Abstract
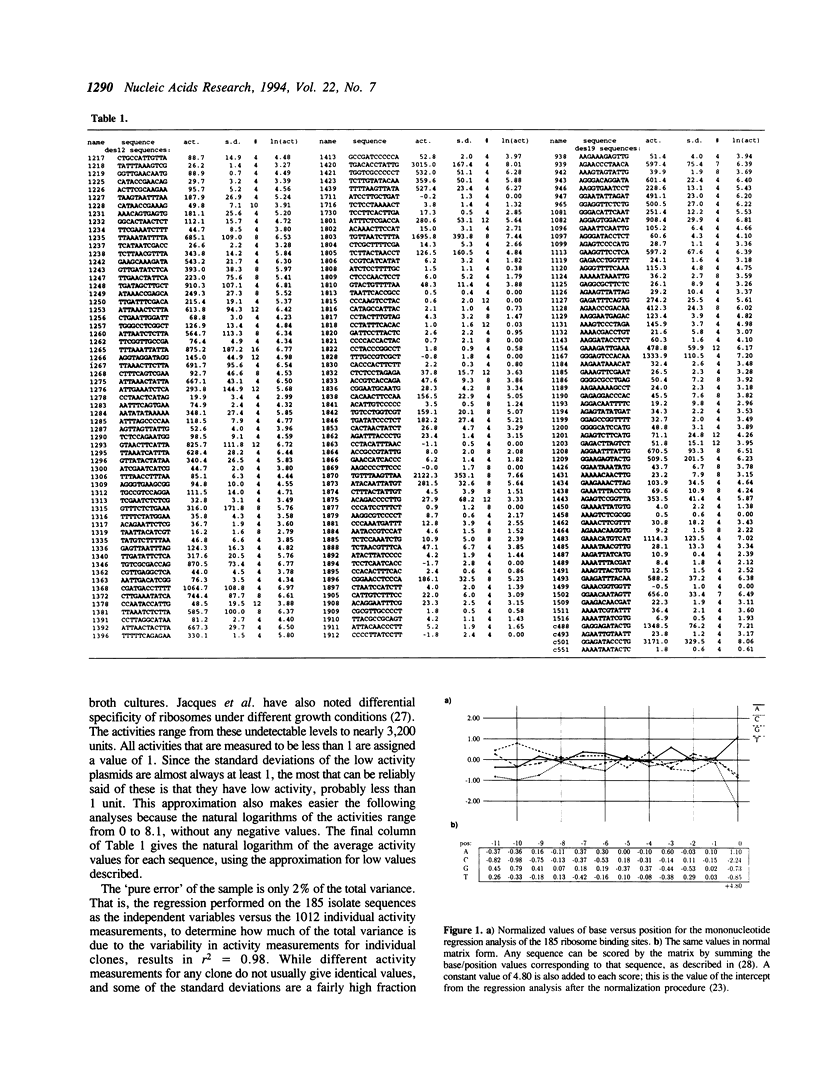
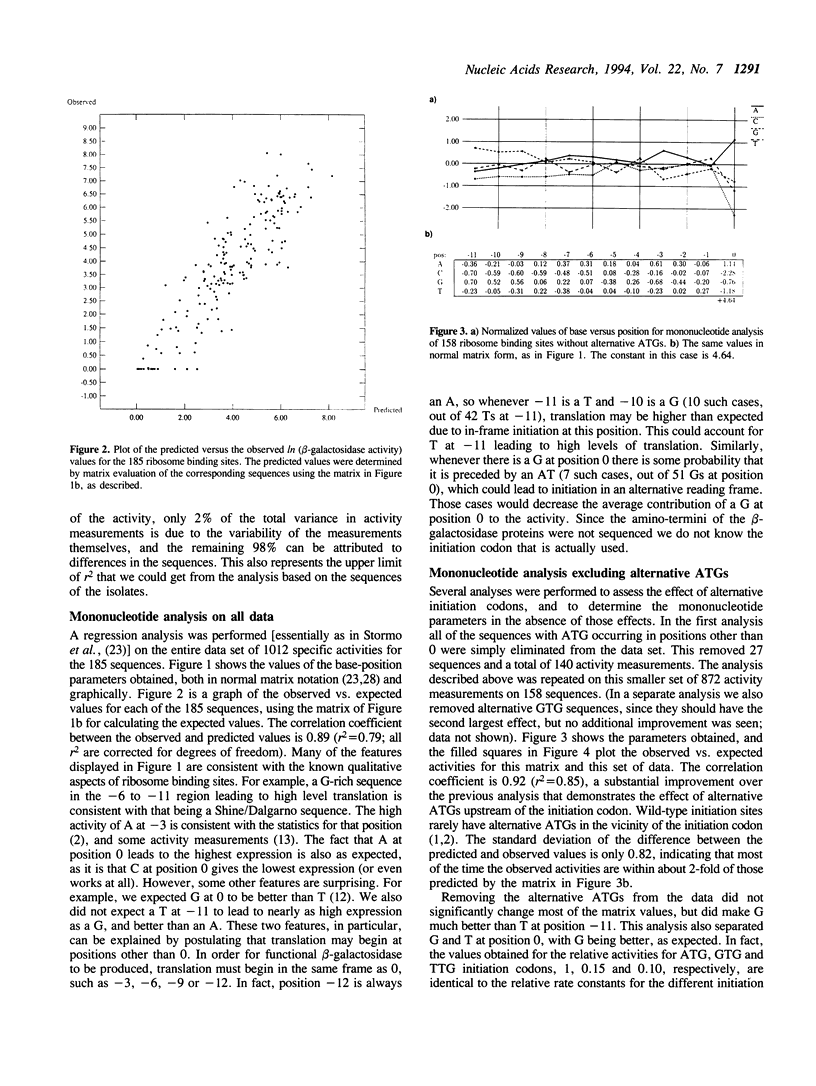
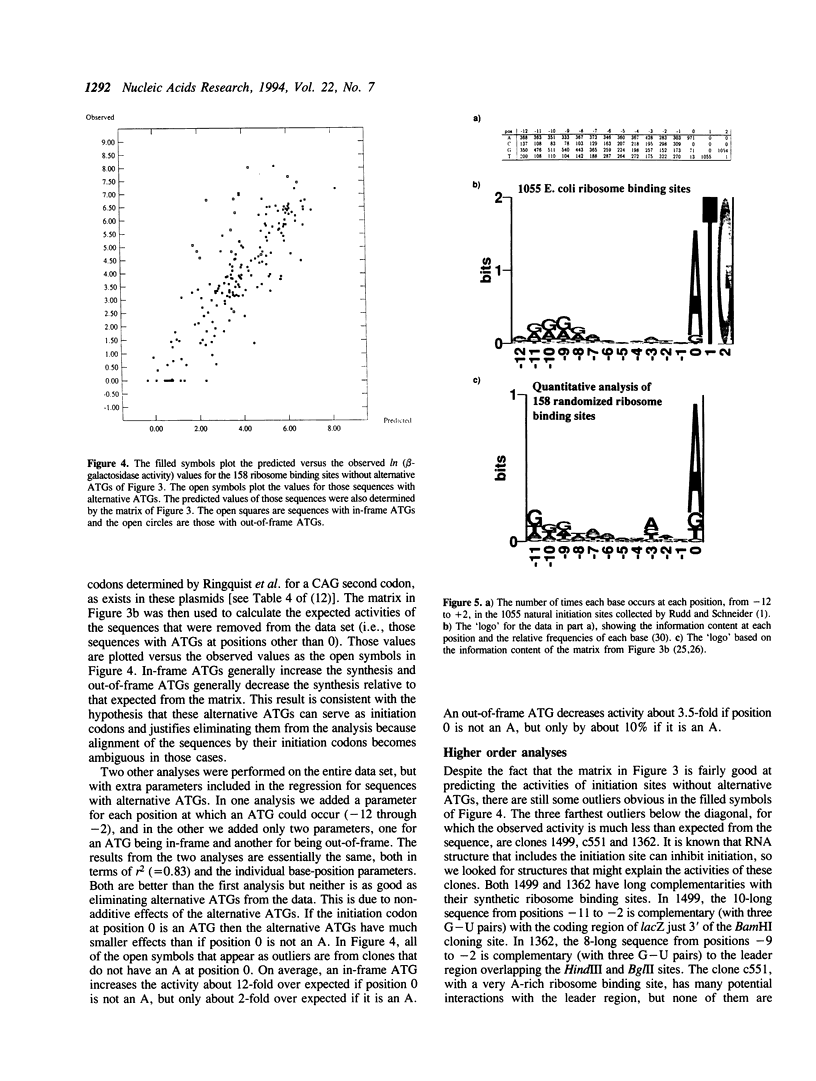
185 clones with randomized ribosome binding sites, from position -11 to 0 preceding the coding region of beta-galactosidase, were selected and sequenced. The translational yield of each clone was determined; they varied by more than 3000-fold. Multiple linear regression analysis was used to determine the contribution to translation initiation activity of each base at each position. Features known to be important for translation initiation, such as the initiation codon, the Shine/Dalgarno sequence, the identity of the base at position -3 and the occurrence of alternative ATGs, are all found to be important quantitatively for activity. No other features are found to be of general significance, although the effects of secondary structure can be seen as outliers. A comparison to a large number of natural E.coli translation initiation sites shows the information profile to be qualitatively similar although differing quantitatively. This is probably due to the selection for good translation initiation sites in the natural set compared to the low average activity of the randomized set.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arvidson D. N., Youderian P., Schneider T. D., Stormo G. D. Automated kinetic assay of beta-galactosidase activity. Biotechniques. 1991 Dec;11(6):733-4, 736, 738. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boni I. V., Isaeva D. M., Musychenko M. L., Tzareva N. V. Ribosome-messenger recognition: mRNA target sites for ribosomal protein S1. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Jan 11;19(1):155–162. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.1.155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dreyfus M. What constitutes the signal for the initiation of protein synthesis on Escherichia coli mRNAs? J Mol Biol. 1988 Nov 5;204(1):79–94. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90601-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gardella T., Moyle H., Susskind M. M. A mutant Escherichia coli sigma 70 subunit of RNA polymerase with altered promoter specificity. J Mol Biol. 1989 Apr 20;206(4):579–590. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(89)90567-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gold L. Posttranscriptional regulatory mechanisms in Escherichia coli. Annu Rev Biochem. 1988;57:199–233. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.57.070188.001215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gold L., Pribnow D., Schneider T., Shinedling S., Singer B. S., Stormo G. Translational initiation in prokaryotes. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1981;35:365–403. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.35.100181.002053. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hui A., de Boer H. A. Specialized ribosome system: preferential translation of a single mRNA species by a subpopulation of mutated ribosomes in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jul;84(14):4762–4766. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.14.4762. