Abstract
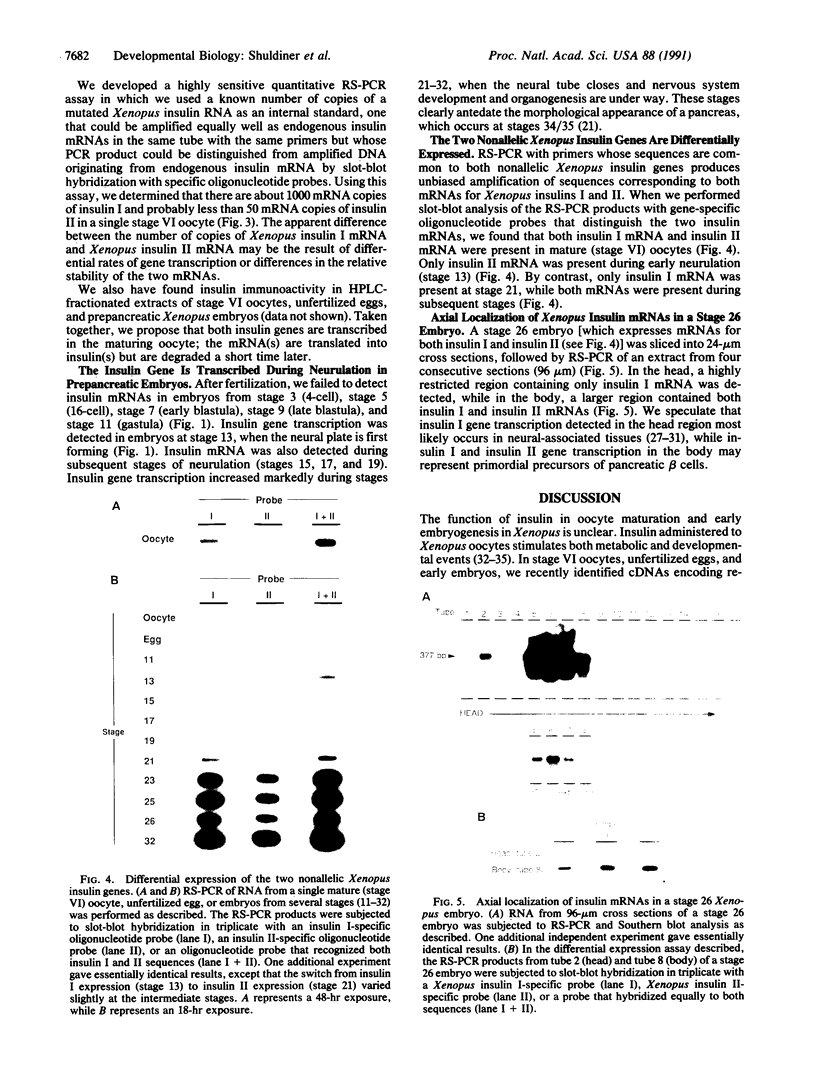
Insulin, traditionally regarded as a metabolic hormone, also can potently stimulate growth and differentiation in many cell types. To study further the potential role of insulin during early embryogenesis, we have used the amphibian Xenopus laevis, a versatile model of vertebrate development. Using (i) nucleotide sequences of two previously cloned cDNAs that correspond to two different nonallelic Xenopus insulin genes (both of which are expressed in the adult pancreas) and (ii) a modification of the highly sensitive reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) method developed in our laboratory, designated RNA template-specific PCR (RS-PCR), we now find that mRNAs for both Xenopus insulins I and II are present in mature (stage VI) oocytes but not in less-mature oocytes (stages I and IV) or in unfertilized eggs. The Xenopus insulin II gene is differentially expressed during early neurulation (stage 13), while only the insulin I gene is expressed at stage 21, when the neural tube is closing and cephalization is beginning. During later stages (i.e., stage 26) there is a region in the head that appears to be transcribing only the insulin I gene, while mRNAs for both insulins I and II are present in the body region. These findings show that the two nonallelic insulin genes are expressed differentially in Xenopus embryos in a stage- and region-specific manner; because appropriate receptors are also present, we suggest a role for insulin during early nervous system development well before the emergence of pancreatic beta cells.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adamo M., Raizada M. K., LeRoith D. Insulin and insulin-like growth factor receptors in the nervous system. Mol Neurobiol. 1989 Spring-Summer;3(1-2):71–100. doi: 10.1007/BF02935589. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alpert S., Hanahan D., Teitelman G. Hybrid insulin genes reveal a developmental lineage for pancreatic endocrine cells and imply a relationship with neurons. Cell. 1988 Apr 22;53(2):295–308. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90391-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bach M. A., Roberts C. T., Jr, Smith E. P., LeRoith D. Alternative splicing produces messenger RNAs encoding insulin-like growth factor-I prohormones that are differentially glycosylated in vitro. Mol Endocrinol. 1990 Jun;4(6):899–904. doi: 10.1210/mend-4-6-899. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bisbee C. A., Baker M. A., Wilson A. C., Haji-Azimi I., Fischberg M. Albumin phylogeny for clawed frogs (Xenopus). Science. 1977 Feb 25;195(4280):785–787. doi: 10.1126/science.65013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Pablo F., Roth J., Hernandez E., Pruss R. M. Insulin is present in chicken eggs and early chick embryos. Endocrinology. 1982 Dec;111(6):1909–1916. doi: 10.1210/endo-111-6-1909. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doe C. Q., Hiromi Y., Gehring W. J., Goodman C. S. Expression and function of the segmentation gene fushi tarazu during Drosophila neurogenesis. Science. 1988 Jan 8;239(4836):170–175. doi: 10.1126/science.2892267. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dumont J. N. Oogenesis in Xenopus laevis (Daudin). I. Stages of oocyte development in laboratory maintained animals. J Morphol. 1972 Feb;136(2):153–179. doi: 10.1002/jmor.1051360203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freinkel N. Diabetic embryopathy and fuel-mediated organ teratogenesis: lessons from animal models. Horm Metab Res. 1988 Aug;20(8):463–475. doi: 10.1055/s-2007-1010861. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garofalo R. S., Rosen O. M. Tissue localization of Drosophila melanogaster insulin receptor transcripts during development. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Apr;8(4):1638–1647. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.4.1638. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giddings S. J., Carnaghi L. R. Selective expression and developmental regulation of the ancestral rat insulin II gene in fetal liver. Mol Endocrinol. 1990 Sep;4(9):1363–1369. doi: 10.1210/mend-4-9-1363. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giebelhaus D. H., Zelus B. D., Henchman S. K., Moon R. T. Changes in the expression of alpha-fodrin during embryonic development of Xenopus laevis. J Cell Biol. 1987 Aug;105(2):843–853. doi: 10.1083/jcb.105.2.843. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Havrankova J., Roth J., Brownstein M. Insulin receptors are widely distributed in the central nervous system of the rat. Nature. 