical to a previously described component of heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein particles, hnRNP U, on the basis of amino acid sequence analysis of tryptic peptides. p120 binds to multiple MAR fragments provided they have a minimal length of approximately 700 bp. Binding of MAR fragments is specifically competed by homoribopolymers poly(G) and poly(I), which form four-stranded structures. Our results suggest that p120/hnRNP U may serve a dual function, first as a component of hnRNP particles, and second as an element in the higher-order organization of chromatin.
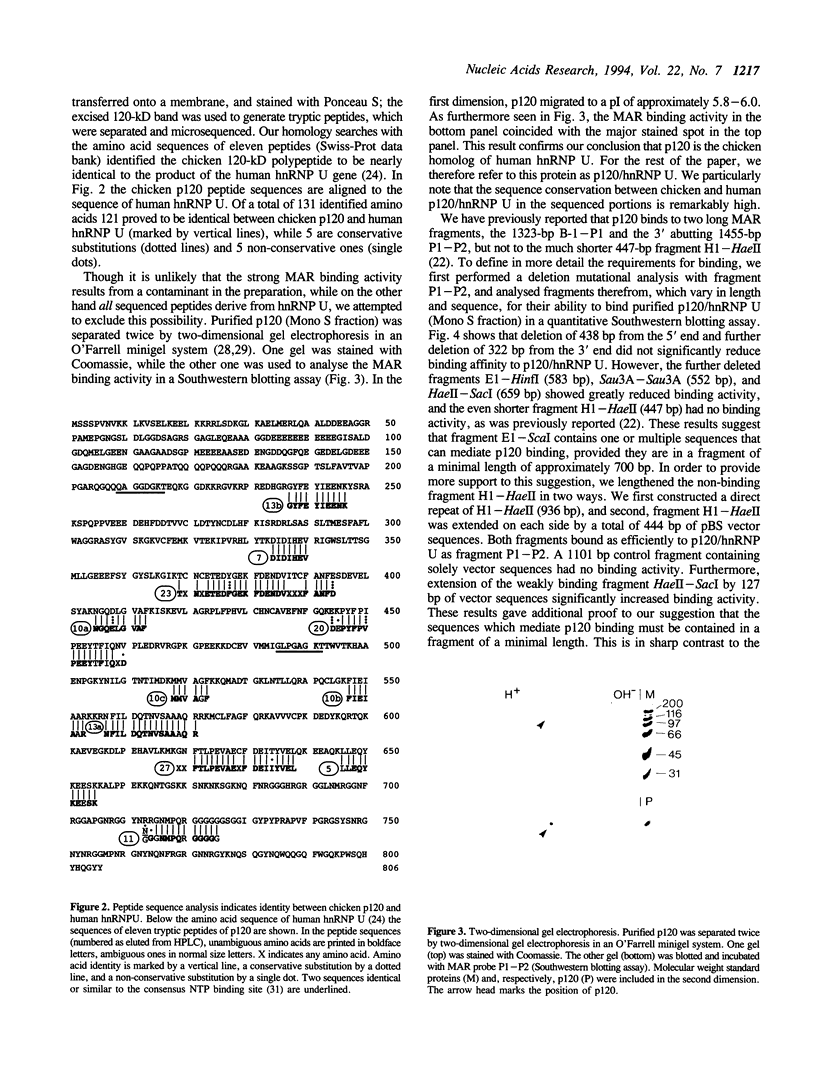
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bellini M., Lacroix J. C., Gall J. G. A putative zinc-binding protein on lampbrush chromosome loops. EMBO J. 1993 Jan;12(1):107–114. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05636.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benyajati C., Worcel A. Isolation, characterization, and structure of the folded interphase genome of Drosophila melanogaster. Cell. 1976 Nov;9(3):393–407. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(76)90084-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bidwell J. P., Van Wijnen A. J., Fey E. G., Dworetzky S., Penman S., Stein J. L., Lian J. B., Stein G. S. Osteocalcin gene promoter-binding factors are tissue-specific nuclear matrix components. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Apr 15;90(8):3162–3166. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.8.3162. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boy de la Tour E., Laemmli U. K. The metaphase scaffold is helically folded: sister chromatids have predominantly opposite helical handedness. Cell. 1988 Dec 23;55(6):937–944. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90239-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breyne P., van Montagu M., Depicker N., Gheysen G. Characterization of a plant scaffold attachment region in a DNA fragment that normalizes transgene expression in tobacco. Plant Cell. 1992 Apr;4(4):463–471. doi: 10.1105/tpc.4.4.463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cockerill P. N., Garrard W. T. Chromosomal loop anchorage of the kappa immunoglobulin gene occurs next to the enhancer in a region containing topoisomerase II sites. Cell. 1986 Jan 31;44(2):273–282. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90761-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conrad M. N., Wright J. H., Wolf A. J., Zakian V. A. RAP1 protein interacts with yeast telomeres in vivo: overproduction alters telomere structure and decreases chromosome stability. Cell. 1990 Nov 16;63(4):739–750. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90140-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cook P. R., Brazell I. A. Spectrofluorometric measurement of the binding of ethidium to superhelical DNA from cell nuclei. Eur J Biochem. 1978 Mar 15;84(2):465–477. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1978.tb12188.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deschamps S., Viel A., Garrigos M., Denis H., le Maire M. mRNP4, a major mRNA-binding protein from Xenopus oocytes is identical to transcription factor FRG Y2. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jul 15;267(20):13799–13802. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dickinson L. A., Joh T., Kohwi Y., Kohwi-Shigematsu T. A tissue-specific MAR/SAR DNA-binding protein with unusual binding site recognition. Cell. 1992 Aug 21;70(4):631–645. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90432-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dreyfuss G., Choi Y. D., Adam S. A. Characterization of heterogeneous nuclear RNA-protein complexes in vivo with monoclonal antibodies. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Jun;4(6):1104–1114. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.6.1104. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Earnshaw W. C., Halligan B., Cooke C. A., Heck M. M., Liu L. F. Topoisomerase II is a structural component of mitotic chromosome scaffolds. J Cell Biol. 1985 May;100(5):1706–1715. doi: 10.1083/jcb.100.5.1706. