Abstract
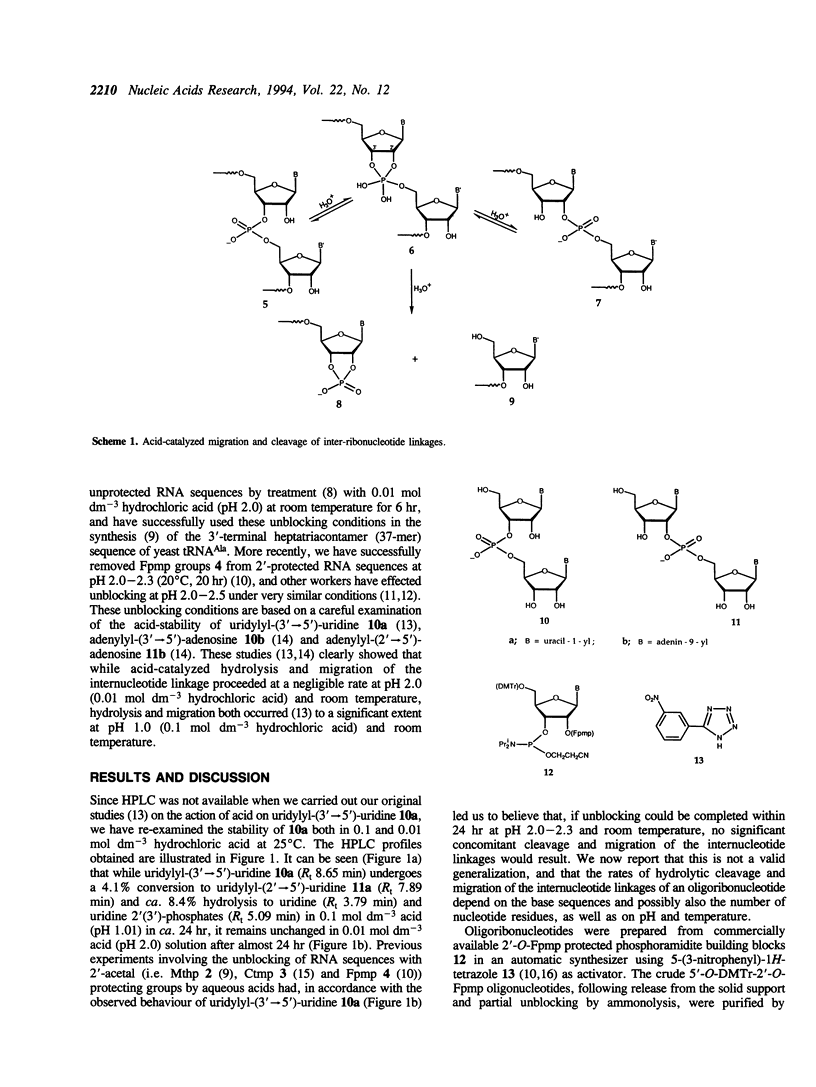
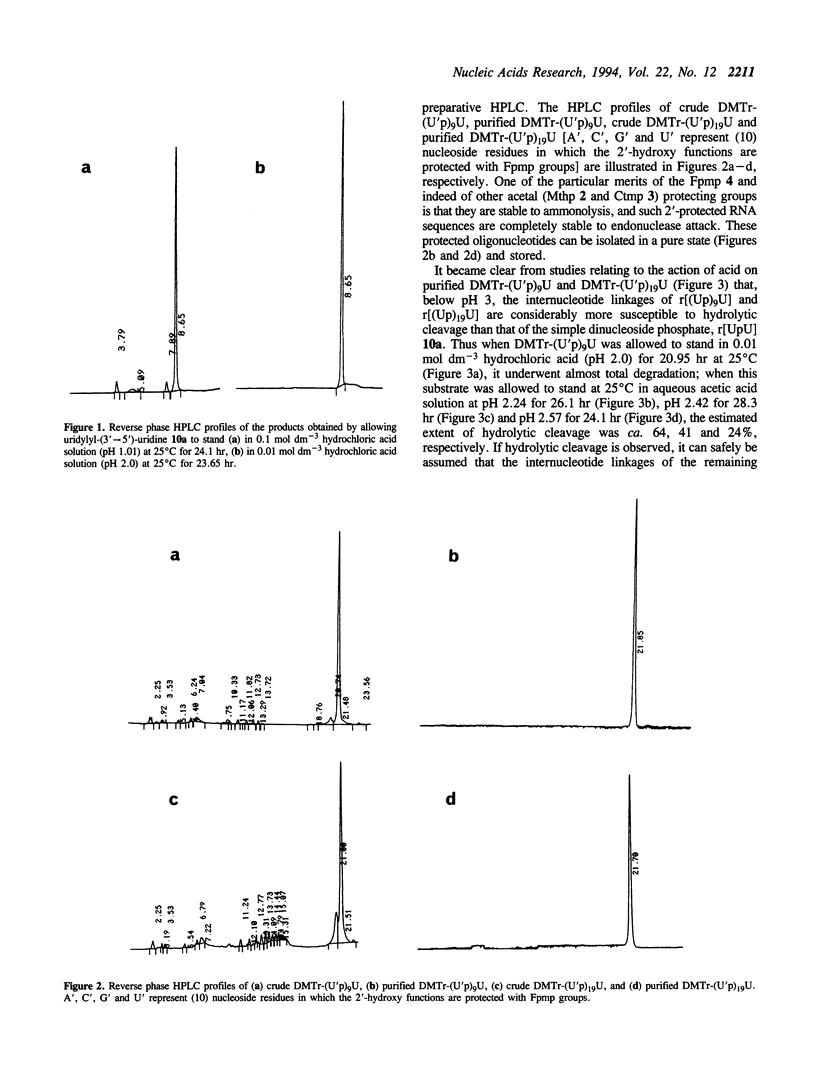
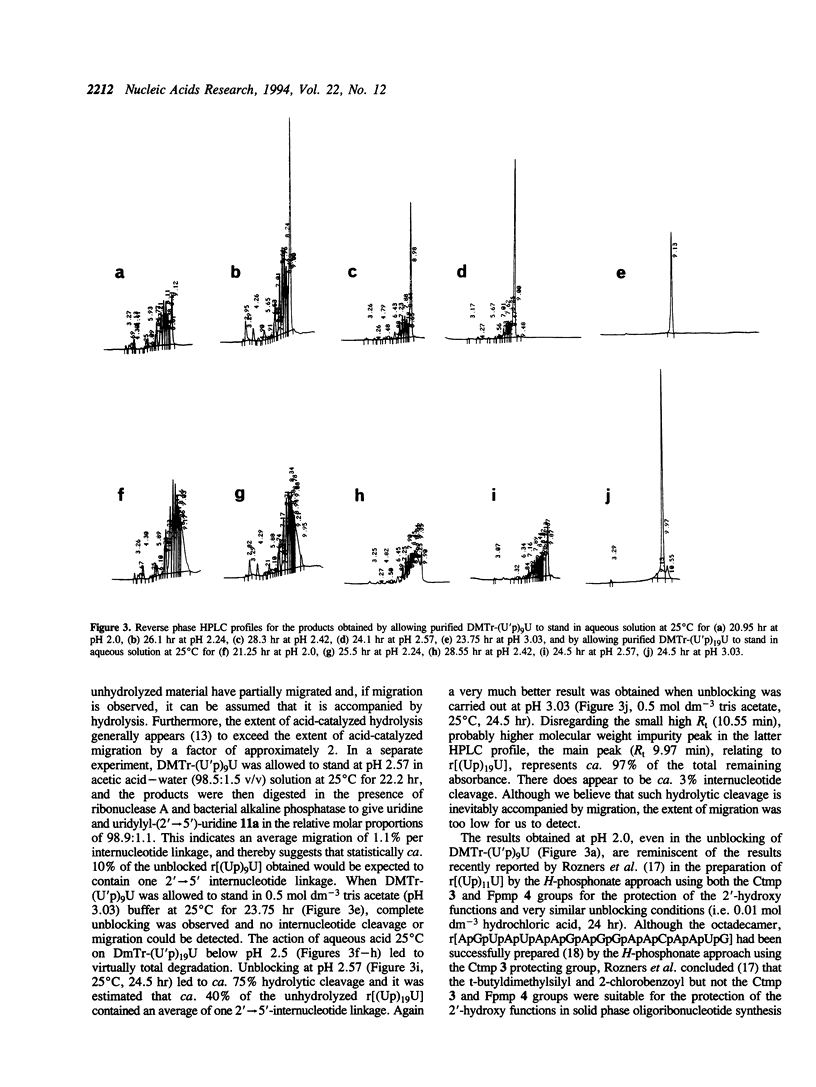
The internucleotide linkage of uridylyl-(3'-->5')-uridine (r[UpU]) does not undergo detectable hydrolytic cleavage or migration in ca. 24 hr in 0.01 mol dm-3 hydrochloric acid (pH 2.0) at 25 degrees C. However, unlike r[UpU] and previously examined relatively high molecular weight oligoribonucleotides, oligouridylic acids are very sensitive to aqueous acid under the latter conditions (pH 2.0, 25 degrees C). Thus when the 1-(2-fluorophenyl)-4-methoxypiperidin-4-yl (Fpmp) group is used to protect the 2'-hydroxy functions in the synthesis of r[(Up)9U] and r[(Up)19U], the final unblocking process must be carried out above pH 3 if hydrolytic cleavage and migration are to be avoided. It is demonstrated that the rate of acid-catalyzed hydrolysis of the internucleotide linkages of oligoribonucleotides is sequence dependent. As Fpmp groups may be virtually completely removed from average partially-protected oligoribonucleotides within ca. 24 hr at pH 3 and 25 degrees C, it is concluded that Fpmp is a suitable 2'-protecting group even in the synthesis of particularly acid-sensitive sequences.