1978 Apr 27;272(5656):827–829. doi: 10.1038/272827a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heidenreich K. A., Toledo S. P. Insulin receptors mediate growth effects in cultured fetal neurons. I. Rapid stimulation of protein synthesis. Endocrinology. 1989 Sep;125(3):1451–1457. doi: 10.1210/endo-125-3-1451. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higuchi R., Krummel B., Saiki R. K. A general method of in vitro preparation and specific mutagenesis of DNA fragments: study of protein and DNA interactions. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Aug 11;16(15):7351–7367. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.15.7351. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janicot M., Lane M. D. Activation of glucose uptake by insulin and insulin-like growth factor I in Xenopus oocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Apr;86(8):2642–2646. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.8.2642. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawasaki E. S., Clark S. S., Coyne M. Y., Smith S. D., Champlin R., Witte O. N., McCormick F. P. Diagnosis of chronic myeloid and acute lymphocytic leukemias by detection of leukemia-specific mRNA sequences amplified in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Aug;85(15):5698–5702. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.15.5698. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimelman D., Kirschner M. Synergistic induction of mesoderm by FGF and TGF-beta and the identification of an mRNA coding for FGF in the early Xenopus embryo. Cell. 1987 Dec 4;51(5):869–877. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90110-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klemsz M. J., McKercher S. R., Celada A., Van Beveren C., Maki R. A. The macrophage and B cell-specific transcription factor PU.1 is related to the ets oncogene. Cell. 1990 Apr 6;61(1):113–124. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90219-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LeRoith D., Adamo M., Shemer J., Waldbillig R., Lesniak M. A., dePablo F., Hart C., Roth J. Insulin-related materials in the nervous system of vertebrates and non-vertebrates: possible extrapancreatic production. Horm Metab Res. 1988 Jul;20(7):411–420. doi: 10.1055/s-2007-1010850. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mercola M., Melton D. A., Stiles C. D. Platelet-derived growth factor A chain is maternally encoded in Xenopus embryos. Science. 1988 Sep 2;241(4870):1223–1225. doi: 10.1126/science.3413486. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller D. S. Stimulation of protein synthesis in stage IV Xenopus oocytes by microinjected insulin. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jun 25;264(18):10438–10446. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mills J. L., Knopp R. H., Simpson J. L., Jovanovic-Peterson L., Metzger B. E., Holmes L. B., Aarons J. H., Brown Z., Reed G. F., Bieber F. R. Lack of relation of increased malformation rates in infants of diabetic mothers to glycemic control during organogenesis. N Engl J Med. 1988 Mar 17;318(11):671–676. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198803173181104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagasawa H., Kataoka H., Isogai A., Tamura S., Suzuki A., Ishizaki H., Mizoguchi A., Fujiwara Y., Suzuki A. Amino-terminal amino Acid sequence of the silkworm prothoracicotropic hormone: homology with insulin. Science. 1984 Dec 14;226(4680):1344–1345. doi: 10.1126/science.226.4680.1344. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagasawa H., Kataoka H., Isogai A., Tamura S., Suzuki A., Mizoguchi A., Fujiwara Y., Suzuki A., Takahashi S. Y., Ishizaki H. Amino acid sequence of a prothoracicotropic hormone of the silkworm Bombyx mori. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Aug;83(16):5840–5843. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.16.5840. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perrimon N., Smouse D. Multiple functions of a Drosophila homeotic gene, zeste-white 3, during segmentation and neurogenesis. Dev Biol. 1989 Oct;135(2):287–305. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(89)90180-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rappolee D. A., Mark D., Banda M. J., Werb Z. Wound macrophages express TGF-alpha and other growth factors in vivo: analysis by mRNA phenotyping. Science. 1988 Aug 5;241(4866):708–712. doi: 10.1126/science.3041594. