Abstract
An activated transcription system was constructed using substantially purified liver factors, Hela TFIID and GAL4-VP16. The system was used to study the relationship between RNA polymerase II large subunit phosphorylation and other ATP-dependent processes occurring during activated transcription. When C-terminal domain (CTD) kinase activity was inhibited, activator dependent open promoter complex formation proceeded normally. These open complexes could function to produce RNA in the absence of CTD phosphorylation, although the level of RNA produced was changed somewhat. The results demonstrate that RNA polymerase II CTD phosphorylation is not generally required for the formation of activator-dependent, functional open promoter complexes. Taken together with prior results the experiments suggest that a requirement for CTD phosphorylation may be situation-dependent and thus serve a regulatory function.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allison L. A., Ingles C. J. Mutations in RNA polymerase II enhance or suppress mutations in GAL4. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Apr;86(8):2794–2798. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.8.2794. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arias J. A., Peterson S. R., Dynan W. S. Promoter-dependent phosphorylation of RNA polymerase II by a template-bound kinase. Association with transcriptional initiation. J Biol Chem. 1991 May 5;266(13):8055–8061. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aso T., Serizawa H., Conaway R. C., Conaway J. W. A TATA sequence-dependent transcriptional repressor activity associated with mammalian transcription factor IIA. EMBO J. 1994 Jan 15;13(2):435–445. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06278.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buermeyer A. B., Thompson N. E., Strasheim L. A., Burgess R. R., Farnham P. J. The HIP1 initiator element plays a role in determining the in vitro requirement of the dihydrofolate reductase gene promoter for the C-terminal domain of RNA polymerase II. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 May;12(5):2250–2259. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.5.2250. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bunick D., Zandomeni R., Ackerman S., Weinmann R. Mechanism of RNA polymerase II--specific initiation of transcription in vitro: ATP requirement and uncapped runoff transcripts. Cell. 1982 Jul;29(3):877–886. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90449-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buratowski S., Sharp P. A. Transcription initiation complexes and upstream activation with RNA polymerase II lacking the C-terminal domain of the largest subunit. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Oct;10(10):5562–5564. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.10.5562. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cadena D. L., Dahmus M. E. Messenger RNA synthesis in mammalian cells is catalyzed by the phosphorylated form of RNA polymerase II. J Biol Chem. 1987 Sep 15;262(26):12468–12474. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carey M., Leatherwood J., Ptashne M. A potent GAL4 derivative activates transcription at a distance in vitro. Science. 1990 Feb 9;247(4943):710–712. doi: 10.1126/science.2405489. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carey M., Lin Y. S., Green M. R., Ptashne M. A mechanism for synergistic activation of a mammalian gene by GAL4 derivatives. Nature. 1990 May 24;345(6273):361–364. doi: 10.1038/345361a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chesnut J. D., Stephens J. H., Dahmus M. E. The interaction of RNA polymerase II with the adenovirus-2 major late promoter is precluded by phosphorylation of the C-terminal domain of subunit IIa. J Biol Chem. 1992 May 25;267(15):10500–10506. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cisek L. J., Corden J. L. Phosphorylation of RNA polymerase by the murine homologue of the cell-cycle control protein cdc2. Nature. 1989 Jun 29;339(6227):679–684. doi: 10.1038/339679a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conaway J. W., Conaway R. C. A multisubunit transcription factor essential for accurate initiation by RNA polymerase II. J Biol Chem. 1989 Feb 5;264(4):2357–2362. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conaway J. W., Conaway R. C. An RNA polymerase II transcription factor shares functional properties with Escherichia coli sigma 70. Science. 1990 Jun 22;248(4962):1550–1553. doi: 10.1126/science.2193400. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conaway R. C., Conaway J. W. ATP activates transcription initiation from promoters by RNA polymerase II in a reversible step prior to RNA synthesis. J Biol Chem. 1988 Feb 25;263(6):2962–2968. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conaway R. C., Conaway J. W. An RNA polymerase II transcription factor has an associated DNA-dependent ATPase (dATPase) activity strongly stimulated by the TATA region of promoters. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Oct;86(19):7356–7360. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.19.7356. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corden J. L. Tails of RNA polymerase II. Trends Biochem Sci. 1990 Oct;15(10):383–387. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(90)90236-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dignam J. D., Martin P. L., Shastry B. S., Roeder R. G. Eukaryotic gene transcription with purified components. Methods Enzymol. 1983;101:582–598. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)01039-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dvir A., Stein L. Y., Calore B. L., Dynan W. S. Purification and characterization of a template-associated protein kinase that phosphorylates RNA polymerase II. J Biol Chem. 1993 May 15;268(14):10440–10447. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feaver W. J., Gileadi O., Li Y., Kornberg R. D. CTD kinase associated with yeast RNA polymerase II initiation factor b. Cell. 1991 Dec 20;67(6):1223–1230. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90298-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guzder S. N., Sung P., Bailly V., Prakash L., Prakash S. RAD25 is a DNA helicase required for DNA repair and RNA polymerase II transcription. Nature. 1994 Jun 16;369(6481):578–581. doi: 10.1038/369578a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hidaka H., Inagaki M., Kawamoto S., Sasaki Y. Isoquinolinesulfonamides, novel and potent inhibitors of cyclic nucleotide dependent protein kinase and protein kinase C. Biochemistry. 1984 Oct 9;23(21):5036–5041. doi: 10.1021/bi00316a032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jiang Y., Gralla J. D. Uncoupling of initiation and reinitiation rates during HeLa RNA polymerase II transcription in vitro. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Aug;13(8):4572–4577. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.8.4572. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jiang Y., Smale S. T., Gralla J. D. A common ATP requirement for open complex formation and transcription at promoters containing initiator or TATA elements. J Biol Chem. 1993 Mar 25;268(9):6535–6540. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jiang Y., Triezenberg S. J., Gralla J. D. Defective transcriptional activation by diverse VP16 mutants associated with a common inability to form open promoter complexes. J Biol Chem. 1994 Feb 25;269(8):5505–5508. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim W. Y., Dahmus M. E. The major late promoter of adenovirus-2 is accurately transcribed by RNA polymerases IIO, IIA, and IIB. J Biol Chem. 1989 Feb 25;264(6):3169–3176. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kolodziej P. A., Woychik N., Liao S. M., Young R. A. RNA polymerase II subunit composition, stoichiometry, and phosphorylation. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 May;10(5):1915–1920. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.5.1915. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laybourn P. J., Dahmus M. E. Phosphorylation of RNA polymerase IIA occurs subsequent to interaction with the promoter and before the initiation of transcription. J Biol Chem. 1990 Aug 5;265(22):13165–13173. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laybourn P. J., Dahmus M. E. Transcription-dependent structural changes in the C-terminal domain of mammalian RNA polymerase subunit IIa/o. J Biol Chem. 1989 Apr 25;264(12):6693–6698. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee J. M., Greenleaf A. L. A protein kinase that phosphorylates the C-terminal repeat domain of the largest subunit of RNA polymerase II. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 May;86(10):3624–3628. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.10.3624. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li Y., Kornberg R. D. Interplay of positive and negative effectors in function of the C-terminal repeat domain of RNA polymerase II. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Mar 15;91(6):2362–2366. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.6.2362. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liao S. M., Taylor I. C., Kingston R. E., Young R. A. RNA polymerase II carboxy-terminal domain contributes to the response to multiple acidic activators in vitro. Genes Dev. 1991 Dec;5(12B):2431–2440. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.12b.2431. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lu H., Flores O., Weinmann R., Reinberg D. The nonphosphorylated form of RNA polymerase II preferentially associates with the preinitiation complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Nov 15;88(22):10004–10008. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.22.10004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lu H., Zawel L., Fisher L., Egly J. M., Reinberg D. Human general transcription factor IIH phosphorylates the C-terminal domain of RNA polymerase II. Nature. 1992 Aug 20;358(6388):641–645. doi: 10.1038/358641a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Payne J. M., Dahmus M. E. Partial purification and characterization of two distinct protein kinases that differentially phosphorylate the carboxyl-terminal domain of RNA polymerase subunit IIa. J Biol Chem. 1993 Jan 5;268(1):80–87. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Payne J. M., Laybourn P. J., Dahmus M. E. The transition of RNA polymerase II from initiation to elongation is associated with phosphorylation of the carboxyl-terminal domain of subunit IIa. J Biol Chem. 1989 Nov 25;264(33):19621–19629. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson C. L., Kruger W., Herskowitz I. A functional interaction between the C-terminal domain of RNA polymerase II and the negative regulator SIN1. Cell. 1991 Mar 22;64(6):1135–1143. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90268-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson S. R., Dvir A., Anderson C. W., Dynan W. S. DNA binding provides a signal for phosphorylation of the RNA polymerase II heptapeptide repeats. Genes Dev. 1992 Mar;6(3):426–438. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.3.426. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawadogo M., Roeder R. G. Energy requirement for specific transcription initiation by the human RNA polymerase II system. J Biol Chem. 1984 Apr 25;259(8):5321–5326. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scafe C., Chao D., Lopes J., Hirsch J. P., Henry S., Young R. A. RNA polymerase II C-terminal repeat influences response to transcriptional enhancer signals. Nature. 1990 Oct 4;347(6292):491–494. doi: 10.1038/347491a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaeffer L., Roy R., Humbert S., Moncollin V., Vermeulen W., Hoeijmakers J. H., Chambon P., Egly J. M. DNA repair helicase: a component of BTF2 (TFIIH) basic transcription factor. Science. 1993 Apr 2;260(5104):58–63. doi: 10.1126/science.8465201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Serizawa H., Conaway J. W., Conaway R. C. Phosphorylation of C-terminal domain of RNA polymerase II is not required in basal transcription. Nature. 1993 May 27;363(6427):371–374. doi: 10.1038/363371a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Serizawa H., Conaway R. C., Conaway J. W. A carboxyl-terminal-domain kinase associated with RNA polymerase II transcription factor delta from rat liver. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Aug 15;89(16):7476–7480. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.16.7476. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Serizawa H., Conaway R. C., Conaway J. W. Multifunctional RNA polymerase II initiation factor delta from rat liver. Relationship between carboxyl-terminal domain kinase, ATPase, and DNA helicase activities. J Biol Chem. 1993 Aug 15;268(23):17300–17308. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sigler P. B. Transcriptional activation. Acid blobs and negative noodles. Nature. 1988 May 19;333(6170):210–212. doi: 10.1038/333210a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stelzer G., Goppelt A., Lottspeich F., Meisterernst M. Repression of basal transcription by HMG2 is counteracted by TFIIH-associated factors in an ATP-dependent process. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 Jul;14(7):4712–4721. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.7.4712. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson C. M., Koleske A. J., Chao D. M., Young R. A. A multisubunit complex associated with the RNA polymerase II CTD and TATA-binding protein in yeast. Cell. 1993 Jul 2;73(7):1361–1375. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90362-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Usheva A., Maldonado E., Goldring A., Lu H., Houbavi C., Reinberg D., Aloni Y. Specific interaction between the nonphosphorylated form of RNA polymerase II and the TATA-binding protein. Cell. 1992 May 29;69(5):871–881. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90297-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
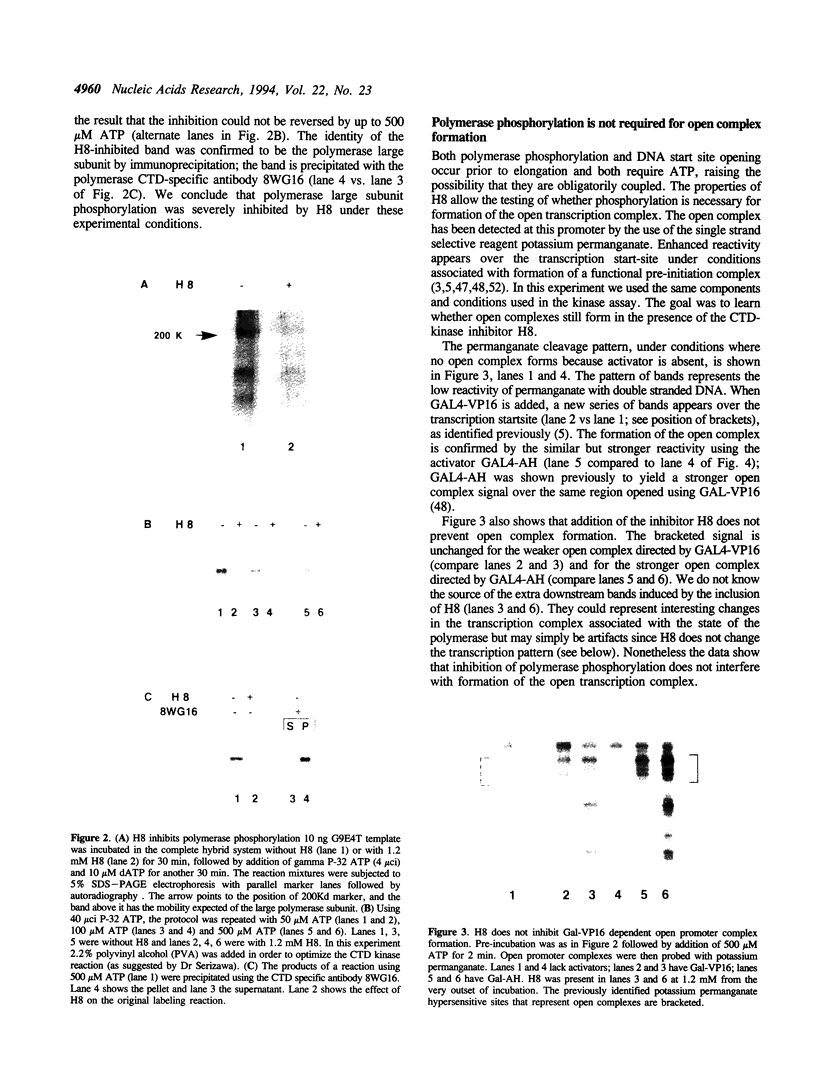
- Wang W., Carey M., Gralla J. D. Polymerase II promoter activation: closed complex formation and ATP-driven start site opening. Science. 1992 Jan 24;255(5043):450–453. doi: 10.1126/science.1310361. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang W., Gralla J. D., Carey M. The acidic activator GAL4-AH can stimulate polymerase II transcription by promoting assembly of a closed complex requiring TFIID and TFIIA. Genes Dev. 1992 Sep;6(9):1716–1727. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.9.1716. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young R. A. RNA polymerase II. Annu Rev Biochem. 1991;60:689–715. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.60.070191.003353. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zehring W. A., Greenleaf A. L. The carboxyl-terminal repeat domain of RNA polymerase II is not required for transcription factor Sp1 to function in vitro. J Biol Chem. 1990 May 25;265(15):8351–8353. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang J., Corden J. L. Identification of phosphorylation sites in the repetitive carboxyl-terminal domain of the mouse RNA polymerase II largest subunit. J Biol Chem. 1991 Feb 5;266(4):2290–2296. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]