Abstract
DNA sequences upstream of the rrnB P1 core promoter (-10, -35 region) increase transcription more than 300-fold in vivo and in vitro. This stimulation results from a cis-acting DNA sequence, the UP element, which interacts directly with the alpha subunit of RNA polymerase, increasing transcription about 30-fold, and from a positively acting transcription factor, FIS, which increases expression another 10-fold. A DNA region exhibiting a high degree of intrinsic curvature has been observed upstream of the rrnB P1 core promoter and has thus been often cited as an example of the effect of bending on transcription. However, the precise position of the curvature has not been determined. We address here whether this bend is in fact related to activation of rRNA transcription. Electrophoretic analyses were used to localize the major bend in the rrnB P1 upstream region to position approximately -100 with respect to the transcription initiation site. Since most of the effect of upstream sequences on transcription results from DNA between the -35 hexamer and position -88, i.e. downstream of the bend center, these studies indicate that the curvature leading to the unusual electrophoretic behavior of the upstream region does not play a major role in activation of rRNA transcription. Minor deviations from normal electrophoretic behavior were associated with the region just upstream of the -35 hexamer and could conceivably influence interactions between the UP element and the alpha subunit of RNA polymerase.
Full text
PDF

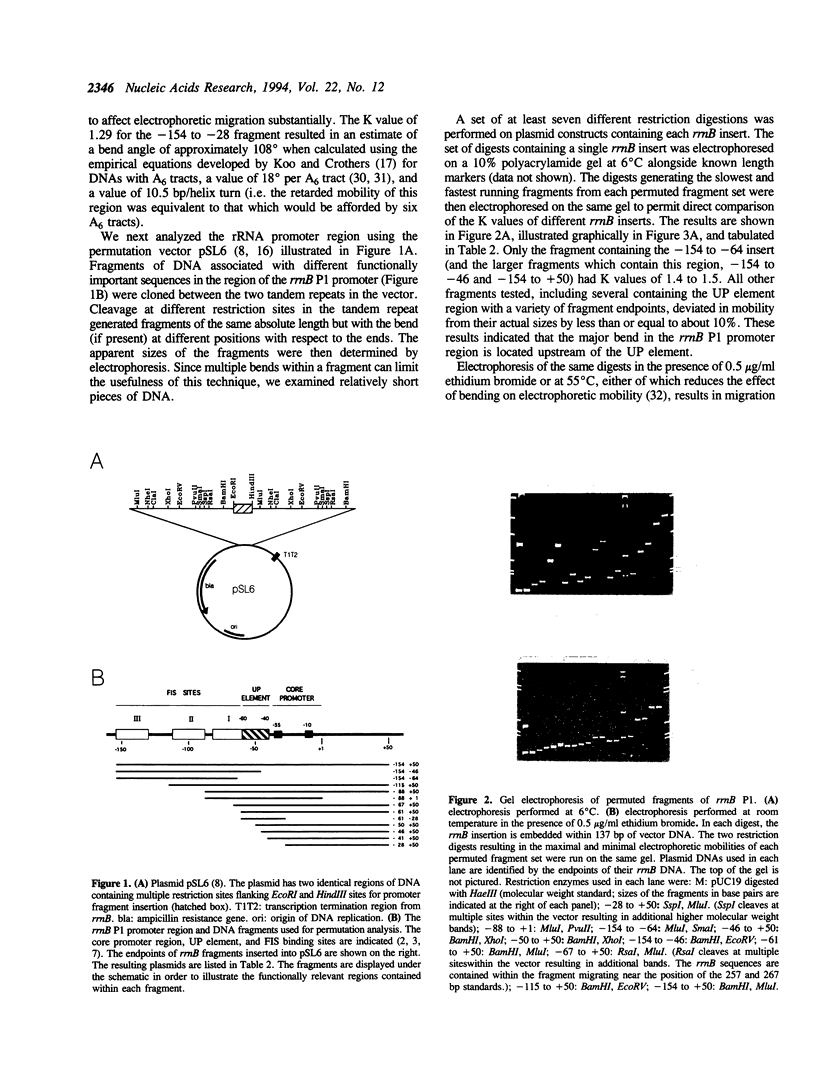



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bolshoy A., McNamara P., Harrington R. E., Trifonov E. N. Curved DNA without A-A: experimental estimation of all 16 DNA wedge angles. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Mar 15;88(6):2312–2316. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.6.2312. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bracco L., Kotlarz D., Kolb A., Diekmann S., Buc H. Synthetic curved DNA sequences can act as transcriptional activators in Escherichia coli. EMBO J. 1989 Dec 20;8(13):4289–4296. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08615.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brosius J., Dull T. J., Sleeter D. D., Noller H. F. Gene organization and primary structure of a ribosomal RNA operon from Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1981 May 15;148(2):107–127. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90508-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Condon C., Philips J., Fu Z. Y., Squires C., Squires C. L. Comparison of the expression of the seven ribosomal RNA operons in Escherichia coli. EMBO J. 1992 Nov;11(11):4175–4185. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05511.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dickson R. R., Gaal T., deBoer H. A., deHaseth P. L., Gourse R. L. Identification of promoter mutants defective in growth-rate-dependent regulation of rRNA transcription in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1989 Sep;171(9):4862–4870. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.9.4862-4870.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diekmann S. Analyzing DNA curvature in polyacrylamide gels. Methods Enzymol. 1992;212:30–46. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(92)12004-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diekmann S., Lilley D. M. The anomalous gel migration of a stable cruciform: temperature and salt dependence, and some comparisons with curved DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Jul 24;15(14):5765–5774. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.14.5765. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diekmann S., Wang J. C. On the sequence determinants and flexibility of the kinetoplast DNA fragment with abnormal gel electrophoretic mobilities. J Mol Biol. 1985 Nov 5;186(1):1–11. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90251-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaal T., Barkei J., Dickson R. R., deBoer H. A., deHaseth P. L., Alavi H., Gourse R. L. Saturation mutagenesis of an Escherichia coli rRNA promoter and initial characterization of promoter variants. J Bacteriol. 1989 Sep;171(9):4852–4861. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.9.4852-4861.