Abstract
Although the tRNA species directing selenocysteine insertion in prokaryotes differ greatly in their primary structure from that of their eukaryotic homologues they share very similar three-dimensional structures. To analyse whether this conservation of the overall shape of the molecules reflects a conservation of their functional interactions it was tested whether the selenocysteine inserting tRNA species from Homo sapiens supports selenoprotein synthesis in E. coli. It was found that the expression of the human tRNA(Sec) gene in E.coli can complement a lesion in the tRNA(Sec) gene of this organism. Transcripts of the Homo sapiens and Xenopus laevis tRNA(Sec) genes synthesised in vitro were amino-acylated by the E.coli seryl-tRNA ligase although at a very low rate and the resulting seryl-tRNA(Sec) was bound to and converted into selenocysteyl-tRNA(Sec) by the selenocysteine synthase of this organism. Selenocysteyl-tRNA(Sec) from both eukaryotes was able to form a complex with translation factor SELB from E.coli. Although the mechanism of selenocysteine incorporation into seleno-proteins appears to be rather different in E.coli and in vertebrates, we observe here a surprising conservation of functions over an enormous evolutionary distance.
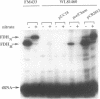
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Achsel T., Gross H. J. Identity determinants of human tRNA(Ser): sequence elements necessary for serylation and maturation of a tRNA with a long extra arm. EMBO J. 1993 Aug;12(8):3333–3338. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb06003.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baron C., Böck A. The length of the aminoacyl-acceptor stem of the selenocysteine-specific tRNA(Sec) of Escherichia coli is the determinant for binding to elongation factors SELB or Tu. J Biol Chem. 1991 Oct 25;266(30):20375–20379. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baron C., Heider J., Böck A. Interaction of translation factor SELB with the formate dehydrogenase H selenopolypeptide mRNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 May 1;90(9):4181–4185. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.9.4181. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baron C., Heider J., Böck A. Mutagenesis of selC, the gene for the selenocysteine-inserting tRNA-species in E. coli: effects on in vivo function. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Dec 11;18(23):6761–6766. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.23.6761. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baron C., Westhof E., Böck A., Giegé R. Solution structure of selenocysteine-inserting tRNA(Sec) from Escherichia coli. Comparison with canonical tRNA(Ser). J Mol Biol. 1993 May 20;231(2):274–292. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1993.1282. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berry M. J., Banu L., Chen Y. Y., Mandel S. J., Kieffer J. D., Harney J. W., Larsen P. R. Recognition of UGA as a selenocysteine codon in type I deiodinase requires sequences in the 3' untranslated region. Nature. 1991 Sep 19;353(6341):273–276. doi: 10.1038/353273a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berry M. J., Banu L., Harney J. W., Larsen P. R. Functional characterization of the eukaryotic SECIS elements which direct selenocysteine insertion at UGA codons. EMBO J. 1993 Aug;12(8):3315–3322. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb06001.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Böck A., Forchhammer K., Heider J., Leinfelder W., Sawers G., Veprek B., Zinoni F. Selenocysteine: the 21st amino acid. Mol Microbiol. 1991 Mar;5(3):515–520. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1991.tb00722.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen G. F., Fang L., Inouye M. Effect of the relative position of the UGA codon to the unique secondary structure in the fdhF mRNA on its decoding by selenocysteinyl tRNA in Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1993 Nov 5;268(31):23128–23131. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diamond A. M., Choi I. S., Crain P. F., Hashizume T., Pomerantz S. C., Cruz R., Steer C. J., Hill K. E., Burk R. F., McCloskey J. A. Dietary selenium affects methylation of the wobble nucleoside in the anticodon of selenocysteine tRNA([Ser]Sec). J Biol Chem. 1993 Jul 5;268(19):14215–14223. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forchhammer K., Böck A. Selenocysteine synthase from Escherichia coli. Analysis of the reaction sequence. J Biol Chem. 1991 Apr 5;266(10):6324–6328. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forchhammer K., Leinfelder W., Boesmiller K., Veprek B., Böck A. Selenocysteine synthase from Escherichia coli. Nucleotide sequence of the gene (selA) and purification of the protein. J Biol Chem. 1991 Apr 5;266(10):6318–6323. