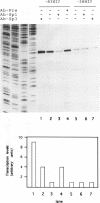
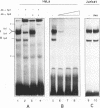
Abstract
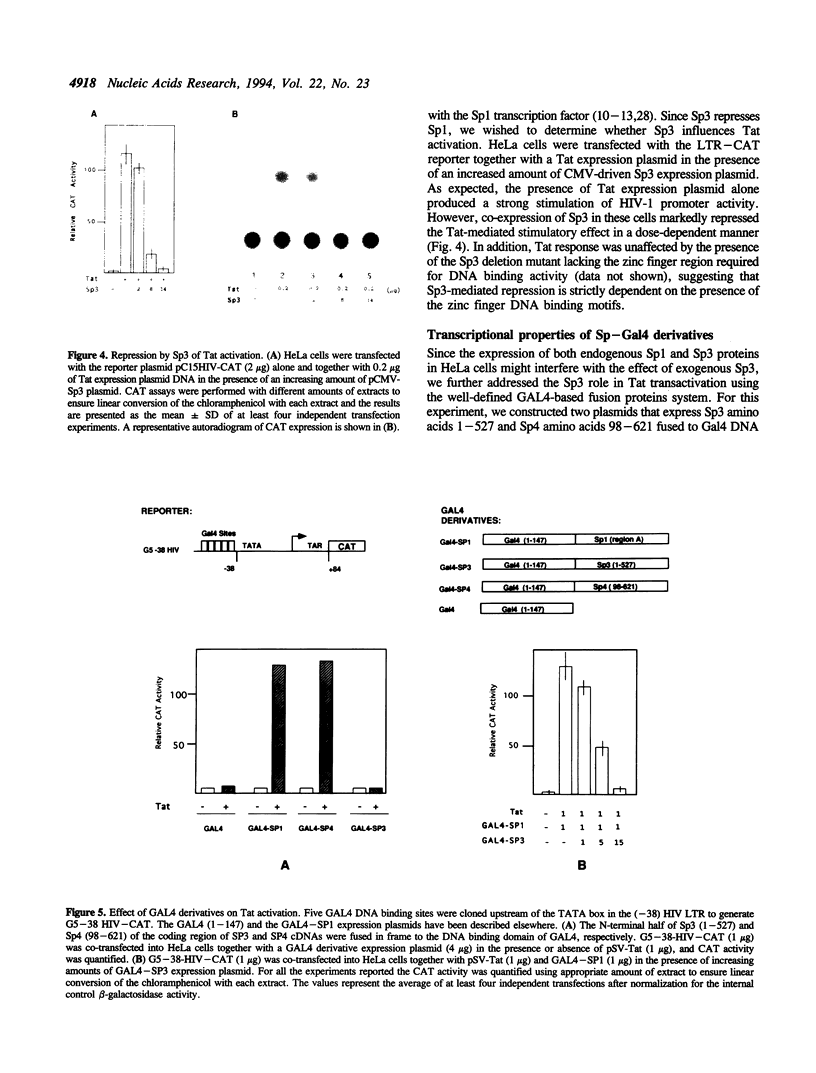
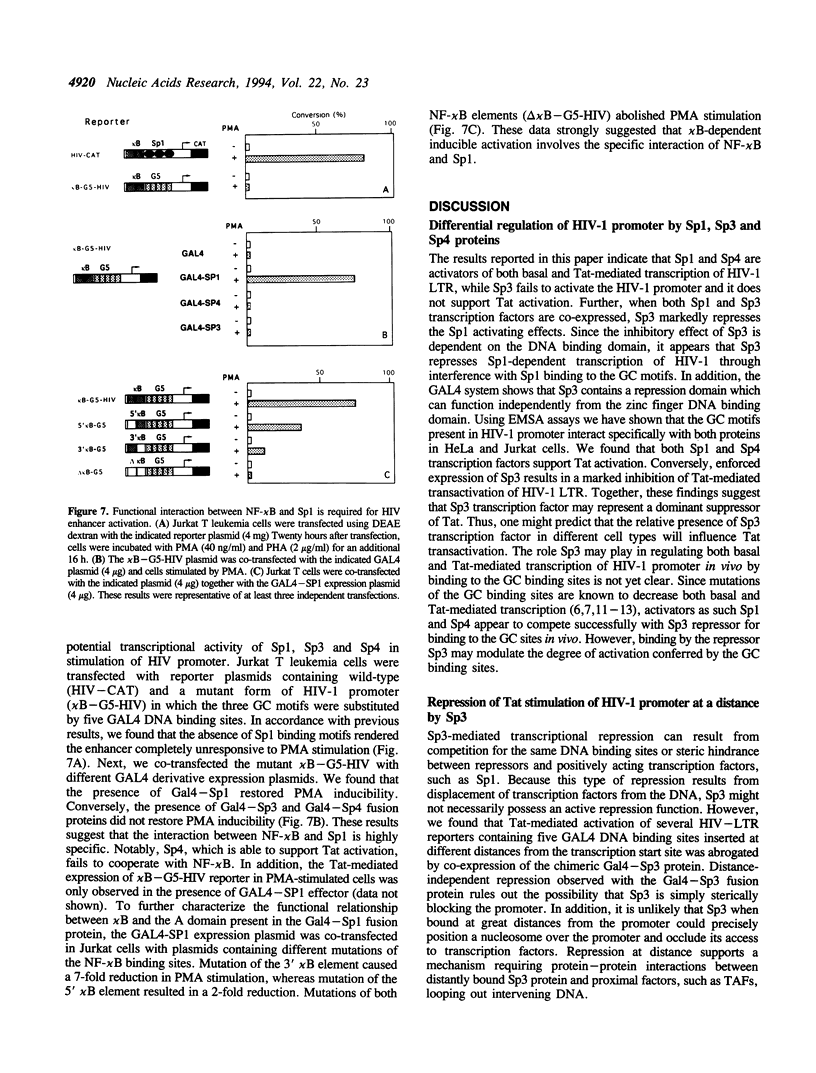
Recently, a family of transcription factors structurally related to Sp1 has been described; thus, more than one activator may bind to the GC boxes present in a number of viral and cellular promoters. We have compared the transactivation potentials of Sp1, Sp3 and Sp4 proteins on the human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) promoter. The long terminal repeat (LTR) of HIV-1 contains three binding sites for the transcription factor Sp1 (GC boxes) which are involved in both basal and Tat-mediated transcriptional activation. Moreover, a cooperative interaction between NF-kappa B and Sp1 is required for HIV enhancer activation. We now demonstrate that Sp4 is an activator, while the Sp3 protein represses basal expression of HIV promoter. Remarkably, we found that over-expression of the transcription factor Sp3 was able to suppress Tat-mediated transactivation. These inhibitory effects of Sp3 correlate with its DNA binding activity, suggesting that Sp3 inhibition involves competition with Sp1 for occupancy of the GC boxes. Next, we have analyzed the role of different Sp1-related proteins in the stimulation of HIV-1 promoter in response to mitogens. We found that the binding of NF-kappa B is not by itself sufficient to induce HIV gene expression. Instead, an interaction between NF-kappa B and the trans-acting domain (A domain) of Sp1 bound to an adjacent site must occur. We found that the cooperative interaction between NF-kappa B and Sp1 is highly specific, since neither Sp3 nor Sp4 is capable of cooperating with NF-kappa B.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beg A. A., Baldwin A. S., Jr The I kappa B proteins: multifunctional regulators of Rel/NF-kappa B transcription factors. Genes Dev. 1993 Nov;7(11):2064–2070. doi: 10.1101/gad.7.11.2064. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berkhout B., Jeang K. T. Functional roles for the TATA promoter and enhancers in basal and Tat-induced expression of the human immunodeficiency virus type 1 long terminal repeat. J Virol. 1992 Jan;66(1):139–149. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.1.139-149.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang L. J., McNulty E., Martin M. Human immunodeficiency viruses containing heterologous enhancer/promoters are replication competent and exhibit different lymphocyte tropisms. J Virol. 1993 Feb;67(2):743–752. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.2.743-752.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Courey A. J., Holtzman D. A., Jackson S. P., Tjian R. Synergistic activation by the glutamine-rich domains of human transcription factor Sp1. Cell. 1989 Dec 1;59(5):827–836. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90606-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Courey A. J., Tjian R. Analysis of Sp1 in vivo reveals multiple transcriptional domains, including a novel glutamine-rich activation motif. Cell. 1988 Dec 2;55(5):887–898. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90144-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cullen B. R. Does HIV-1 Tat induce a change in viral initiation rights? Cell. 1993 May 7;73(3):417–420. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90126-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frankel A. D. Activation of HIV transcription by Tat. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 1992 Apr;2(2):293–298. doi: 10.1016/s0959-437x(05)80287-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greene W. C. Regulation of HIV-1 gene expression. Annu Rev Immunol. 1990;8:453–475. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.08.040190.002321. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grilli M., Chiu J. J., Lenardo M. J. NF-kappa B and Rel: participants in a multiform transcriptional regulatory system. Int Rev Cytol. 1993;143:1–62. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7696(08)61873-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagen G., Müller S., Beato M., Suske G. Cloning by recognition site screening of two novel GT box binding proteins: a family of Sp1 related genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Nov 11;20(21):5519–5525. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.21.5519. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagen G., Müller S., Beato M., Suske G. Sp1-mediated transcriptional activation is repressed by Sp3. EMBO J. 1994 Aug 15;13(16):3843–3851. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06695.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harrich D., Garcia J., Wu F., Mitsuyasu R., Gonazalez J., Gaynor R. Role of SP1-binding domains in in vivo transcriptional regulation of the human immunodeficiency virus type 1 long terminal repeat. J Virol. 1989 Jun;63(6):2585–2591. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.6.2585-2591.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang L. M., Jeang K. T. Increased spacing between Sp1 and TATAA renders human immunodeficiency virus type 1 replication defective: implication for Tat function. J Virol. 1993 Dec;67(12):6937–6944. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.12.6937-6944.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones K. A., Kadonaga J. T., Luciw P. A., Tjian R. Activation of the AIDS retrovirus promoter by the cellular transcription factor, Sp1. Science. 1986 May 9;232(4751):755–759. doi: 10.1126/science.3008338. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kadonaga J. T., Carner K. R., Masiarz F. R., Tjian R. Isolation of cDNA encoding transcription factor Sp1 and functional analysis of the DNA binding domain. Cell. 1987 Dec 24;51(6):1079–1090. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90594-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamine J., Subramanian T., Chinnadurai G. Sp1-dependent activation of a synthetic promoter by human immunodeficiency virus type 1 Tat protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Oct 1;88(19):8510–8514. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.19.8510. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim J. Y., Gonzalez-Scarano F., Zeichner S. L., Alwine J. C. Replication of type 1 human immunodeficiency viruses containing linker substitution mutations in the -201 to -130 region of the long terminal repeat. J Virol. 1993 Mar;67(3):1658–1662. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.3.1658-1662.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kingsley C., Winoto A. Cloning of GT box-binding proteins: a novel Sp1 multigene family regulating T-cell receptor gene expression. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Oct;12(10):4251–4261. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.10.4251. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leung K., Nabel G. J. HTLV-1 transactivator induces interleukin-2 receptor expression through an NF-kappa B-like factor. Nature. 