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gartenberg M. R., Crothers D. M. Synthetic DNA bending sequences increase the rate of in vitro transcription initiation at the Escherichia coli lac promoter. J Mol Biol. 1991 May 20;219(2):217–230. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(91)90563-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gosink K. K., Ross W., Leirmo S., Osuna R., Finkel S. E., Johnson R. C., Gourse R. L. DNA binding and bending are necessary but not sufficient for Fis-dependent activation of rrnB P1. J Bacteriol. 1993 Mar;175(6):1580–1589. doi: 10.1128/jb.175.6.1580-1589.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gourse R. L., de Boer H. A., Nomura M. DNA determinants of rRNA synthesis in E. coli: growth rate dependent regulation, feedback inhibition, upstream activation, antitermination. Cell. 1986 Jan 17;44(1):197–205. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90498-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffith J., Bleyman M., Rauch C. A., Kitchin P. A., Englund P. T. Visualization of the bent helix in kinetoplast DNA by electron microscopy. Cell. 1986 Aug 29;46(5):717–724. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90347-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagerman P. J. Sequence-directed curvature of DNA. Annu Rev Biochem. 1990;59:755–781. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.59.070190.003543. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haran T. E., Crothers D. M. Cooperativity in A-tract structure and bending properties of composite TnAn blocks. Biochemistry. 1989 Apr 4;28(7):2763–2767. doi: 10.1021/bi00433a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Josaitis C. A., Gaal T., Ross W., Gourse R. L. Sequences upstream of the-35 hexamer of rrnB P1 affect promoter strength and upstream activation. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1990 Aug 27;1050(1-3):307–311. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(90)90186-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim J., Zwieb C., Wu C., Adhya S. Bending of DNA by gene-regulatory proteins: construction and use of a DNA bending vector. Gene. 1989 Dec 21;85(1):15–23. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(89)90459-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koo H. S., Crothers D. M. Calibration of DNA curvature and a unified description of sequence-directed bending. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Mar;85(6):1763–1767. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.6.1763. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel T. A. Rapid and efficient site-specific mutagenesis without phenotypic selection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jan;82(2):488–492. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.2.488. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leirmo S., Gourse R. L. Factor-independent activation of Escherichia coli rRNA transcription. I. Kinetic analysis of the roles of the upstream activator region and supercoiling on transcription of the rrnB P1 promoter in vitro. J Mol Biol. 1991 Aug 5;220(3):555–568. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(91)90100-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levene S. D., Wu H. M., Crothers D. M. Bending and flexibility of kinetoplast DNA. Biochemistry. 1986 Jul 15;25(14):3988–3995. doi: 10.1021/bi00362a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marini J. C., Levene S. D., Crothers D. M., Englund P. T. Bent helical structure in kinetoplast DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Dec;79(24):7664–7668. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.24.7664. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nachaliel N., Melnick J., Gafny R., Glaser G. Ribosome associated protein(s) specifically bind(s) to the upstream activator sequence of the E. coli rrnA P1 promoter. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Dec 11;17(23):9811–9822. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.23.9811. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newlands J. T., Josaitis C. A., Ross W., Gourse R. L. Both fis-dependent and factor-independent upstream activation of the rrnB P1 promoter are face of the helix dependent. