Abstract
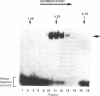
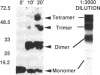
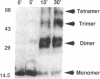
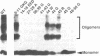
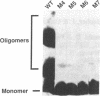
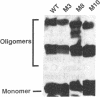
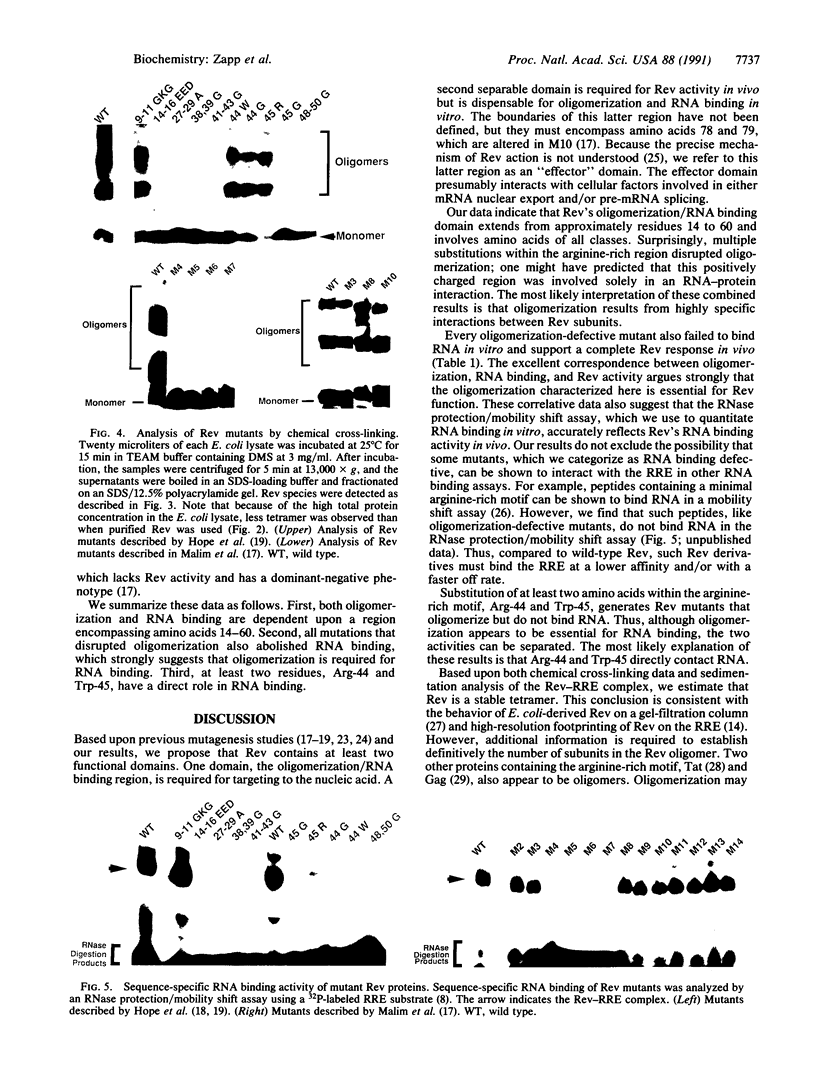
The Rev protein of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 is a sequence-specific RNA binding protein that is essential for viral replication. Here we present evidence that Rev is a stable oligomer both in vitro and in vivo. Analysis of Rev mutants indicates that oligomerization is essential for RNA binding and hence Rev function. The oligomerization and RNA binding domains overlap over 47 amino acids. Within this region is a short arginine-rich motif found in a large class of RNA binding proteins. Substitution of multiple residues within the arginine-rich motif abolishes oligomerization, whereas several single-amino-acid substitution mutants oligomerize but do not bind RNA. Thus, Rev's arginine-rich motif participates in two distinct functions: oligomerization and RNA binding.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Calnan B. J., Biancalana S., Hudson D., Frankel A. D. Analysis of arginine-rich peptides from the HIV Tat protein reveals unusual features of RNA-protein recognition. Genes Dev. 1991 Feb;5(2):201–210. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.2.201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cochrane A. W., Chen C. H., Rosen C. A. Specific interaction of the human immunodeficiency virus Rev protein with a structured region in the env mRNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Feb;87(3):1198–1202. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.3.1198. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daefler S., Klotman M. E., Wong-Staal F. Trans-activating rev protein of the human immunodeficiency virus 1 interacts directly and specifically with its target RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jun;87(12):4571–4575. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.12.4571. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daly T. J., Cook K. S., Gray G. S., Maione T. E., Rusche J. R. Specific binding of HIV-1 recombinant Rev protein to the Rev-responsive element in vitro. Nature. 1989 Dec 14;342(6251):816–819. doi: 10.1038/342816a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emerman M., Vazeux R., Peden K. The rev gene product of the human immunodeficiency virus affects envelope-specific RNA localization. Cell. 1989 Jun 30;57(7):1155–1165. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90053-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg M. B., Jarrett R. F., Aldovini A., Gallo R. C., Wong-Staal F. HTLV-III expression and production involve complex regulation at the levels of splicing and translation of viral RNA. Cell. 1986 Sep 12;46(6):807–817. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90062-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Felber B. K., Hadzopoulou-Cladaras M., Cladaras C., Copeland T., Pavlakis G. N. rev protein of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 affects the stability and transport of the viral mRNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Mar;86(5):1495–1499. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.5.1495. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frankel A. D., Bredt D. S., Pabo C. O. Tat protein from human immunodeficiency virus forms a metal-linked dimer. Science. 1988 Apr 1;240(4848):70–73. doi: 10.1126/science.2832944. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green M. R., Zapp M. L. Human immunodeficiency virus. Revving up gene expression. Nature. 1989 Mar 16;338(6212):200–201. doi: 10.1038/338200a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hadzopoulou-Cladaras M., Felber B. K., Cladaras C., Athanassopoulos A., Tse A., Pavlakis G. N. The rev (trs/art) protein of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 affects viral mRNA and protein expression via a cis-acting sequence in the env region. J Virol. 1989 Mar;63(3):1265–1274. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.3.1265-1274.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hammarskjöld M. L., Heimer J., Hammarskjöld B., Sangwan I., Albert L., Rekosh D. Regulation of human immunodeficiency virus env expression by the rev gene product. J Virol. 1989 May;63(5):1959–1966. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.5.1959-1966.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heaphy S., Dingwall C., Ernberg I., Gait M. J., Green S. M., Karn J., Lowe A. D., Singh M., Skinner M. A. HIV-1 regulator of virion expression (Rev) protein binds to an RNA stem-loop structure located within the Rev response element region. Cell. 1990 Feb 23;60(4):685–693. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90671-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hope T. J., Huang X. J., McDonald D., Parslow T. G. Steroid-receptor fusion of the human immunodeficiency virus type 1 Rev transactivator: mapping cryptic functions of the arginine-rich motif. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Oct;87(19):7787–7791. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.19.7787. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hope T. J., McDonald D., Huang X. J., Low J., Parslow T. G. Mutational analysis of the human immunodeficiency virus type 1 Rev transactivator: essential residues near the amino terminus. J Virol. 1990 Nov;64(11):5360–5366. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.11.5360-5366.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kjems J., Brown M., Chang D. D., Sharp P. A. Structural analysis of the interaction between the human immunodeficiency virus Rev protein and the Rev response element. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Feb 1;88(3):683–687. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.3.683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lazinski D., Grzadzielska E., Das A. Sequence-specific recognition of RNA hairpins by bacteriophage antiterminators requires a conserved arginine-rich motif. Cell. 1989 Oct 6;59(1):207–218. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90882-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin Y. S., Green M. R. Similarities between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cyclic AMP-responsive promoter elements. Nature. 1989 Aug 24;340(6235):656–659. doi: 10.1038/340656a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malim M. H., Böhnlein S., Hauber J., Cullen B. R. Functional dissection of the HIV-1 Rev trans-activator--derivation of a trans-dominant repressor of Rev function. Cell. 1989 Jul 14;58(1):205–214. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90416-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malim M. H., Cullen B. R. HIV-1 structural gene expression requires the binding of multiple Rev monomers to the viral RRE: implications for HIV-1 latency. Cell. 1991 Apr 19;65(2):241–248. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90158-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malim M. H., Hauber J., Le S. Y., Maizel J. V., Cullen B. R. The HIV-1 rev trans-activator acts through a structured target sequence to activate nuclear export of unspliced viral mRNA. Nature. 1989 Mar 16;338(6212):254–257. doi: 10.1038/338254a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malim M. H., Tiley L. S., McCarn D. F., Rusche J. R., Hauber J., Cullen B. R. HIV-1 structural gene expression requires binding of the Rev trans-activator to its RNA target sequence. Cell. 1990 Feb 23;60(4):675–683. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90670-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mermer B., Felber B. K., Campbell M., Pavlakis G. N. Identification of trans-dominant HIV-1 rev protein mutants by direct transfer of bacterially produced proteins into human cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Apr 25;18(8):2037–2044. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.8.2037. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nalin C. M., Purcell R. D., Antelman D., Mueller D., Tomchak L., Wegrzynski B., McCarney E., Toome V., Kramer R., Hsu M. C. Purification and characterization of recombinant Rev protein of human immunodeficiency virus type 1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Oct;87(19):7593–7597. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.19.7593. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olsen H. S., Cochrane A. W., Dillon P. J., Nalin C. M., Rosen C. A. Interaction of the human immunodeficiency virus type 1 Rev protein with a structured region in env mRNA is dependent on multimer formation mediated through a basic stretch of amino acids. Genes Dev. 1990 Aug;4(8):1357–1364. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.8.1357. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sodroski J., Goh W. C., Rosen C., Dayton A., Terwilliger E., Haseltine W. A second post-transcriptional trans-activator gene required for HTLV-III replication. Nature. 1986 May 22;321(6068):412–417. doi: 10.1038/321412a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Solomon M. J., Varshavsky A. Formaldehyde-mediated DNA-protein crosslinking: a probe for in vivo chromatin structures. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Oct;82(19):6470–6474. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.19.6470. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trono D., Feinberg M. B., Baltimore D. HIV-1 Gag mutants can dominantly interfere with the replication of the wild-type virus. Cell. 1989 Oct 6;59(1):113–120. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90874-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zamore P. D., Zapp M. L., Green M. R. Gene expression. RNA binding: beta s and basics. Nature. 1990 Dec 6;348(6301):485–486. doi: 10.1038/348485a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zapp M. L., Green M. R. Sequence-specific RNA binding by the HIV-1 Rev protein. Nature. 1989 Dec 7;342(6250):714–716. doi: 10.1038/342714a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]