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacques N., Guillerez J., Dreyfus M. Culture conditions differentially affect the translation of individual Escherichia coli mRNAs. J Mol Biol. 1992 Aug 5;226(3):597–608. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(92)90618-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Looman A. C., Bodlaender J., de Gruyter M., Vogelaar A., van Knippenberg P. H. Secondary structure as primary determinant of the efficiency of ribosomal binding sites in Escherichia coli. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Jul 11;14(13):5481–5497. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.13.5481. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCarthy J. E., Gualerzi C. Translational control of prokaryotic gene expression. Trends Genet. 1990 Mar;6(3):78–85. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(90)90098-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olins P. O., Rangwala S. H. A novel sequence element derived from bacteriophage T7 mRNA acts as an enhancer of translation of the lacZ gene in Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1989 Oct 15;264(29):16973–16976. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ringquist S., Shinedling S., Barrick D., Green L., Binkley J., Stormo G. D., Gold L. Translation initiation in Escherichia coli: sequences within the ribosome-binding site. Mol Microbiol. 1992 May;6(9):1219–1229. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1992.tb01561.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Coulson A. R., Hong G. F., Hill D. F., Petersen G. B. Nucleotide sequence of bacteriophage lambda DNA. J Mol Biol. 1982 Dec 25;162(4):729–773. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90546-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider T. D., Stephens R. M. Sequence logos: a new way to display consensus sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Oct 25;18(20):6097–6100. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.20.6097. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider T. D., Stormo G. D., Gold L., Ehrenfeucht A. Information content of binding sites on nucleotide sequences. J Mol Biol. 1986 Apr 5;188(3):415–431. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90165-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider T. D., Stormo G. D., Haemer J. S., Gold L. A design for computer nucleic-acid-sequence storage, retrieval, and manipulation. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 May 11;10(9):3013–3024. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.9.3013. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider T. D., Stormo G. D., Yarus M. A., Gold L. Delila system tools. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 11;12(1 Pt 1):129–140. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.1part1.129. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shine J., Dalgarno L. The 3'-terminal sequence of Escherichia coli 16S ribosomal RNA: complementarity to nonsense triplets and ribosome binding sites. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Apr;71(4):1342–1346. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.4.1342. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shinedling S., Gayle M., Pribnow D., Gold L. Mutations affecting translation of the bacteriophage T4 rIIB gene cloned in Escherichia coli. Mol Gen Genet. 1987 May;207(2-3):224–232. doi: 10.1007/BF00331582. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stormo G. D. Computer methods for analyzing sequence recognition of nucleic acids. Annu Rev Biophys Biophys Chem. 1988;17:241–263. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.17.060188.001325. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stormo G. D. Consensus patterns in DNA. Methods Enzymol. 1990;183:211–221. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(90)83015-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stormo G. D. Probing information content of DNA-binding sites. Methods Enzymol. 1991;208:458–468. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(91)08024-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stormo G. D., Schneider T. D., Gold L. M. Characterization of translational initiation sites in E. coli. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 May 11;10(9):2971–2996. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.9.2971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stormo G. D., Schneider T. D., Gold L., Ehrenfeucht A. Use of the 'Perceptron' algorithm to distinguish translational initiation sites in E. coli. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 May 11;10(9):2997–3011. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.9.2997. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stormo G. D., Schneider T. D., Gold L. Quantitative analysis of the relationship between nucleotide sequence and functional activity. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Aug 26;14(16):6661–6679. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.16.6661. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stormo G. D., Yoshioka M. Specificity of the Mnt protein determined by binding to randomized operators. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jul 1;88(13):5699–5703. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.13.5699. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang J., Deutscher M. P. A uridine-rich sequence required for translation of prokaryotic mRNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Apr 1;89(7):2605–2609. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.7.2605. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zuker M. On finding all suboptimal foldings of an RNA molecule. Science. 1989 Apr 7;244(4900):48–52. doi: 10.1126/science.2468181. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Boer H. A., Comstock L. J., Vasser M. The tac promoter: a functional hybrid derived from the trp and lac promoters. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jan;80(1):21–25. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.1.21. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Smit M. H., van Duin J. Secondary structure of the ribosome binding site determines translational efficiency: a quantitative analysis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Oct;87(19):7668–7672. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.19.7668. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