Full text
PDF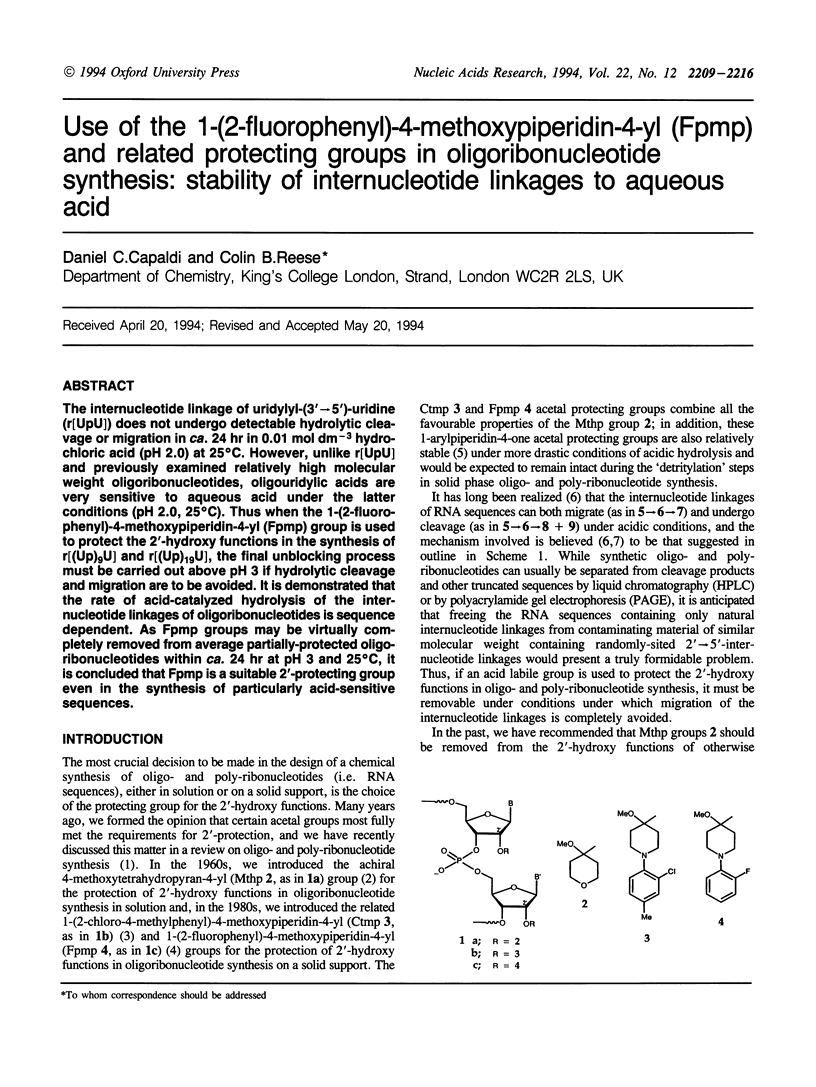



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beijer B., Sulston I., Sproat B. S., Rider P., Lamond A. I., Neuner P. Synthesis and applications of oligoribonucleotides with selected 2'-O-methylation using the 2'-O-[1-(2-fluorophenyl)-4-methoxypiperidin-4-yl] protecting group. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Sep 11;18(17):5143–5151. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.17.5143. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffin B. E., Jarman M., Reese C. B. The synthesis of oligoribonucleotides. IV. Preparation of dinucleoside phosphates from 2',5'-protected ribonucleoside derivatives. Tetrahedron. 1968 Jan;24(2):639–662. doi: 10.1016/0040-4020(68)88015-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jeffries A. C., Symons R. H. A catalytic 13-mer ribozyme. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Feb 25;17(4):1371–1377. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.4.1371. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rozners E., Westman E., Strömberg R. Evaluation of 2'-hydroxyl protection in RNA-synthesis using the H-phosphonate approach. Nucleic Acids Res. 1994 Jan 11;22(1):94–99. doi: 10.1093/nar/22.1.94. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakatsume O., Ohtsuki M., Takaku H., Reese C. B. Solid phase synthesis of oligoribonucleotides using the 1-[(2-chloro-4-methyl)phenyl]-4-methoxypiperidin-4-yl (Ctmp) group for the protection of the 2'-hydroxy functions and the H-phosphonate approach. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 May 25;17(10):3689–3697. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.10.3689. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uhlenbeck O. C. A small catalytic oligoribonucleotide. Nature. 1987 Aug 13;328(6131):596–600. doi: 10.1038/328596a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



