Abstract
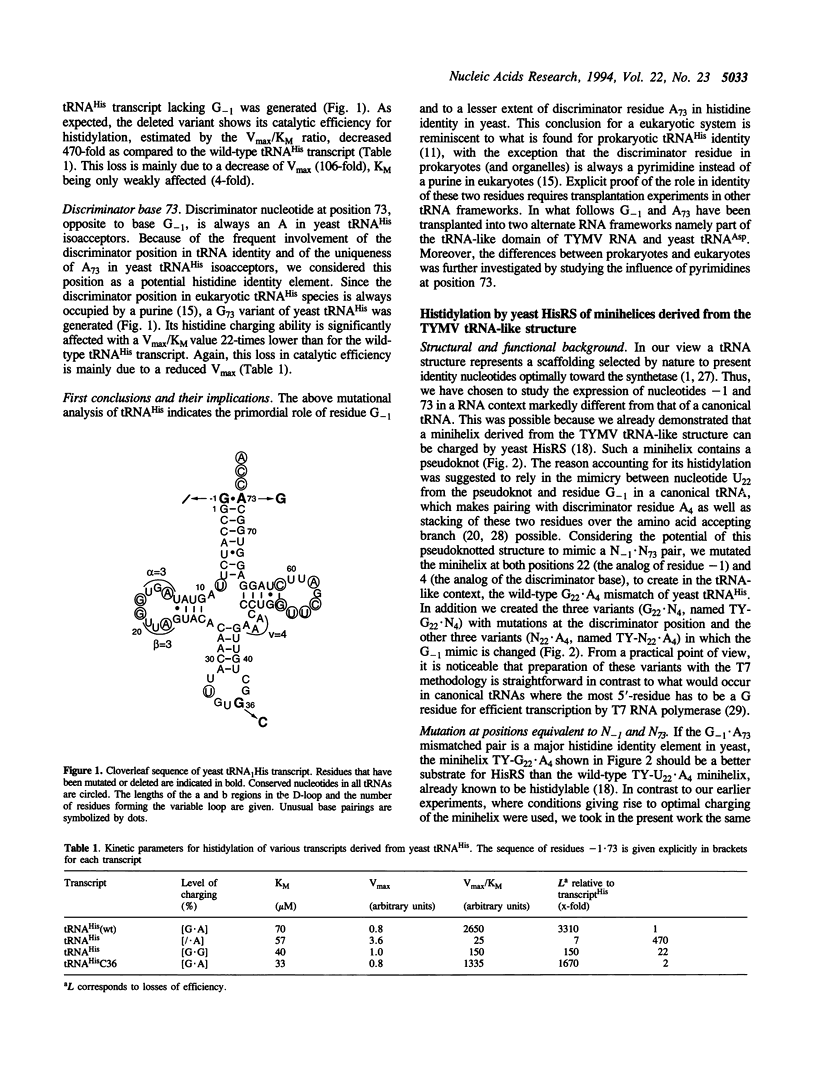
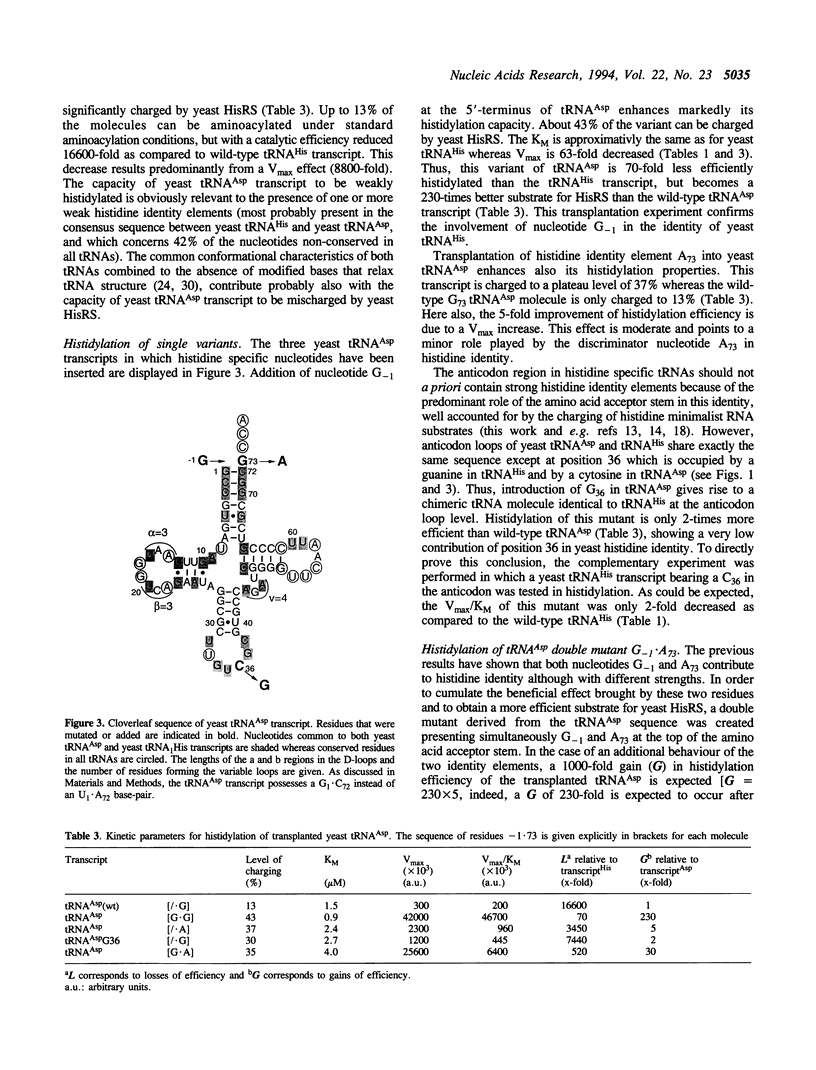
Residue G-1 and discriminator base C73 are the major histidine identity elements in prokaryotes. Here we evaluate the importance of these two nucleotides in yeast histidine aminoacylation identity. Deletion of G-1 in yeast tRNA(His) transcript leads to a drastic loss of histidylation specificity (about 500-fold). Mutation of discriminator base A73, common to all yeast tRNA(His) species, into G73 has a more moderate but still significant effect with a 22-fold decrease in histidylation specificity. Changes at position 36 in the anticodon loop has negligible effect on histidylation. The role of residues -1 and 73 for specific aminoacylation by yeast HisRS was further investigated by studying the histidylation capacities of seven minihelices derived from the Turnip Yellow Mosaic Virus tRNA-like structure. Changes in the nature of nucleotides -1 and 73 modulate this activity but do not suppress it. The optimal mini-substrate for HisRS presents a G.A mismatch at the position equivalent to residues G-1.A73 in yeast tRNA(His), confirms the importance of this structural feature in yeast histidine identity. The fact that the minisubstrates contain a pseudoknot in which position -1 is mimicked by an internal nucleotide from the pseudoknot highlights further the necessity of a stacking interaction of this position over the amino acid accepting branch of the tRNA during the aminoacylation process. Individual transplantation of G-1 or A73 into yeast tRNA(Asp) transcript improves the histidylation efficiency of the engineered tRNA(Asp). However, a tRNA(Asp) transcript presenting simultaneously both residues G-1 and A73 becomes a less good substrate for HisRS, suggesting the importance of the structural context and/or the presence of antideterminants for an optimal expression of these two identity elements.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Dumas P., Moras D., Florentz C., Giegé R., Verlaan P., Van Belkum A., Pleij C. W. 3-D graphics modelling of the tRNA-like 3'-end of turnip yellow mosaic virus RNA: structural and functional implications. J Biomol Struct Dyn. 1987 Apr;4(5):707–728. doi: 10.1080/07391102.1987.10507674. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eriani G., Delarue M., Poch O., Gangloff J., Moras D. Partition of tRNA synthetases into two classes based on mutually exclusive sets of sequence motifs. Nature. 