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forchhammer K., Leinfelder W., Böck A. Identification of a novel translation factor necessary for the incorporation of selenocysteine into protein. Nature. 1989 Nov 23;342(6248):453–456. doi: 10.1038/342453a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forchhammer K., Rücknagel K. P., Böck A. Purification and biochemical characterization of SELB, a translation factor involved in selenoprotein synthesis. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jun 5;265(16):9346–9350. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heider J., Baron C., Böck A. Coding from a distance: dissection of the mRNA determinants required for the incorporation of selenocysteine into protein. EMBO J. 1992 Oct;11(10):3759–3766. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05461.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill K. E., Lloyd R. S., Burk R. F. Conserved nucleotide sequences in the open reading frame and 3' untranslated region of selenoprotein P mRNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jan 15;90(2):537–541. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.2.537. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leinfelder W., Zehelein E., Mandrand-Berthelot M. A., Böck A. Gene for a novel tRNA species that accepts L-serine and cotranslationally inserts selenocysteine. Nature. 1988 Feb 25;331(6158):723–725. doi: 10.1038/331723a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li W. Q., Yarus M. Bar to normal UGA translation by the selenocysteine tRNA. J Mol Biol. 1992 Jan 5;223(1):9–15. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(92)90709-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizutani T., Hashimoto A. Purification and properties of suppressor seryl-tRNA: ATP phosphotransferase from bovine liver. FEBS Lett. 1984 Apr 24;169(2):319–322. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(84)80342-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Normanly J., Ollick T., Abelson J. Eight base changes are sufficient to convert a leucine-inserting tRNA into a serine-inserting tRNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jun 15;89(12):5680–5684. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.12.5680. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schön A., Böck A., Ott G., Sprinzl M., Söll D. The selenocysteine-inserting opal suppressor serine tRNA from E. coli is highly unusual in structure and modification. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Sep 25;17(18):7159–7165. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.18.7159. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shen Q., Chu F. F., Newburger P. E. Sequences in the 3'-untranslated region of the human cellular glutathione peroxidase gene are necessary and sufficient for selenocysteine incorporation at the UGA codon. J Biol Chem. 1993 May 25;268(15):11463–11469. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinberg S., Misch A., Sprinzl M. Compilation of tRNA sequences and sequences of tRNA genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993 Jul 1;21(13):3011–3015. doi: 10.1093/nar/21.13.3011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sturchler C., Westhof E., Carbon P., Krol A. Unique secondary and tertiary structural features of the eucaryotic selenocysteine tRNA(Sec). Nucleic Acids Res. 1993 Mar 11;21(5):1073–1079. doi: 10.1093/nar/21.5.1073. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu X. Q., Gross H. J. The length and the secondary structure of the D-stem of human selenocysteine tRNA are the major identity determinants for serine phosphorylation. EMBO J. 1994 Jan 1;13(1):241–248. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06254.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu X. Q., Gross H. J. The long extra arms of human tRNA((Ser)Sec) and tRNA(Ser) function as major identify elements for serylation in an orientation-dependent, but not sequence-specific manner. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993 Dec 11;21(24):5589–5594. doi: 10.1093/nar/21.24.5589. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wyatt J. R., Puglisi J. D., Tinoco I., Jr RNA folding: pseudoknots, loops and bulges. Bioessays. 1989 Oct;11(4):100–106. doi: 10.1002/bies.950110406. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zawadzki V., Gross H. J. Rapid and simple purification of T7 RNA polymerase. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Apr 25;19(8):1948–1948. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.8.1948. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]