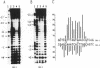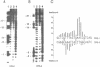Abstract
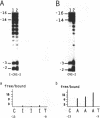
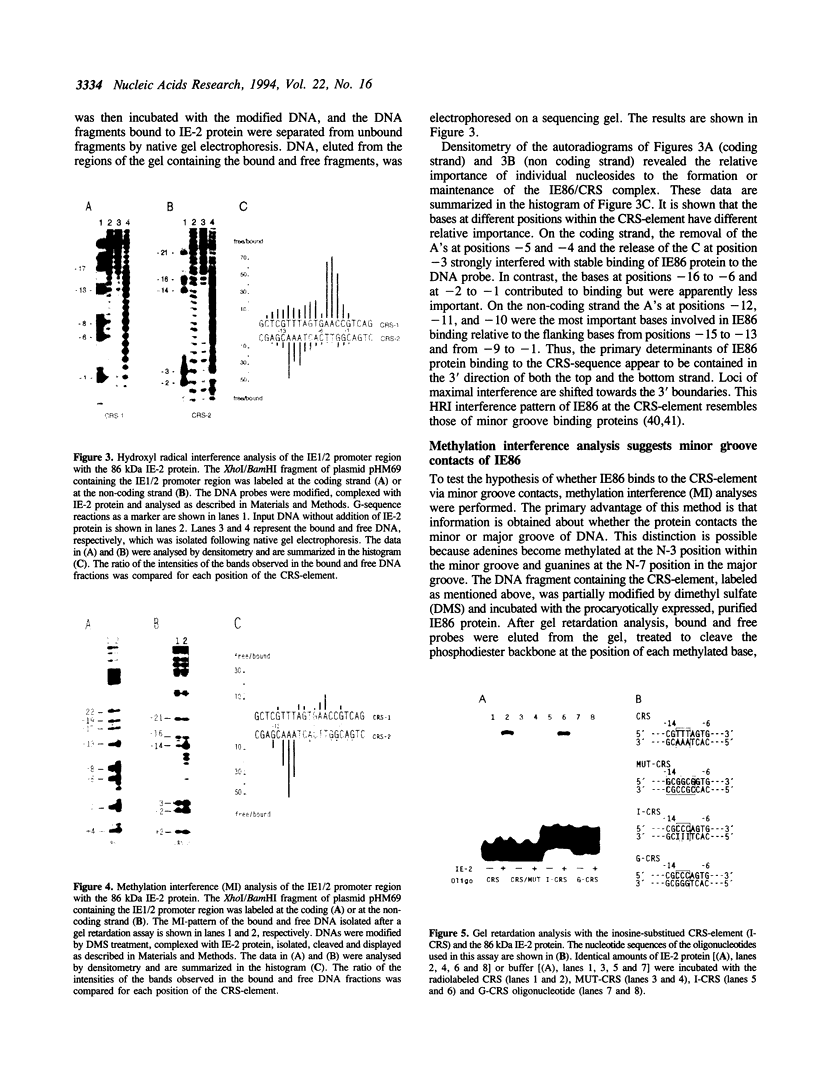
The 86 kDa immediate early-2 protein (IE2, IE86) of human cytomegalovirus (HCMV) is a multifunctional polypeptide that can regulate gene expression both positively and negatively. In particular, it represses its own mRNA synthesis by binding directly to a sequence element, termed cis repression signal (CRS), that is located between the TATA box and the transcriptional start site of the major IE enhancer/promoter of HCMV. Here, we provide evidence that IE86, unlike most sequence-specific DNA-binding proteins, interacts primarily within the minor groove of the DNA helix. This was shown by hydroxyl radical and methylation interference assays. In addition, binding studies with inosine-substituted oligonucleotides which have an altered major groove morphology without changing the surface of the minor groove, confirmed the results obtained in interference analyses. This establishes IE86 as a member of a small group of DNA binding proteins that interact with A - T rich sequences within the minor groove and which also includes the TATA-box binding protein TBP. Remarkably, IE86 and TBP are able to bind simultaneously in an immediate vicinity at the major IE enhancer/promoter of HCMV. As minor groove binding proteins are known to bend DNA heavily this could contribute to the observed negative regulation of transcription by IE86.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arlt H., Lang D., Gebert S., Stamminger T. Identification of binding sites for the 86-kilodalton IE2 protein of human cytomegalovirus within an IE2-responsive viral early promoter. J Virol. 1994 Jul;68(7):4117–4125. doi: 10.1128/jvi.68.7.4117-4125.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonnefoy E., Rouvière-Yaniv J. HU and IHF, two homologous histone-like proteins of Escherichia coli, form different protein-DNA complexes with short DNA fragments. EMBO J. 1991 Mar;10(3):687–696. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07998.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boshart M., Weber F., Jahn G., Dorsch-Häsler K., Fleckenstein B., Schaffner W. A very strong enhancer is located upstream of an immediate early gene of human cytomegalovirus. Cell. 1985 Jun;41(2):521–530. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80025-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang C. P., Malone C. L., Stinski M. F. A human cytomegalovirus early gene has three inducible promoters that are regulated differentially at various times after infection. J Virol. 1989 Jan;63(1):281–290. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.1.281-290.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chee M. S., Bankier A. T., Beck S., Bohni R., Brown C. M., Cerny R., Horsnell T., Hutchison C. A., 3rd, Kouzarides T., Martignetti J. A. Analysis of the protein-coding content of the sequence of human cytomegalovirus strain AD169. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1990;154:125–169. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-74980-3_6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cherrington J. M., Khoury E. L., Mocarski E. S. Human cytomegalovirus ie2 negatively regulates alpha gene expression via a short target sequence near the transcription start site. J Virol. 1991 Feb;65(2):887–896. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.2.887-896.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiou C. J., Zong J., Waheed I., Hayward G. S. Identification and mapping of dimerization and DNA-binding domains in the C terminus of the IE2 regulatory protein of human cytomegalovirus. J Virol. 1993 Oct;67(10):6201–6214. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.10.6201-6214.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Churchill M. E., Travers A. A. Protein motifs that recognize structural features of DNA. Trends Biochem Sci. 1991 Mar;16(3):92–97. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(91)90040-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colberg-Poley A. M., Santomenna L. D., Harlow P. P., Benfield P. A., Tenney D. J. Human cytomegalovirus US3 and UL36-38 immediate-early proteins regulate gene expression. J Virol. 1992 Jan;66(1):95–105. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.1.95-105.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drew H. R., Travers A. A. DNA bending and its relation to nucleosome positioning. J Mol Biol. 1985 Dec 20;186(4):773–790. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90396-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furnari B. A., Poma E., Kowalik T. F., Huong S. M., Huang E. S. Human cytomegalovirus immediate-early gene 2 protein interacts with itself and with several novel cellular proteins. J Virol. 