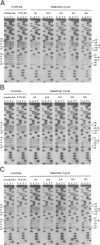
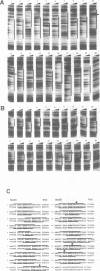
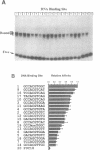
Abstract
EmBP-1 is a wheat DNA binding protein of the basic leucine zipper (bZIP) class of transcription factors implicated in the mechanisms of abscisic acid mediated gene activation. Understanding the role of EmBP-1 in regulating gene transcription requires elucidation of its DNA binding specificity. The binding of EmBP-1 was studied using gel shift selection of DNA from random sequence pools. DNA binding sites were identified by sequencing of a selected pool and by cloning and sequencing individual sites. The binding sites were compared by mobility shift assay and DNase I footprinting, which show that EmBP-1 binds to a family of sequences with varying degrees of affinity. The highest affinity site bound by EmBP-1 is the palindrome GCCACGTGGC. EmBP-1 also binds several other sequences with high affinity, however most of these are asymmetric. While nearly all sequences bound by EmBP-1 contain an ACGT core sequence, EmBP-1 can also bind at least two sites with altered cores. These results provide a basis for comparing the DNA binding specificity of EmBP-1 with those of other plant bZIP proteins and provide insight into the possible target sites which EmBP-1 might bind in vivo.
Full text
PDF




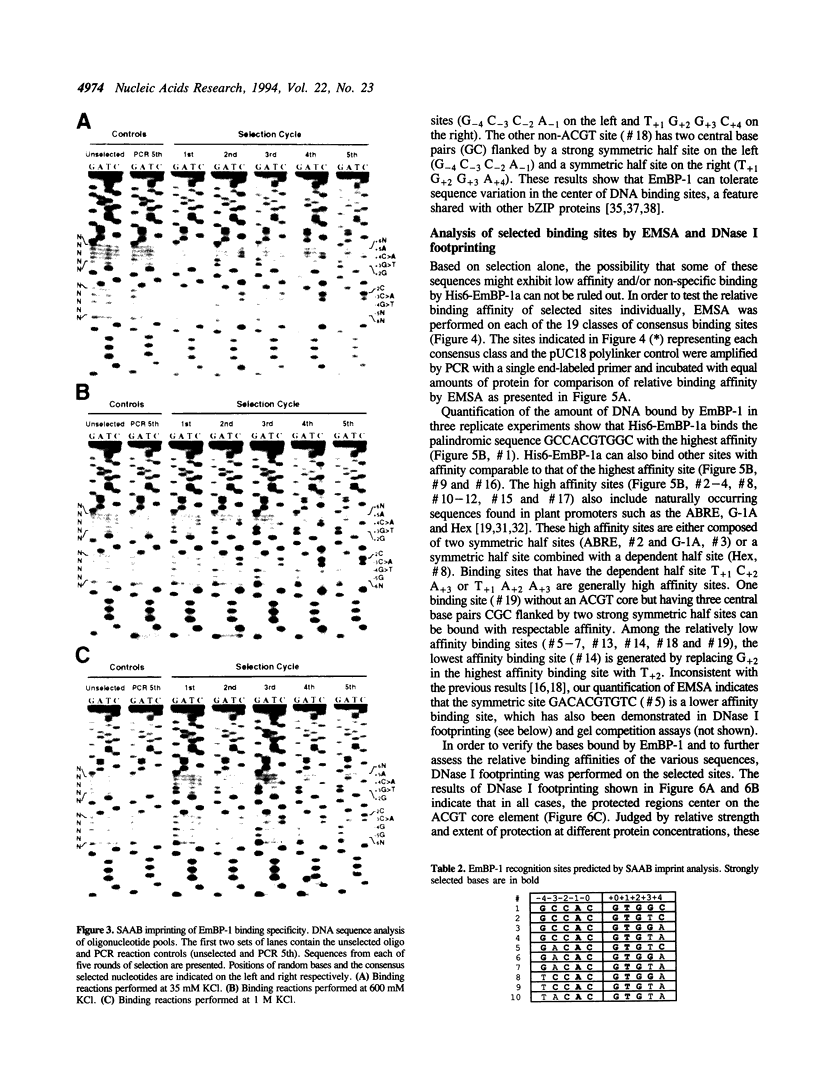

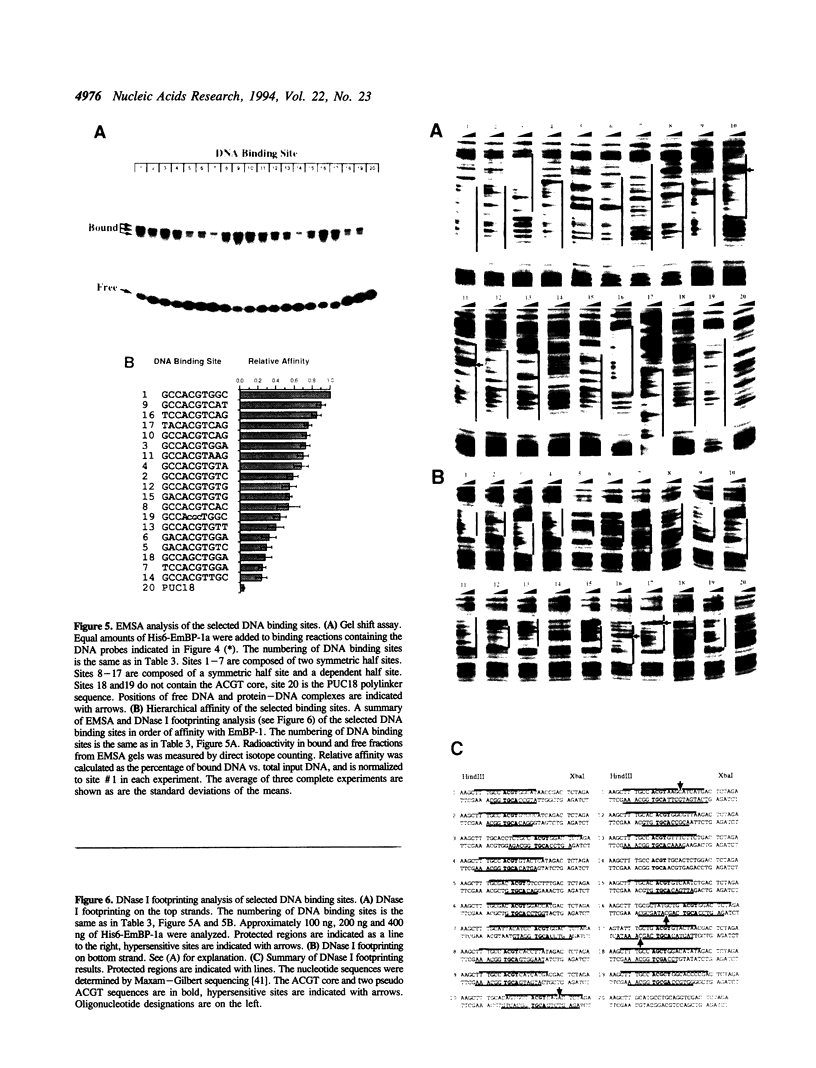


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Agre P., Johnson P. F., McKnight S. L. Cognate DNA binding specificity retained after leucine zipper exchange between GCN4 and C/EBP. Science. 1989 Nov 17;246(4932):922–926. doi: 10.1126/science.2530632. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Armstrong G. A., Weisshaar B., Hahlbrock K. Homodimeric and heterodimeric leucine zipper proteins and nuclear factors from parsley recognize diverse promoter elements with ACGT cores. Plant Cell. 1992 May;4(5):525–537. doi: 10.1105/tpc.4.5.525. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biggin M. D., Bickel S., Benson M., Pirrotta V., Tjian R. Zeste encodes a sequence-specific transcription factor that activates the Ultrabithorax promoter in vitro. Cell. 1988 Jun 3;53(5):713–722. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90089-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackwell T. K., Weintraub H. Differences and similarities in DNA-binding preferences of MyoD and E2A protein complexes revealed by binding site selection. Science. 1990 Nov 23;250(4984):1104–1110. doi: 10.1126/science.2174572. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blochlinger K., Bodmer R., Jack J., Jan L. Y., Jan Y. N. Primary structure and expression of a product from cut, a locus involved in specifying sensory organ identity in Drosophila. Nature. 1988 Jun 16;333(6174):629–635. doi: 10.1038/333629a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cuenoud B., Schepartz A. Altered specificity of DNA-binding proteins with transition metal dimerization domains. Science. 1993 Jan 22;259(5094):510–513. doi: 10.1126/science.8424173. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cuenoud B., Schepartz A. Design of a metallo-bZIP protein that discriminates between CRE and AP1 target sites: selection against AP1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Feb 15;90(4):1154–1159. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.4.1154. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foster R., Izawa T., Chua N. H. Plant bZIP proteins gather at ACGT elements. FASEB J. 1994 Feb;8(2):192–200. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.8.2.8119490. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fromm H., Katagiri F., Chua N. H. The tobacco transcription activator TGA1a binds to a sequence in the 5' upstream region of a gene encoding a TGA1a-related protein. Mol Gen Genet. 