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Feb 25;20(4):719–726. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.4.719. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newlands J. T., Ross W., Gosink K. K., Gourse R. L. Factor-independent activation of Escherichia coli rRNA transcription. II. characterization of complexes of rrnB P1 promoters containing or lacking the upstream activator region with Escherichia coli RNA polymerase. J Mol Biol. 1991 Aug 5;220(3):569–583. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(91)90101-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peacock A. C., Dingman C. W. Molecular weight estimation and separation of ribonucleic acid by electrophoresis in agarose-acrylamide composite gels. Biochemistry. 1968 Feb;7(2):668–674. doi: 10.1021/bi00842a023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plaskon R. R., Wartell R. M. Sequence distributions associated with DNA curvature are found upstream of strong E. coli promoters. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Jan 26;15(2):785–796. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.2.785. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prentki P., Pham M. H., Galas D. J. Plasmid permutation vectors to monitor DNA bending. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Dec 10;15(23):10060–10060. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.23.10060. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rao L., Ross W., Appleman J. A., Gaal T., Leirmo S., Schlax P. J., Record M. T., Jr, Gourse R. L. Factor independent activation of rrnB P1. An "extended" promoter with an upstream element that dramatically increases promoter strength. J Mol Biol. 1994 Feb 4;235(5):1421–1435. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1994.1098. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross W., Gosink K. K., Salomon J., Igarashi K., Zou C., Ishihama A., Severinov K., Gourse R. L. A third recognition element in bacterial promoters: DNA binding by the alpha subunit of RNA polymerase. Science. 1993 Nov 26;262(5138):1407–1413. doi: 10.1126/science.8248780. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross W., Thompson J. F., Newlands J. T., Gourse R. L. E.coli Fis protein activates ribosomal RNA transcription in vitro and in vivo. EMBO J. 1990 Nov;9(11):3733–3742. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07586.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka K., Muramatsu S., Yamada H., Mizuno T. Systematic characterization of curved DNA segments randomly cloned from Escherichia coli and their functional significance. Mol Gen Genet. 1991 May;226(3):367–376. doi: 10.1007/BF00260648. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson J. F., Landy A. Empirical estimation of protein-induced DNA bending angles: applications to lambda site-specific recombination complexes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Oct 25;16(20):9687–9705. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.20.9687. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trifonov E. N. Curved DNA. CRC Crit Rev Biochem. 1985;19(2):89–106. doi: 10.3109/10409238509082540. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VanWye J. D., Bronson E. C., Anderson J. N. Species-specific patterns of DNA bending and sequence. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Oct 11;19(19):5253–5261. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.19.5253. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu H. M., Crothers D. M. The locus of sequence-directed and protein-induced DNA bending. Nature. 1984 Apr 5;308(5959):509–513. doi: 10.1038/308509a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zacharias M., Göringer H. U., Wagner R. Analysis of the Fis-dependent and Fis-independent transcription activation mechanisms of the Escherichia coli ribosomal RNA P1 promoter. Biochemistry. 1992 Mar 10;31(9):2621–2628. doi: 10.1021/bi00124a024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zacharias M., Göringer H. U., Wagner R. Influence of the GCGC discriminator motif introduced into the ribosomal RNA P2- and tac promoter on growth-rate control and stringent sensitivity. EMBO J. 1989 Nov;8(11):3357–3363. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08498.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]