1988 Jun 23;333(6175):776–778. doi: 10.1038/333776a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Licht J. D., Ro M., English M. A., Grossel M., Hansen U. Selective repression of transcriptional activators at a distance by the Drosophila Krüppel protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Dec 1;90(23):11361–11365. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.23.11361. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Majello B., Arcone R., Toniatti C., Ciliberto G. Constitutive and IL-6-induced nuclear factors that interact with the human C-reactive protein promoter. EMBO J. 1990 Feb;9(2):457–465. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08131.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minchiotti G., Di Nocera P. P. Convergent transcription initiates from oppositely oriented promoters within the 5' end regions of Drosophila melanogaster F elements. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Oct;11(10):5171–5180. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.10.5171. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nabel G., Baltimore D. An inducible transcription factor activates expression of human immunodeficiency virus in T cells. Nature. 1987 Apr 16;326(6114):711–713. doi: 10.1038/326711a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pascal E., Tjian R. Different activation domains of Sp1 govern formation of multimers and mediate transcriptional synergism. Genes Dev. 1991 Sep;5(9):1646–1656. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.9.1646. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perkins N. D., Edwards N. L., Duckett C. S., Agranoff A. B., Schmid R. M., Nabel G. J. A cooperative interaction between NF-kappa B and Sp1 is required for HIV-1 enhancer activation. EMBO J. 1993 Sep;12(9):3551–3558. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb06029.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross E. K., Buckler-White A. J., Rabson A. B., Englund G., Martin M. A. Contribution of NF-kappa B and Sp1 binding motifs to the replicative capacity of human immunodeficiency virus type 1: distinct patterns of viral growth are determined by T-cell types. J Virol. 1991 Aug;65(8):4350–4358. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.8.4350-4358.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sadowski I., Ptashne M. A vector for expressing GAL4(1-147) fusions in mammalian cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Sep 25;17(18):7539–7539. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.18.7539. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southgate C. D., Green M. R. The HIV-1 Tat protein activates transcription from an upstream DNA-binding site: implications for Tat function. Genes Dev. 1991 Dec;5(12B):2496–2507. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.12b.2496. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strazzullo M., Majello B., Lania L., La Mantia G. Mutational analysis of the human endogenous ERV9 proviruses promoter region. Virology. 1994 May 1;200(2):686–695. doi: 10.1006/viro.1994.1232. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ursini M. V., Lettieri T., Braddock M., Martini G. Enhanced activity of human G6PD promoter transfected in HeLa cells producing high levels of HIV-1 Tat. Virology. 1993 Sep;196(1):338–343. doi: 10.1006/viro.1993.1485. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zeichner S. L., Kim J. Y., Alwine J. C. Linker-scanning mutational analysis of the transcriptional activity of the human immunodeficiency virus type 1 long terminal repeat. J Virol. 1991 May;65(5):2436–2444. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.5.2436-2444.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]