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Recio-Pinto E., Lang F. F., Ishii D. N. Insulin and insulin-like growth factor II permit nerve growth factor binding and the neurite formation response in cultured human neuroblastoma cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Apr;81(8):2562–2566. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.8.2562. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Coulson A. R., Barrell B. G., Smith A. J., Roe B. A. Cloning in single-stranded bacteriophage as an aid to rapid DNA sequencing. J Mol Biol. 1980 Oct 25;143(2):161–178. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(80)90196-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scavo L., Shuldiner A. R., Serrano J., Dashner R., Roth J., de Pablo F. Genes encoding receptors for insulin and insulin-like growth factor I are expressed in Xenopus oocytes and embryos. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jul 15;88(14):6214–6218. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.14.6214. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Serrano J., Bevins C. L., Young S. W., de Pablo F. Insulin gene expression in chicken ontogeny: pancreatic, extrapancreatic, and prepancreatic. Dev Biol. 1989 Apr;132(2):410–418. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(89)90237-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shuldiner A. R., Bennett C., Robinson E. A., Roth J. Isolation and characterization of two different insulins from an amphibian, Xenopus laevis. Endocrinology. 1989 Jul;125(1):469–477. doi: 10.1210/endo-125-1-469. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shuldiner A. R., Nirula A., Roth J. RNA template-specific polymerase chain reaction (RS-PCR): a novel strategy to reduce dramatically false positives. Gene. 1990 Jul 2;91(1):139–142. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(90)90176-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shuldiner A. R., Phillips S., Roberts C. T., Jr, LeRoith D., Roth J. Xenopus laevis contains two nonallelic preproinsulin genes. cDNA cloning and evolutionary perspective. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jun 5;264(16):9428–9432. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smit A. B., Vreugdenhil E., Ebberink R. H., Geraerts W. P., Klootwijk J., Joosse J. Growth-controlling molluscan neurons produce the precursor of an insulin-related peptide. Nature. 1988 Feb 11;331(6156):535–538. doi: 10.1038/331535a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith J. C., Price B. M., Van Nimmen K., Huylebroeck D. Identification of a potent Xenopus mesoderm-inducing factor as a homologue of activin A. Nature. 1990 Jun 21;345(6277):729–731. doi: 10.1038/345729a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sokol S., Wong G. G., Melton D. A. A mouse macrophage factor induces head structures and organizes a body axis in Xenopus. Science. 1990 Aug 3;249(4968):561–564. doi: 10.1126/science.2382134. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stefanovic D., Erikson E., Pike L. J., Maller J. L. Activation of a ribosomal protein S6 protein kinase in Xenopus oocytes by insulin and insulin-receptor kinase. EMBO J. 1986 Jan;5(1):157–160. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04190.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stith B. J., Maller J. L. The effect of insulin on intracellular ph and ribosomal protein S6 phosphorylation in oocytes of Xenopus laevis. Dev Biol. 1984 Mar;102(1):79–89. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(84)90176-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weeks D. L., Melton D. A. A maternal mRNA localized to the vegetal hemisphere in Xenopus eggs codes for a growth factor related to TGF-beta. Cell. 1987 Dec 4;51(5):861–867. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90109-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wharton K. A., Johansen K. M., Xu T., Artavanis-Tsakonas S. Nucleotide sequence from the neurogenic locus notch implies a gene product that shares homology with proteins containing EGF-like repeats. Cell. 1985 Dec;43(3 Pt 2):567–581. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90229-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Pablo F., Girbau M., Gomez J. A., Hernandez E., Roth J. Insulin antibodies retard and insulin accelerates growth and differentiation in early embryos. Diabetes. 1985 Oct;34(10):1063–1067. doi: 10.2337/diab.34.10.1063. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Pablo F., Roth J. Endocrinization of the early embryo: an emerging role for hormones and hormone-like factors. Trends Biochem Sci. 1990 Sep;15(9):339–342. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(90)90072-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]