1993 Aug;67(8):4981–4991. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.8.4981-4991.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giangrande A., Mettling C., Martin M., Ruiz C., Richards G. Drosophila Sgs3 TATA: effects of point mutations on expression in vivo and protein binding in vitro with staged nuclear extracts. EMBO J. 1989 Nov;8(11):3459–3466. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08510.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giese K., Amsterdam A., Grosschedl R. DNA-binding properties of the HMG domain of the lymphoid-specific transcriptional regulator LEF-1. Genes Dev. 1991 Dec;5(12B):2567–2578. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.12b.2567. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giese K., Cox J., Grosschedl R. The HMG domain of lymphoid enhancer factor 1 bends DNA and facilitates assembly of functional nucleoprotein structures. Cell. 1992 Apr 3;69(1):185–195. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90129-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodman S. D., Nash H. A. Functional replacement of a protein-induced bend in a DNA recombination site. Nature. 1989 Sep 21;341(6239):251–254. doi: 10.1038/341251a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagemeier C., Walker S. M., Sissons P. J., Sinclair J. H. The 72K IE1 and 80K IE2 proteins of human cytomegalovirus independently trans-activate the c-fos, c-myc and hsp70 promoters via basal promoter elements. J Gen Virol. 1992 Sep;73(Pt 9):2385–2393. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-73-9-2385. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagemeier C., Walker S., Caswell R., Kouzarides T., Sinclair J. The human cytomegalovirus 80-kilodalton but not the 72-kilodalton immediate-early protein transactivates heterologous promoters in a TATA box-dependent mechanism and interacts directly with TFIID. J Virol. 1992 Jul;66(7):4452–4456. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.7.4452-4456.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hermiston T. W., Malone C. L., Stinski M. F. Human cytomegalovirus immediate-early two protein region involved in negative regulation of the major immediate-early promoter. J Virol. 1990 Jul;64(7):3532–3536. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.7.3532-3536.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hermiston T. W., Malone C. L., Witte P. R., Stinski M. F. Identification and characterization of the human cytomegalovirus immediate-early region 2 gene that stimulates gene expression from an inducible promoter. J Virol. 1987 Oct;61(10):3214–3221. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.10.3214-3221.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jupp R., Hoffmann S., Depto A., Stenberg R. M., Ghazal P., Nelson J. A. Direct interaction of the human cytomegalovirus IE86 protein with the cis repression signal does not preclude TBP from binding to the TATA box. J Virol. 1993 Sep;67(9):5595–5604. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.9.5595-5604.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim J. L., Nikolov D. B., Burley S. K. Co-crystal structure of TBP recognizing the minor groove of a TATA element. Nature. 1993 Oct 7;365(6446):520–527. doi: 10.1038/365520a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim Y., Geiger J. H., Hahn S., Sigler P. B. Crystal structure of a yeast TBP/TATA-box complex. Nature. 1993 Oct 7;365(6446):512–520. doi: 10.1038/365512a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klucher K. M., Sommer M., Kadonaga J. T., Spector D. H. In vivo and in vitro analysis of transcriptional activation mediated by the human cytomegalovirus major immediate-early proteins. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Feb;13(2):1238–1250. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.2.1238. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuwabara M. D., Sigman D. S. Footprinting DNA-protein complexes in situ following gel retardation assays using 1,10-phenanthroline-copper ion: Escherichia coli RNA polymerase-lac promoter complexes. Biochemistry. 1987 Nov 17;26(23):7234–7238. doi: 10.1021/bi00397a006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lang D., Stamminger T. The 86-kilodalton IE-2 protein of human cytomegalovirus is a sequence-specific DNA-binding protein that interacts directly with the negative autoregulatory response element located near the cap site of the IE-1/2 enhancer-promoter. J Virol. 1993 Jan;67(1):323–331. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.1.323-331.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee D. K., Horikoshi M., Roeder R. G. Interaction of TFIID in the minor groove of the TATA element. Cell. 1991 Dec 20;67(6):1241–1250. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90300-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu B., Hermiston T. W., Stinski M. F. A cis-acting element in the major immediate-early (IE) promoter of human cytomegalovirus is required for negative regulation by IE2. J Virol. 1991 Feb;65(2):897–903. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.2.897-903.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lu A. L., Jack W. E., Modrich P. DNA determinants important in sequence recognition by Eco RI endonuclease. J Biol Chem. 1981 Dec 25;256(24):13200–13206. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macias M. P., Stinski M. F. An in vitro system for human cytomegalovirus immediate early 2 protein (IE2)-mediated site-dependent repression of transcription and direct binding of IE2 to the major immediate early promoter. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jan 15;90(2):707–711. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.2.707. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malone C. L., Vesole D. H., Stinski M. F. Transactivation of a human cytomegalovirus early promoter by gene products from the immediate-early gene IE2 and augmentation by IE1: mutational analysis of the viral proteins. J Virol. 1990 Apr;64(4):1498–1506. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.4.1498-1506.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McClarin J. A., Frederick C. A., Wang B. C., Greene P., Boyer H. W., Grable J., Rosenberg J. M. Structure of the DNA-Eco RI endonuclease recognition complex at 3 A resolution. Science. 1986 Dec 19;234(4783):1526–1541. doi: 10.1126/science.3024321. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDonough S. H., Spector D. H. Transcription in human fibroblasts permissively infected by human cytomegalovirus strain AD169. Virology. 1983 Feb;125(1):31–46. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(83)90061-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pizzorno M. C., Hayward G. S. The IE2 gene products of human cytomegalovirus specifically down-regulate expression from the major immediate-early promoter through a target sequence located near the cap site. J Virol. 1990 Dec;64(12):6154–6165. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.12.6154-6165.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pizzorno M. C., Mullen M. A., Chang Y. N., Hayward G. S. The functionally active IE2 immediate-early regulatory protein of human cytomegalovirus is an 80-kilodalton polypeptide that contains two distinct activator domains and a duplicated nuclear localization signal. J Virol. 1991 Jul;65(7):3839–3852. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.7.3839-3852.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pizzorno M. C., O'Hare P., Sha L., LaFemina R. L., Hayward G. S. trans-activation and autoregulation of gene expression by the immediate-early region 2 gene products of human cytomegalovirus. J Virol. 1988 Apr;62(4):1167–1179. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.4.1167-1179.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reichert C. M., O'Leary T. J., Levens D. L., Simrell C. R., Macher A. M. Autopsy pathology in the acquired immune deficiency syndrome. Am J Pathol. 1983 Sep;112(3):357–382. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robertson C. A., Nash H. A. Bending of the bacteriophage lambda attachment site by Escherichia coli integration host factor. J Biol Chem. 1988 Mar 15;263(8):3554–3557. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheit K. H., Holy A. Die Methylierung von Inosin und Uridylyl-(3'-5')inosin durch Dimethylsulfat. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1967 Dec 19;149(2):344–354. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seeman N. C., Rosenberg J. M., Rich A. Sequence-specific recognition of double helical nucleic acids by proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Mar;73(3):804–808. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.3.804. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siebenlist U., Gilbert W. Contacts between Escherichia coli RNA polymerase and an early promoter of phage T7. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jan;77(1):122–126. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.1.122. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staprans S. I., Rabert D. K., Spector D. H. Identification of sequence requirements and trans-acting functions necessary for regulated expression of a human cytomegalovirus early gene. J Virol. 1988 Sep;62(9):3463–3473. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.9.3463-3473.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Starr D. B., Hawley D. K. TFIID binds in the minor groove of the TATA box. Cell. 1991 Dec 20;67(6):1231–1240. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90299-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stasiak P. C., Mocarski E. S. Transactivation of the cytomegalovirus ICP36 gene promoter requires the alpha gene product TRS1 in addition to IE1 and IE2. J Virol. 1992 Feb;66(2):1050–1058. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.2.1050-1058.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stenberg R. M., Depto A. S., Fortney J., Nelson J. A. Regulated expression of early and late RNAs and proteins from the human cytomegalovirus immediate-early gene region. J Virol. 1989 Jun;63(6):2699–2708. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.6.2699-2708.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stenberg R. M., Fortney J., Barlow S. W., Magrane B. P., Nelson J. A., Ghazal P. Promoter-specific trans activation and repression by human cytomegalovirus immediate-early proteins involves common and unique protein domains. J Virol. 1990 Apr;64(4):1556–1565. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.4.1556-1565.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stenberg R. M., Witte P. R., Stinski M. F. Multiple spliced and unspliced transcripts from human cytomegalovirus immediate-early region 2 and evidence for a common initiation site within immediate-early region 1. J Virol. 1985 Dec;56(3):665–675. doi: 10.1128/jvi.56.3.665-675.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Struhl K. Duality of TBP, the universal transcription factor. Science. 1994 Feb 25;263(5150):1103–1104. doi: 10.1126/science.8108728. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tevethia M. J., Spector D. J., Leisure K. M., Stinski M. F. Participation of two human cytomegalovirus immediate early gene regions in transcriptional activation of adenovirus promoters. Virology. 1987 Dec;161(2):276–285. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(87)90119-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson J. F., Landy A. Empirical estimation of protein-induced DNA bending angles: applications to lambda site-specific recombination complexes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Oct 25;16(20):9687–9705. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.20.9687. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomsen D. R., Stenberg R. M., Goins W. F., Stinski M. F. Promoter-regulatory region of the major immediate early gene of human cytomegalovirus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Feb;81(3):659–663. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.3.659. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tullius T. D., Dombroski B. A. Hydroxyl radical "footprinting": high-resolution information about DNA-protein contacts and application to lambda repressor and Cro protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Aug;83(15):5469–5473. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.15.5469. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Dyke M. W., Hertzberg R. P., Dervan P. B. Map of distamycin, netropsin, and actinomycin binding sites on heterogeneous DNA: DNA cleavage-inhibition patterns with methidiumpropyl-EDTA.Fe(II). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Sep;79(18):5470–5474. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.18.5470. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wathen M. W., Stinski M. F. Temporal patterns of human cytomegalovirus transcription: mapping the viral RNAs synthesized at immediate early, early, and late times after infection. J Virol. 1982 Feb;41(2):462–477. doi: 10.1128/jvi.41.2.462-477.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wathen M. W., Thomsen D. R., Stinski M. F. Temporal regulation of human cytomegalovirus transcription at immediate early and early times after infection. J Virol. 1981 May;38(2):446–459. doi: 10.1128/jvi.38.2.446-459.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wobbe C. R., Struhl K. Yeast and human TATA-binding proteins have nearly identical DNA sequence requirements for transcription in vitro. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Aug;10(8):3859–3867. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.8.3859. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Workman J. L., Roeder R. G. Binding of transcription factor TFIID to the major late promoter during in vitro nucleosome assembly potentiates subsequent initiation by RNA polymerase II. Cell. 1987 Nov 20;51(4):613–622. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90130-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang C. C., Nash H. A. The interaction of E. coli IHF protein with its specific binding sites. Cell. 1989 Jun 2;57(5):869–880. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90801-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]