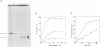Abstract
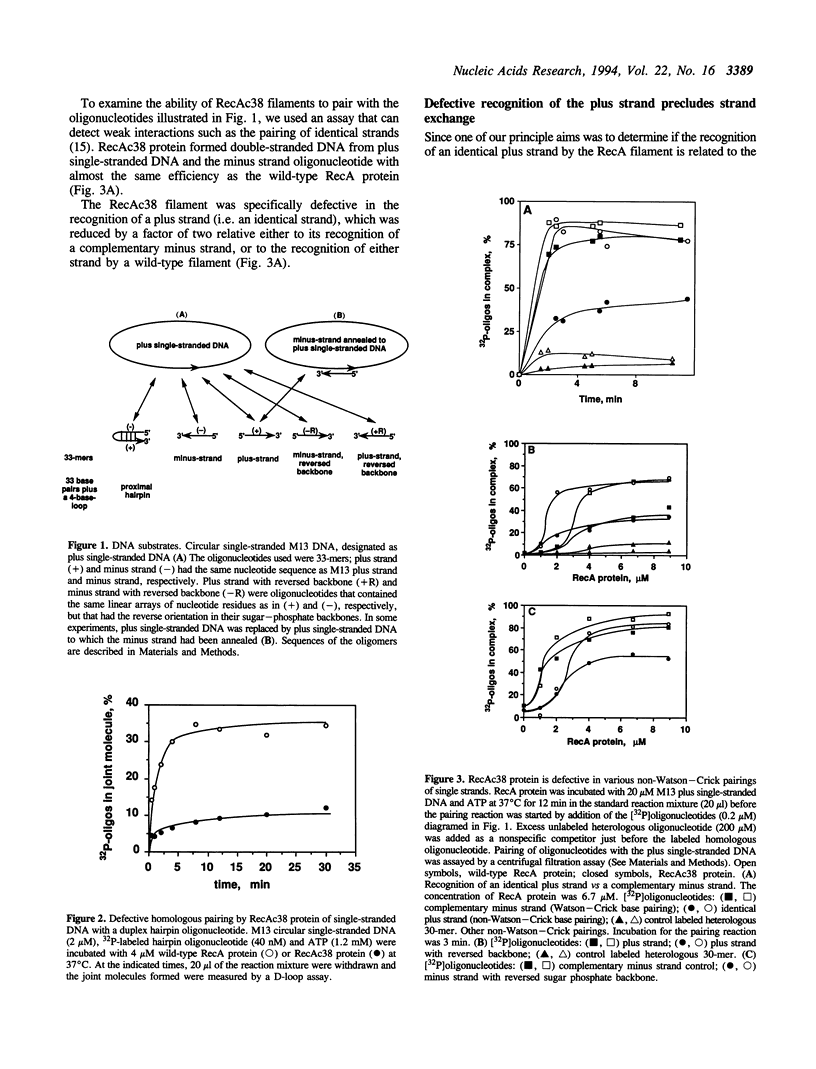
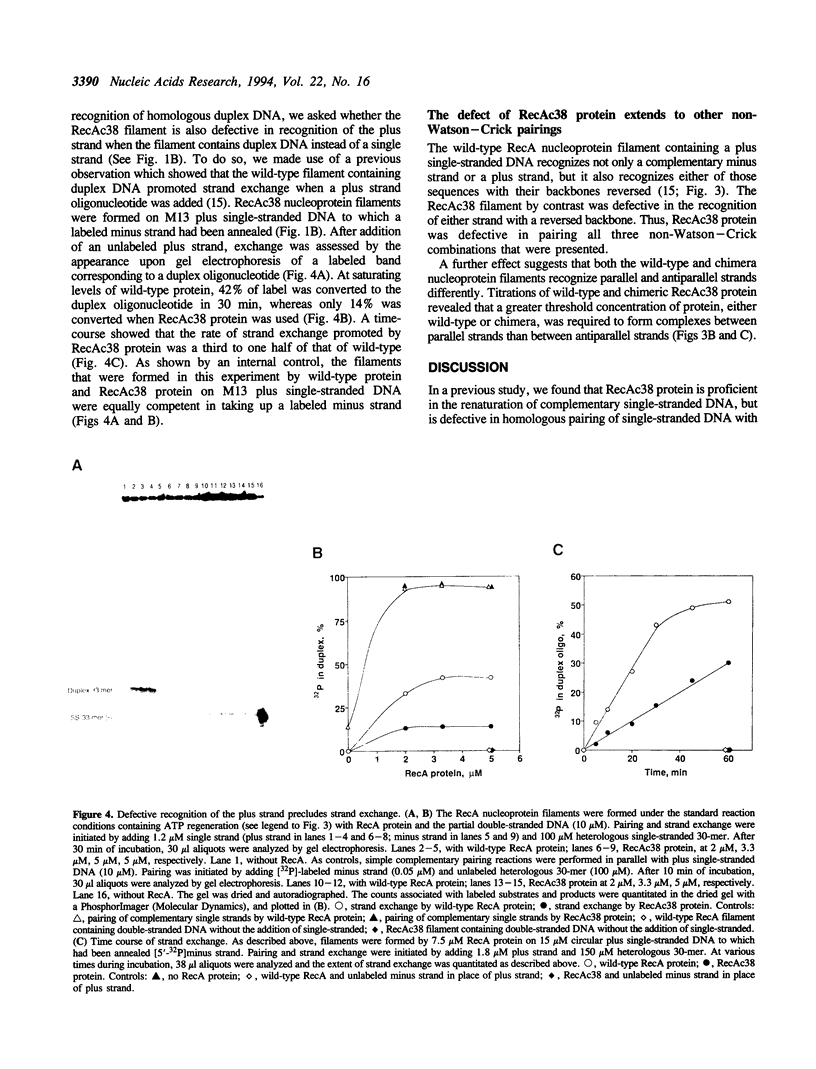
The helical filament formed by RecA protein on single-stranded DNA plays an important role in homologous recombination and pairs with a complementary single strand or homologous duplex DNA. The RecA nucleoprotein filament also recognizes an identical single strand. The chimeric protein, RecAc38, forms a nucleoprotein filament that recognizes a complementary strand but is defective in recognition of duplex DNA, and is associated with phenotypic defects in repair and recombination. As described here, RecAc38 nucleoprotein filament is also defective in recognition of an identical strand, either when the filament has within it a single strand or duplex DNA. A model that postulates three DNA binding sites rationalizes these observations and suggests that the third binding site mediates non-Watson-Crick interactions that are instrumental in recognition of homology in duplex DNA.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bezzubova O., Shinohara A., Mueller R. G., Ogawa H., Buerstedde J. M. A chicken RAD51 homologue is expressed at high levels in lymphoid and reproductive organs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993 Apr 11;21(7):1577–1580. doi: 10.1093/nar/21.7.1577. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bishop D. K., Park D., Xu L., Kleckner N. DMC1: a meiosis-specific yeast homolog of E. coli recA required for recombination, synaptonemal complex formation, and cell cycle progression. Cell. 1992 May 1;69(3):439–456. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90446-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cunningham R. P., DasGupta C., Shibata T., Radding C. M. Homologous pairing in genetic recombination: recA protein makes joint molecules of gapped circular DNA and closed circular DNA. Cell. 1980 May;20(1):223–235. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90250-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DasGupta C., Shibata T., Cunningham R. P., Radding C. M. The topology of homologous pairing promoted by RecA protein. Cell. 1980 Nov;22(2 Pt 2):437–446. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90354-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flory S. S., Tsang J., Muniyappa K., Bianchi M., Gonda D., Kahn R., Azhderian E., Egner C., Shaner S., Radding C. M. Intermediates in homologous pairing promoted by RecA protein and correlations of recombination in vitro and in vivo. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1984;49:513–523. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1984.049.01.058. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kowalczykowski S. C. Biochemistry of genetic recombination: energetics and mechanism of DNA strand exchange. Annu Rev Biophys Biophys Chem. 1991;20:539–575. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.20.060191.002543. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurumizaka H., Ikawa S., Ikeya T., Ogawa T., Shibata T. A chimeric RecA protein exhibits altered double-stranded DNA binding. J Biol Chem. 1994 Jan 28;269(4):3068–3075. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McEntee K., Weinstock G. M., Lehman I. R. Initiation of general recombination catalyzed in vitro by the recA protein of Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jun;76(6):2615–2619. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.6.2615. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogawa T., Shinohara A., Ogawa H., Tomizawa J. Functional structures of the recA protein found by chimera analysis. J Mol Biol. 1992 Aug 5;226(3):651–660. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(92)90622-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogawa T., Yu X., Shinohara A., Egelman E. H. Similarity of the yeast RAD51 filament to the bacterial RecA filament. Science. 1993 Mar 26;259(5103):1896–1899. doi: 10.1126/science.8456314. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radding C. M. Helical RecA nucleoprotein filaments mediate homologous pairing and strand exchange. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1989 Jul 7;1008(2):131–145. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(80)90001-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radding C. M. Helical interactions in homologous pairing and strand exchange driven by RecA protein. J Biol Chem. 1991 Mar 25;266(9):5355–5358. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rao B. J., Chiu S. K., Radding C. M. Homologous recognition and triplex formation promoted by RecA protein between duplex oligonucleotides and single-stranded DNA. J Mol Biol. 1993 Jan 20;229(2):328–343. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1993.1038. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rao B. J., Radding C. M. Homologous recognition promoted by RecA protein via non-Watson-Crick bonds between identical DNA strands. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jul 15;90(14):6646–6650. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.14.6646. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roca A. I., Cox M. M. The RecA protein: structure and function. Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol. 1990;25(6):415–456. doi: 10.3109/10409239009090617. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shibata T., Cunningham R. P., Radding C. M. Homologous pairing in genetic recombination. Purification and characterization of Escherichia coli recA protein. J Biol Chem. 1981 Jul 25;256(14):7557–7564. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shibata T., DasGupta C., Cunningham R. P., Radding C. M. Purified Escherichia coli recA protein catalyzes homologous pairing of superhelical DNA and single-stranded fragments. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Apr;76(4):1638–1642. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.4.1638. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shibata T., Osber L., Radding C. M. Purification of recA protein from Escherichia coli. Methods Enzymol. 1983;100:197–209. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)00056-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shinohara A., Ogawa H., Matsuda Y., Ushio N., Ikeo K., Ogawa T. Cloning of human, mouse and fission yeast recombination genes homologous to RAD51 and recA. Nat Genet. 1993 Jul;4(3):239–243. doi: 10.1038/ng0793-239. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Story R. M., Bishop D. K., Kleckner N., Steitz T. A. Structural relationship of bacterial RecA proteins to recombination proteins from bacteriophage T4 and yeast. Science. 1993 Mar 26;259(5103):1892–1896. doi: 10.1126/science.8456313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsang S. S., Muniyappa K., Azhderian E., Gonda D. K., Radding C. M., Flory J., Chase J. W. Intermediates in homologous pairing promoted by recA protein. Isolation and characterization of active presynaptic complexes. J Mol Biol. 1985 Sep 20;185(2):295–309. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90405-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- West S. C. Enzymes and molecular mechanisms of genetic recombination. Annu Rev Biochem. 1992;61:603–640. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.61.070192.003131. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]