1991 Oct;229(2):181–188. doi: 10.1007/BF00272154. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gentz R., Rauscher F. J., 3rd, Abate C., Curran T. Parallel association of Fos and Jun leucine zippers juxtaposes DNA binding domains. Science. 1989 Mar 31;243(4899):1695–1699. doi: 10.1126/science.2494702. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gubler U., Hoffman B. J. A simple and very efficient method for generating cDNA libraries. Gene. 1983 Nov;25(2-3):263–269. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(83)90230-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guiltinan M. J., Marcotte W. R., Jr, Quatrano R. S. A plant leucine zipper protein that recognizes an abscisic acid response element. Science. 1990 Oct 12;250(4978):267–271. doi: 10.1126/science.2145628. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill D. E., Hope I. A., Macke J. P., Struhl K. Saturation mutagenesis of the yeast his3 regulatory site: requirements for transcriptional induction and for binding by GCN4 activator protein. Science. 1986 Oct 24;234(4775):451–457. doi: 10.1126/science.3532321. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Izawa T., Foster R., Chua N. H. Plant bZIP protein DNA binding specificity. J Mol Biol. 1993 Apr 20;230(4):1131–1144. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1993.1230. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson P. F. Identification of C/EBP basic region residues involved in DNA sequence recognition and half-site spacing preference. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Nov;13(11):6919–6930. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.11.6919. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson P. F., McKnight S. L. Eukaryotic transcriptional regulatory proteins. Annu Rev Biochem. 1989;58:799–839. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.58.070189.004055. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katagiri F., Lam E., Chua N. H. Two tobacco DNA-binding proteins with homology to the nuclear factor CREB. Nature. 1989 Aug 31;340(6236):727–730. doi: 10.1038/340727a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- König P., Richmond T. J. The X-ray structure of the GCN4-bZIP bound to ATF/CREB site DNA shows the complex depends on DNA flexibility. J Mol Biol. 1993 Sep 5;233(1):139–154. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1993.1490. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landschulz W. H., Johnson P. F., McKnight S. L. The DNA binding domain of the rat liver nuclear protein C/EBP is bipartite. Science. 1989 Mar 31;243(4899):1681–1688. doi: 10.1126/science.2494700. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landschulz W. H., Johnson P. F., McKnight S. L. The leucine zipper: a hypothetical structure common to a new class of DNA binding proteins. Science. 1988 Jun 24;240(4860):1759–1764. doi: 10.1126/science.3289117. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mavrothalassitis G., Beal G., Papas T. S. Defining target sequences of DNA-binding proteins by random selection and PCR: determination of the GCN4 binding sequence repertoire. DNA Cell Biol. 1990 Dec;9(10):783–788. doi: 10.1089/dna.1990.9.783. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meier I., Gruissem W. Novel conserved sequence motifs in plant G-box binding proteins and implications for interactive domains. Nucleic Acids Res. 1994 Feb 11;22(3):470–478. doi: 10.1093/nar/22.3.470. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neuberg M., Schuermann M., Hunter J. B., Müller R. Two functionally different regions in Fos are required for the sequence-specific DNA interaction of the Fos/Jun protein complex. Nature. 