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fang G., Cech T. R. The beta subunit of Oxytricha telomere-binding protein promotes G-quartet formation by telomeric DNA. Cell. 1993 Sep 10;74(5):875–885. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90467-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hicke B. J., Celander D. W., MacDonald G. H., Price C. M., Cech T. R. Two versions of the gene encoding the 41-kilodalton subunit of the telomere binding protein of Oxytricha nova. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Feb;87(4):1481–1485. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.4.1481. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hofmann J. F., Laroche T., Brand A. H., Gasser S. M. RAP-1 factor is necessary for DNA loop formation in vitro at the silent mating type locus HML. Cell. 1989 Jun 2;57(5):725–737. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90788-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holm C., Goto T., Wang J. C., Botstein D. DNA topoisomerase II is required at the time of mitosis in yeast. Cell. 1985 Jun;41(2):553–563. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80028-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kellum R., Schedl P. A position-effect assay for boundaries of higher order chromosomal domains. Cell. 1991 Mar 8;64(5):941–950. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90318-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kiledjian M., Dreyfuss G. Primary structure and binding activity of the hnRNP U protein: binding RNA through RGG box. EMBO J. 1992 Jul;11(7):2655–2664. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05331.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klehr D., Maass K., Bode J. Scaffold-attached regions from the human interferon beta domain can be used to enhance the stable expression of genes under the control of various promoters. Biochemistry. 1991 Feb 5;30(5):1264–1270. doi: 10.1021/bi00219a015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis C. D., Laemmli U. K. Higher order metaphase chromosome structure: evidence for metalloprotein interactions. Cell. 1982 May;29(1):171–181. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90101-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loc P. V., Strätling W. H. The matrix attachment regions of the chicken lysozyme gene co-map with the boundaries of the chromatin domain. EMBO J. 1988 Mar;7(3):655–664. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02860.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ludérus M. E., de Graaf A., Mattia E., den Blaauwen J. L., Grande M. A., de Jong L., van Driel R. Binding of matrix attachment regions to lamin B1. Cell. 1992 Sep 18;70(6):949–959. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90245-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKay S. J., Cooke H. hnRNP A2/B1 binds specifically to single stranded vertebrate telomeric repeat TTAGGGn. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Dec 25;20(24):6461–6464. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.24.6461. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKnight R. A., Shamay A., Sankaran L., Wall R. J., Hennighausen L. Matrix-attachment regions can impart position-independent regulation of a tissue-specific gene in transgenic mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Aug 1;89(15):6943–6947. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.15.6943. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mirkovitch J., Mirault M. E., Laemmli U. K. Organization of the higher-order chromatin loop: specific DNA attachment sites on nuclear scaffold. Cell. 1984 Nov;39(1):223–232. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90208-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nikaido T., Yamawaki-Kataoka Y., Honjo T. Nucleotide sequences of switch regions of immunoglobulin C epsilon and C gamma genes and their comparison. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jul 10;257(13):7322–7329. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Farrell P. H. High resolution two-dimensional electrophoresis of proteins. J Biol Chem. 1975 May 25;250(10):4007–4021. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelham H. R., Brown D. D. A specific transcription factor that can bind either the 5S RNA gene or 5S RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jul;77(7):4170–4174. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.7.4170. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phi-Van L., von Kries J. P., Ostertag W., Strätling W. H. The chicken lysozyme 5' matrix attachment region increases transcription from a heterologous promoter in heterologous cells and dampens position effects on the expression of transfected genes. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 May;10(5):2302–2307. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.5.2302. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piñol-Roma S., Choi Y. D., Matunis M. J., Dreyfuss G. Immunopurification of heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein particles reveals an assortment of RNA-binding proteins. Genes Dev. 1988 Feb;2(2):215–227. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.2.215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Romig H., Fackelmayer F. O., Renz A., Ramsperger U., Richter A. Characterization of SAF-A, a novel nuclear DNA binding protein from HeLa cells with high affinity for nuclear matrix/scaffold attachment DNA elements. EMBO J. 1992 Sep;11(9):3431–3440. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05422.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stief A., Winter D. M., Strätling W. H., Sippel A. E. A nuclear DNA attachment element mediates elevated and position-independent gene activity. Nature. 1989 Sep 28;341(6240):343–345. doi: 10.1038/341343a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sundquist W. I., Klug A. Telomeric DNA dimerizes by formation of guanine tetrads between hairpin loops. Nature. 1989 Dec 14;342(6251):825–829. doi: 10.1038/342825a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swanson M. S., Dreyfuss G. Classification and purification of proteins of heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein particles by RNA-binding specificities. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 May;8(5):2237–2241. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.5.2237. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tafuri S. R., Familari M., Wolffe A. P. A mouse Y box protein, MSY1, is associated with paternal mRNA in spermatocytes. J Biol Chem. 1993 Jun 5;268(16):12213–12220. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsutsui K., Tsutsui K., Okada S., Watarai S., Seki S., Yasuda T., Shohmori T. Identification and characterization of a nuclear scaffold protein that binds the matrix attachment region DNA. J Biol Chem. 1993 Jun 15;268(17):12886–12894. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker J. E., Saraste M., Runswick M. J., Gay N. J. Distantly related sequences in the alpha- and beta-subunits of ATP synthase, myosin, kinases and other ATP-requiring enzymes and a common nucleotide binding fold. EMBO J. 1982;1(8):945–951. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01276.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Lange T. Human telomeres are attached to the nuclear matrix. EMBO J. 1992 Feb;11(2):717–724. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05104.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Kries J. P., Buhrmester H., Strätling W. H. A matrix/scaffold attachment region binding protein: identification, purification, and mode of binding. Cell. 1991 Jan 11;64(1):123–135. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90214-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Kries J. P., Phi-Van L., Diekmann S., Strätling W. H. A non-curved chicken lysozyme 5' matrix attachment site is 3' followed by a strongly curved DNA sequence. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Jul 11;18(13):3881–3885. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.13.3881. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]