Abstract
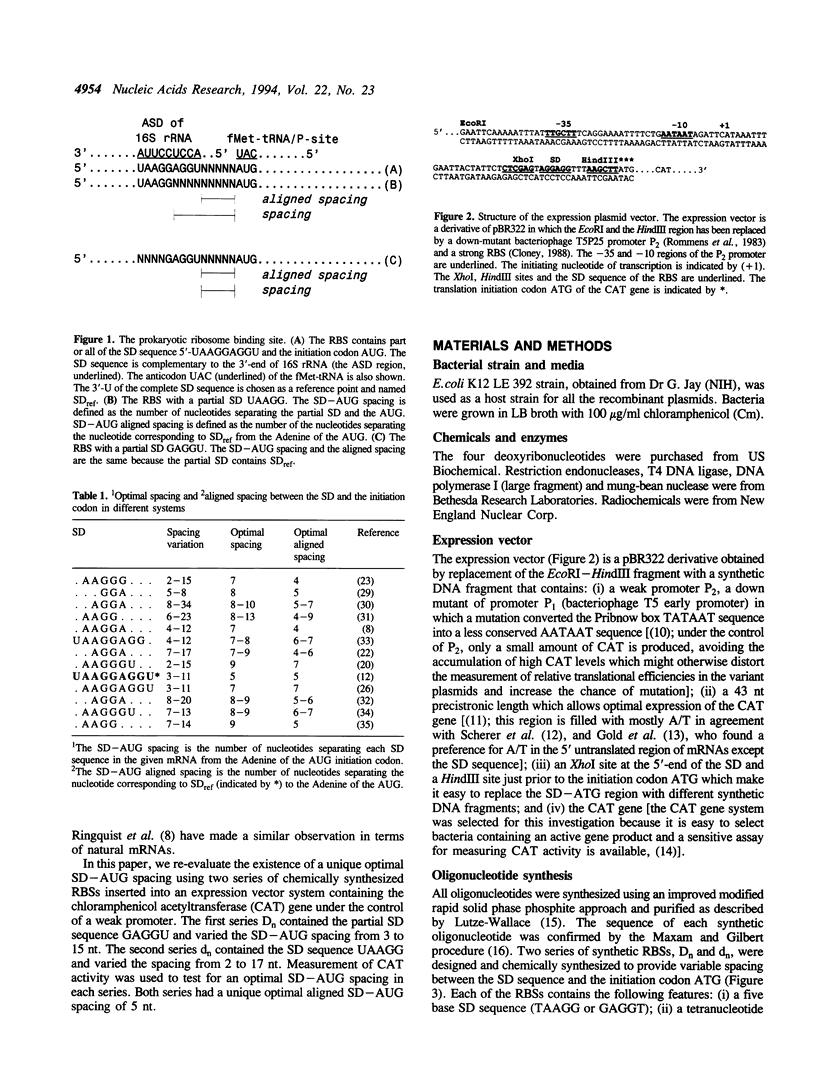
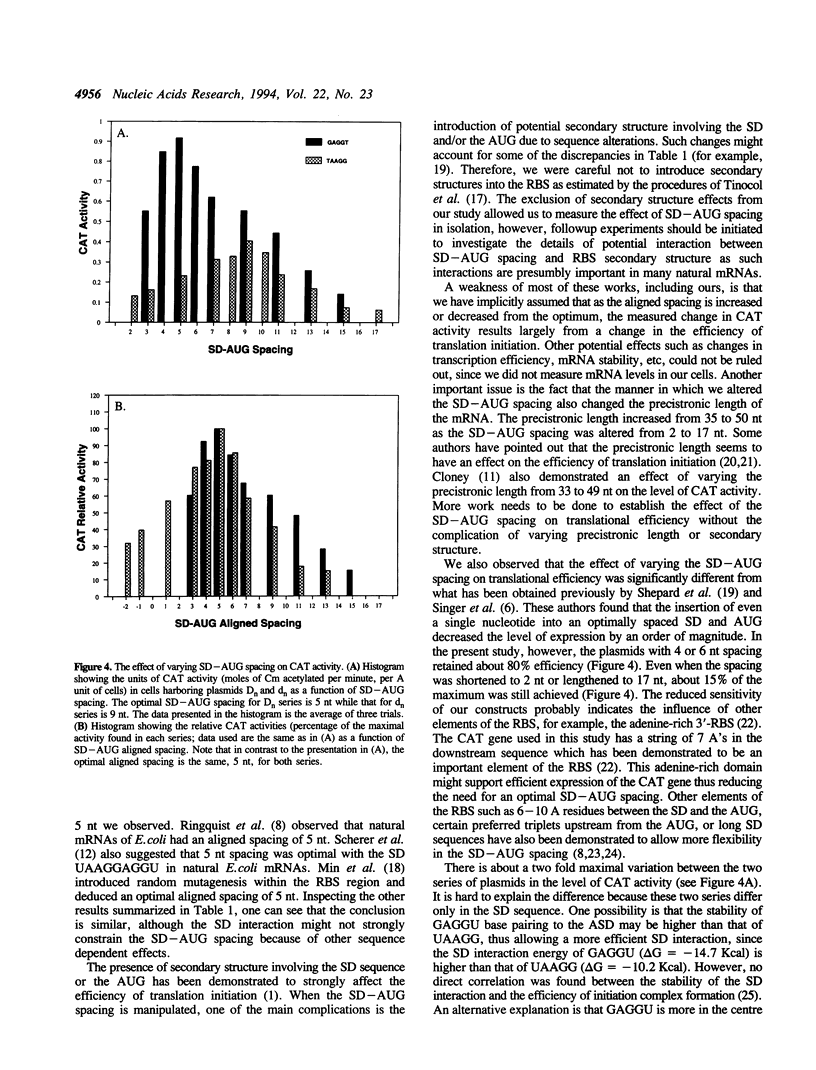
The prokaryotic mRNA ribosome binding site (RBS) usually contains part or all of a polypurine domain UAAGGAGGU known as the Shine-Dalgarno (SD) sequence found just 5' to the translation initiation codon. It is now clear that the SD sequence is important for identification of the translation initiation site on the mRNA by the ribosome, and that as a result, the spacing between the SD and the initiation codon strongly affects translational efficiency (1). It is not as clear, however, whether there is a unique optimal spacing. Complications involving the definition of the spacing as well as secondary structures have obscured matters. We thus undertook a systematic study by inserting two series of synthetic RBSs of varying spacing and SD sequence into a plasmid vector containing the chloramphenicol acetyltransferase gene. Care was taken not to introduce any secondary structure. Measurements of protein expression demonstrated an optimal aligned spacing of 5 nt for both series. Since aligned spacing corresponds naturally to the spacing between the 3'-end of the 16S rRNA and the P-site, we conclude that there is a unique optimal aligned SD-AUG spacing in the absence of other complicating issues.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Chapon C. Expression of malT, the regulator gene of the maltose region in Escherichia coli, is limited both at transcription and translation. EMBO J. 1982;1(3):369–374. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01176.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen H., Pomeroy-Cloney L., Bjerknes M., Tam J., Jay E. The influence of adenine-rich motifs in the 3' portion of the ribosome binding site on human IFN-gamma gene expression in Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1994 Jul 1;240(1):20–27. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1994.1414. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curry K. A., Tomich C. S. Effect of ribosome binding site on gene expression in Escherichia coli. DNA. 1988 Apr;7(3):173–179. doi: 10.1089/dna.1988.7.173. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dalbøge H., Carlsen S., Jensen E. B., Christensen T., Dahl H. H. Expression of recombinant growth hormone in Escherichia coli: effect of the region between the Shine-Dalgarno sequence and the ATG initiation codon. DNA. 1988 Jul-Aug;7(6):399–405. doi: 10.1089/dna.1.1988.7.399. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunn J. J., Studier F. W. Nucleotide sequence from the genetic left end of bacteriophage T7 DNA to the beginning of gene 4. J Mol Biol. 1981 Jun 5;148(4):303–330. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90178-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gheysen D., Iserentant D., Derom C., Fiers W. Systematic alteration of the nucleotide sequence preceding the translation initiation codon and the effects on bacterial expression of the cloned SV40 small-t antigen gene. Gene. 1982 Jan;17(1):55–63. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90100-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillam S., Astell C. R., Smith M. Site-specific mutagenesis using oligodeoxyribonucleotides: isolation of a phenotypically silent phi X174 mutant, with a specific nucleotide deletion, at very high efficiency. Gene. 1980 Dec;12(1-2):129–137. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(80)90023-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gold L. Posttranscriptional regulatory mechanisms in Escherichia coli. Annu Rev Biochem. 1988;57:199–233. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.57.070188.001215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gold L., Pribnow D., Schneider T., Shinedling S., Singer B. S., Stormo G. Translational initiation in prokaryotes. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1981;35:365–403. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.35.100181.002053. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gren E. J. Recognition of messenger RNA during translational initiation in Escherichia coli. Biochimie. 1984 Jan;66(1):1–29. doi: 10.1016/0300-9084(84)90188-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guarente L., Lauer G., Roberts T. M., Ptashne M. Improved methods for maximizing expression of a cloned gene: a bacterium that synthesizes rabbit beta-globin. Cell. 1980 Jun;20(2):543–553. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90640-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Itoh S., Mizukami T., Matsumoto T., Nishi T., Saito A., Oka T., Furuya A., Takaoka C., Taniguchi T. Efficient expression in Escherichia coli of a mature and a modified human interferon-beta 1. DNA. 1984;3(2):157–165. doi: 10.1089/dna.1984.3.157. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. Comparison of initiation of protein synthesis in procaryotes, eucaryotes, and organelles. Microbiol Rev. 1983 Mar;47(1):1–45. doi: 10.1128/mr.47.1.1-45.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. A new method for sequencing DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Feb;74(2):560–564. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.2.560. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Min K. T., Kim M. H., Lee D. S. Search for the optimal sequence of the ribosome binding site by random oligonucleotide-directed mutagenesis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Jun 10;16(11):5075–5088. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.11.5075. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ringquist S., Shinedling S., Barrick D., Green L., Binkley J., Stormo G. D., Gold L. Translation initiation in Escherichia coli: sequences within the ribosome-binding site. Mol Microbiol. 1992 May;6(9):1219–1229. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1992.tb01561.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts T. M., Bikel I., Yocum R. R., Livingston D. M., Ptashne M. Synthesis of simian virus 40 t antigen in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Nov;76(11):5596–5600. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.11.5596. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts T. M., Kacich R., Ptashne M. A general method for maximizing the expression of a cloned gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Feb;76(2):760–764. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.2.760. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rommens J., MacKnight D., Pomeroy-Cloney L., Jay E. Gene expression: chemical synthesis and molecular cloning of a bacteriophage T5 (T5P25) early promoter. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Sep 10;11(17):5921–5940. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.17.5921. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scherer G. F., Walkinshaw M. D., Arnott S., Morré D. J. The ribosome binding sites recognized by E. coli ribosomes have regions with signal character in both the leader and protein coding segments. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Sep 11;8(17):3895–3907. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.17.3895. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw W. V. Chloramphenicol acetyltransferase from chloramphenicol-resistant bacteria. Methods Enzymol. 1975;43:737–755. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(75)43141-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shine J., Dalgarno L. The 3'-terminal sequence of Escherichia coli 16S ribosomal RNA: complementarity to nonsense triplets and ribosome binding sites. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Apr;71(4):1342–1346. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.4.1342. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singer B. S., Gold L., Shinedling S. T., Colkitt M., Hunter L. R., Pribnow D., Nelson M. A. Analysis in vivo of translational mutants of the rIIB cistron of bacteriophage T4. J Mol Biol. 1981 Jul 5;149(3):405–432. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90479-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanssens P., Remaut E., Fiers W. Alterations upstream from the Shine-Dalgarno region and their effect on bacterial gene expression. Gene. 1985;36(3):211–223. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90176-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steitz J. A. Polypeptide chain initiation: nucleotide sequences of the three ribosomal binding sites in bacteriophage R17 RNA. Nature. 1969 Dec 6;224(5223):957–964. doi: 10.1038/224957a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stormo G. D., Schneider T. D., Gold L. M. Characterization of translational initiation sites in E. coli. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 May 11;10(9):2971–2996. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.9.2971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thummel C. S., Burgess T. L., Tjian R. Properties of simian virus 40 small t antigen overproduced in bacteria. J Virol. 1981 Feb;37(2):683–697. doi: 10.1128/jvi.37.2.683-697.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tinoco I., Jr, Borer P. N., Dengler B., Levin M. D., Uhlenbeck O. C., Crothers D. M., Bralla J. Improved estimation of secondary structure in ribonucleic acids. Nat New Biol. 1973 Nov 14;246(150):40–41. doi: 10.1038/newbio246040a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vellanoweth R. L., Rabinowitz J. C. The influence of ribosome-binding-site elements on translational efficiency in Bacillus subtilis and Escherichia coli in vivo. Mol Microbiol. 1992 May;6(9):1105–1114. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1992.tb01548.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitehorn E. A., Livak K. J., Petteway S. R., Jr The effects of hybrid ribosome-binding-site variants on the expression of human interferon-beta in Escherichia coli. Gene. 1985;36(3):375–379. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90194-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood C. R., Boss M. A., Patel T. P., Emtage J. S. The influence of messenger RNA secondary structure on expression of an immunoglobulin heavy chain in Escherichia coli. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 May 11;12(9):3937–3950. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.9.3937. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