1989 Apr 13;338(6216):589–590. doi: 10.1038/338589a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oliphant A. R., Brandl C. J., Struhl K. Defining the sequence specificity of DNA-binding proteins by selecting binding sites from random-sequence oligonucleotides: analysis of yeast GCN4 protein. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Jul;9(7):2944–2949. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.7.2944. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pabo C. O., Sauer R. T. Transcription factors: structural families and principles of DNA recognition. Annu Rev Biochem. 1992;61:1053–1095. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.61.070192.005201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Park C., Campbell J. L., Goddard W. A., 3rd Protein stitchery: design of a protein for selective binding to a specific DNA sequence. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Oct 1;89(19):9094–9096. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.19.9094. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ransone L. J., Wamsley P., Morley K. L., Verma I. M. Domain swapping reveals the modular nature of Fos, Jun, and CREB proteins. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Sep;10(9):4565–4573. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.9.4565. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schindler U., Menkens A. E., Beckmann H., Ecker J. R., Cashmore A. R. Heterodimerization between light-regulated and ubiquitously expressed Arabidopsis GBF bZIP proteins. EMBO J. 1992 Apr;11(4):1261–1273. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05170.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sellers J. W., Vincent A. C., Struhl K. Mutations that define the optimal half-site for binding yeast GCN4 activator protein and identify an ATF/CREB-like repressor that recognizes similar DNA sites. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Oct;10(10):5077–5086. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.10.5077. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singh K., Dennis E. S., Ellis J. G., Llewellyn D. J., Tokuhisa J. G., Wahleithner J. A., Peacock W. J. OCSBF-1, a maize ocs enhancer binding factor: isolation and expression during development. Plant Cell. 1990 Sep;2(9):891–903. doi: 10.1105/tpc.2.9.891. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabata T., Nakayama T., Mikami K., Iwabuchi M. HBP-1a and HBP-1b: leucine zipper-type transcription factors of wheat. EMBO J. 1991 Jun;10(6):1459–1467. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07666.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabata T., Takase H., Takayama S., Mikami K., Nakatsuka A., Kawata T., Nakayama T., Iwabuchi M. A protein that binds to a cis-acting element of wheat histone genes has a leucine zipper motif. Science. 1989 Sep 1;245(4921):965–967. doi: 10.1126/science.2772648. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Talanian R. V., McKnight C. J., Kim P. S. Sequence-specific DNA binding by a short peptide dimer. Science. 1990 Aug 17;249(4970):769–771. doi: 10.1126/science.2389142. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Dyke M. W., Sirito M., Sawadogo M. Single-step purification of bacterially expressed polypeptides containing an oligo-histidine domain. Gene. 1992 Feb 1;111(1):99–104. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(92)90608-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams M. E., Foster R., Chua N. H. Sequences flanking the hexameric G-box core CACGTG affect the specificity of protein binding. Plant Cell. 1992 Apr;4(4):485–496. doi: 10.1105/tpc.4.4.485. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]