Abstract
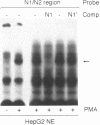
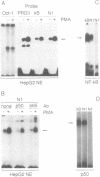
Overproduction of Apo CIII causes elevated plasma triglyceride levels in transgenic animals and is associated with hypertriglyceridemia in humans. The regulation of apo CIII production is likely to play an important role in controlling plasma triglyceride levels. As an initial step in determining the role of transcriptional regulation in the production of apo CIII and in triglyceride metabolism, we have begun to characterize the activity of specific transcriptional regulatory elements in the CIII promoter. In the current study, we have identified and characterized an NF-kappa B regulatory element located 150 nucleotides upstream from the transcriptional start site of the apo CIII gene. Purified NF-kappa B, as well as an NF-kappa B protein in HepG2 cell nuclear extracts, bound specifically to this sequence element. The hepatic protein was induced by phorbol ester (PMA), and reacted with antibodies to the p50 and p65 subunits of NF-kappa B. The NF-kappa B element conferred PMA and IL1-beta inducible transcriptional activity to a heterologous promoter/reporter construct when transfected into HepG2 cells. Analysis of the full length CIII promoter demonstrated that the inducible activity of the NF-kappa B element was suppressed by sequences in the apo CIII enhancer element located approximately 500 nucleotides upstream of the NF-kappa B binding site. A deletion removing the enhancer restored the PMA inducible activity of the NF-kappa B binding site. These results indicate that apo CIII gene expression is regulated by NF-kappa B, and suggest that apo CIII production may be modulated by cellular signals, like inflammatory cytokines, that activate NF-kB.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aalto-Setälä K., Fisher E. A., Chen X., Chajek-Shaul T., Hayek T., Zechner R., Walsh A., Ramakrishnan R., Ginsberg H. N., Breslow J. L. Mechanism of hypertriglyceridemia in human apolipoprotein (apo) CIII transgenic mice. Diminished very low density lipoprotein fractional catabolic rate associated with increased apo CIII and reduced apo E on the particles. J Clin Invest. 1992 Nov;90(5):1889–1900. doi: 10.1172/JCI116066. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anisowicz A., Messineo M., Lee S. W., Sager R. An NF-kappa B-like transcription factor mediates IL-1/TNF-alpha induction of gro in human fibroblasts. J Immunol. 1991 Jul 15;147(2):520–527. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baeuerle P. A. The inducible transcription activator NF-kappa B: regulation by distinct protein subunits. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1991 Apr 16;1072(1):63–80. doi: 10.1016/0304-419x(91)90007-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Banerjee R., Karpen S., Siekevitz M., Lengyel G., Bauer J., Acs G. Tumor necrosis factor-alpha induces a kappa B sequence-specific DNA-binding protein in human hepatoblastoma HepG2 cells. Hepatology. 1989 Dec;10(6):1008–1013. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840100620. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birchbauer A., Knipping G., Juritsch B., Aschauer H., Zechner R. Characterization of the apolipoprotein AI and CIII genes in the domestic pig. Genomics. 1993 Mar;15(3):643–652. doi: 10.1006/geno.1993.1119. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brasier A. R., Ron D., Tate J. E., Habener J. F. A family of constitutive C/EBP-like DNA binding proteins attenuate the IL-1 alpha induced, NF kappa B mediated trans-activation of the angiotensinogen gene acute-phase response element. EMBO J. 1990 Dec;9(12):3933–3944. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07614.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cabana V. G., Siegel J. N., Sabesin S. M. Effects of the acute phase response on the concentration and density distribution of plasma lipids and apolipoproteins. J Lipid Res. 1989 Jan;30(1):39–49. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlson L. A., Ballantyne D. Changing relative proportions of apolipoproteins CII and CIII of very low density lipoproteins in hypertriglyceridaemia. Atherosclerosis. 1976 May-Jun;23(3):563–568. doi: 10.1016/0021-9150(76)90016-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collart M. A., Baeuerle P., Vassalli P. Regulation of tumor necrosis factor alpha transcription in macrophages: involvement of four kappa B-like motifs and of constitutive and inducible forms of NF-kappa B. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Apr;10(4):1498–1506. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.4.1498. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dammerman M., Sandkuijl L. A., Halaas J. L., Chung W., Breslow J. L. An apolipoprotein CIII haplotype protective against hypertriglyceridemia is specified by promoter and 3' untranslated region polymorphisms. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 May 15;90(10):4562–4566. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.10.4562. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dignam J. D., Lebovitz R. M., Roeder R. G. Accurate transcription initiation by RNA polymerase II in a soluble extract from isolated mammalian nuclei. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Mar 11;11(5):1475–1489. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.5.1475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edbrooke M. R., Burt D. W., Cheshire J. K., Woo P. Identification of cis-acting sequences responsible for phorbol ester induction of human serum amyloid A gene expression via a nuclear factor kappaB-like transcription factor. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 May;9(5):1908–1916. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.5.1908. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feingold K. R., Soued M., Serio M. K., Moser A. H., Dinarello C. A., Grunfeld C. Multiple cytokines stimulate hepatic lipid synthesis in vivo. Endocrinology. 1989 Jul;125(1):267–274. doi: 10.1210/endo-125-1-267. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodbourn S., Zinn K., Maniatis T. Human beta-interferon gene expression is regulated by an inducible enhancer element. Cell. 1985 Jun;41(2):509–520. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80024-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman C. M., Moffat L. F., Howard B. H. Recombinant genomes which express chloramphenicol acetyltransferase in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Sep;2(9):1044–1051. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.9.1044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffin G. E., Leung K., Folks T. M., Kunkel S., Nabel G. J. Activation of HIV gene expression during monocyte differentiation by induction of NF-kappa B. Nature. 1989 May 4;339(6219):70–73. doi: 10.1038/339070a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirai H., Fujisawa J., Suzuki T., Ueda K., Muramatsu M., Tsuboi A., Arai N., Yoshida M. Transcriptional activator Tax of HTLV-1 binds to the NF-kappa B precursor p105. Oncogene. 1992 Sep;7(9):1737–1742. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito Y., Azrolan N., O'Connell A., Walsh A., Breslow J. L. Hypertriglyceridemia as a result of human apo CIII gene expression in transgenic mice. Science. 1990 Aug 17;249(4970):790–793. doi: 10.1126/science.2167514. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Januzzi J. L., Azrolan N., O'Connell A., Aalto-Setälä K., Breslow J. L. Characterization of the mouse apolipoprotein Apoa-1/Apoc-3 gene locus: genomic, mRNA, and protein sequences with comparisons to other species. Genomics. 1992 Dec;14(4):1081–1088. doi: 10.1016/s0888-7543(05)80133-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kessler D. J., Duyao M. P., Spicer D. B., Sonenshein G. E. NF-kappa B-like factors mediate interleukin 1 induction of c-myc gene transcription in fibroblasts. J Exp Med. 1992 Sep 1;176(3):787–792. doi: 10.1084/jem.176.3.787. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krauss R. M., Herbert P. N., Levy R. I., Fredrickson D. S. Further observations on the activation and inhibition of lipoprotein lipase by apolipoproteins. Circ Res. 1973 Oct;33(4):403–411. doi: 10.1161/01.res.33.4.403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LeClair K. P., Blanar M. A., Sharp P. A. The p50 subunit of NF-kappa B associates with the NF-IL6 transcription factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Sep 1;89(17):8145–8149. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.17.8145. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le N. A., Gibson J. C., Ginsberg H. N. Independent regulation of plasma apolipoprotein C-II and C-III concentrations in very low density and high density lipoproteins: implications for the regulation of the catabolism of these lipoproteins. J Lipid Res. 1988 May;29(5):669–677. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leff T., Reue K., Melian A., Culver H., Breslow J. L. A regulatory element in the ApoCIII promoter that directs hepatic specific transcription binds to proteins in expressing and nonexpressing cell types. J Biol Chem. 1989 Sep 25;264(27):16132–16137. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lenardo M. J., Fan C. M., Maniatis T., Baltimore D. The involvement of NF-kappa B in beta-interferon gene regulation reveals its role as widely inducible mediator of signal transduction. Cell. 1989 Apr 21;57(2):287–294. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90966-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li X. X., Liao W. S. Expression of rat serum amyloid A1 gene involves both C/EBP-like and NF kappa B-like transcription factors. J Biol Chem. 1991 Aug 15;266(23):15192–15201. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Libermann T. A., Baltimore D. Activation of interleukin-6 gene expression through the NF-kappa B transcription factor. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 May;10(5):2327–2334. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.5.2327. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malmendier C. L., Lontie J. F., Dubois D., Delcroix C., Magot T., De Roy L. In vivo metabolism of apolipoproteins C-II and C-III in normal and hypertriglyceridemic subjects. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1988;243:299–309. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4613-0733-4_38. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mukaida N., Mahe Y., Matsushima K. Cooperative interaction of nuclear factor-kappa B- and cis-regulatory enhancer binding protein-like factor binding elements in activating the interleukin-8 gene by pro-inflammatory cytokines. J Biol Chem. 1990 Dec 5;265(34):21128–21133. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nonaka M., Huang Z. M. Interleukin-1-mediated enhancement of mouse factor B gene expression via NF kappa B-like hepatoma nuclear factor. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Dec;10(12):6283–6289. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.12.6283. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogami K., Hadzopoulou-Cladaras M., Cladaras C., Zannis V. I. Promoter elements and factors required for hepatic and intestinal transcription of the human ApoCIII gene. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jun 15;265(17):9808–9815. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ordovas J. M., Civeira F., Genest J., Jr, Craig S., Robbins A. H., Meade T., Pocovi M., Frossard P. M., Masharani U., Wilson P. W. Restriction fragment length polymorphisms of the apolipoprotein A-I, C-III, A-IV gene locus. Relationships with lipids, apolipoproteins, and premature coronary artery disease. Atherosclerosis. 1991 Mar;87(1):75–86. doi: 10.1016/0021-9150(91)90234-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osborn L., Kunkel S., Nabel G. J. Tumor necrosis factor alpha and interleukin 1 stimulate the human immunodeficiency virus enhancer by activation of the nuclear factor kappa B. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Apr;86(7):2336–2340. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.7.2336. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rees A., Stocks J., Sharpe C. R., Vella M. A., Shoulders C. C., Katz J., Jowett N. I., Baralle F. E., Galton D. J. Deoxyribonucleic acid polymorphism in the apolipoprotein A-1-C-III gene cluster. Association with hypertriglyceridemia. J Clin Invest. 1985 Sep;76(3):1090–1095. doi: 10.1172/JCI112062. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reue K., Leff T., Breslow J. L. Human apolipoprotein CIII gene expression is regulated by positive and negative cis-acting elements and tissue-specific protein factors. J Biol Chem. 1988 May 15;263(14):6857–6864. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ron D., Brasier A. R., Wright K. A., Tate J. E., Habener J. F. An inducible 50-kilodalton NF kappa B-like protein and a constitutive protein both bind the acute-phase response element of the angiotensinogen gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Mar;10(3):1023–1032. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.3.1023. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schonfeld G., George P. K., Miller J., Reilly P., Witztum J. Apolipoprotein C-II and C-III levels in hyperlipoproteinemia. Metabolism. 1979 Oct;28(10):1001–1010. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(79)90004-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sen R., Baltimore D. Inducibility of kappa immunoglobulin enhancer-binding protein Nf-kappa B by a posttranslational mechanism. Cell. 1986 Dec 26;47(6):921–928. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90807-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sen R., Baltimore D. Multiple nuclear factors interact with the immunoglobulin enhancer sequences. Cell. 1986 Aug 29;46(5):705–716. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90346-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shelburne F., Hanks J., Meyers W., Quarfordt S. Effect of apoproteins on hepatic uptake of triglyceride emulsions in the rat. J Clin Invest. 1980 Mar;65(3):652–658. doi: 10.1172/JCI109710. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shoulders C. C., Harry P. J., Lagrost L., White S. E., Shah N. F., North J. D., Gilligan M., Gambert P., Ball M. J. Variation at the apo AI/CIII/AIV gene complex is associated with elevated plasma levels of apo CIII. Atherosclerosis. 1991 Apr;87(2-3):239–247. doi: 10.1016/0021-9150(91)90026-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith J. D., Melián A., Leff T., Breslow J. L. Expression of the human apolipoprotein E gene is regulated by multiple positive and negative elements. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jun 15;263(17):8300–8308. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taş S. Strong association of a single nucleotide substitution in the 3'-untranslated region of the apolipoprotein-CIII gene with common hypertriglyceridemia in Arabs. Clin Chem. 1989 Feb;35(2):256–259. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Visvanathan K. V., Goodbourn S. Double-stranded RNA activates binding of NF-kappa B to an inducible element in the human beta-interferon promoter. EMBO J. 1989 Apr;8(4):1129–1138. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03483.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Windler E., Havel R. J. Inhibitory effects of C apolipoproteins from rats and humans on the uptake of triglyceride-rich lipoproteins and their remnants by the perfused rat liver. J Lipid Res. 1985 May;26(5):556–565. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]