1990 Sep 13;347(6289):203–206. doi: 10.1038/347203a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Felden B., Florentz C., McPherson A., Giegé R. A histidine accepting tRNA-like fold at the 3'-end of satellite tobacco mosaic virus RNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1994 Aug 11;22(15):2882–2886. doi: 10.1093/nar/22.15.2882. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Francklyn C., Schimmel P. Enzymatic aminoacylation of an eight-base-pair microhelix with histidine. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Nov;87(21):8655–8659. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.21.8655. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Francklyn C., Shi J. P., Schimmel P. Overlapping nucleotide determinants for specific aminoacylation of RNA microhelices. Science. 1992 Feb 28;255(5048):1121–1125. doi: 10.1126/science.1546312. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frugier M., Florentz C., Schimmel P., Giegé R. Triple aminoacylation specificity of a chimerized transfer RNA. Biochemistry. 1993 Dec 21;32(50):14053–14061. doi: 10.1021/bi00213a039. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- García-Arenal F. Sequence and structure at the genome 3' end of the U2-strain of tobacco mosaic virus, a histidine-accepting tobamovirus. Virology. 1988 Nov;167(1):201–206. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(88)90070-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giegé R., Florentz C., Dreher T. W. The TYMV tRNA-like structure. Biochimie. 1993;75(7):569–582. doi: 10.1016/0300-9084(93)90063-X. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giegé R., Puglisi J. D., Florentz C. tRNA structure and aminoacylation efficiency. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 1993;45:129–206. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6603(08)60869-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Himeno H., Hasegawa T., Ueda T., Watanabe K., Miura K., Shimizu M. Role of the extra G-C pair at the end of the acceptor stem of tRNA(His) in aminoacylation. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Oct 11;17(19):7855–7863. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.19.7855. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hou Y. M., Westhof E., Giegé R. An unusual RNA tertiary interaction has a role for the specific aminoacylation of a transfer RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jul 15;90(14):6776–6780. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.14.6776. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keith G., Pixa G., Fix C., Dirheimer G. Primary structure of three tRNAs from brewer's yeast: tRNAPro2, tRNAHis1 and tRNAHis2. Biochimie. 1983 Nov-Dec;65(11-12):661–672. doi: 10.1016/s0300-9084(84)80030-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McClain W. H., Foss K. Changing the acceptor identity of a transfer RNA by altering nucleotides in a "variable pocket". Science. 1988 Sep 30;241(4874):1804–1807. doi: 10.1126/science.2459773. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McClain W. H. Rules that govern tRNA identity in protein synthesis. J Mol Biol. 1993 Nov 20;234(2):257–280. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1993.1582. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milligan J. F., Groebe D. R., Witherell G. W., Uhlenbeck O. C. Oligoribonucleotide synthesis using T7 RNA polymerase and synthetic DNA templates. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Nov 11;15(21):8783–8798. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.21.8783. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muramatsu T., Nishikawa K., Nemoto F., Kuchino Y., Nishimura S., Miyazawa T., Yokoyama S. Codon and amino-acid specificities of a transfer RNA are both converted by a single post-transcriptional modification. Nature. 1988 Nov 10;336(6195):179–181. doi: 10.1038/336179a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Normanly J., Ollick T., Abelson J. Eight base changes are sufficient to convert a leucine-inserting tRNA into a serine-inserting tRNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jun 15;89(12):5680–5684. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.12.5680. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oberg B., Philipson L. Binding of histidine to tobacco mosaic virus RNA. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1972 Aug 21;48(4):927–932. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(72)90697-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perret V., Florentz C., Puglisi J. D., Giegé R. Effect of conformational features on the aminoacylation of tRNAs and consequences on the permutation of tRNA specificities. J Mol Biol. 1992 Jul 20;226(2):323–333. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(92)90950-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perret V., Garcia A., Grosjean H., Ebel J. P., Florentz C., Giegé R. Relaxation of a transfer RNA specificity by removal of modified nucleotides. Nature. 1990 Apr 19;344(6268):787–789. doi: 10.1038/344787a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perret V., Garcia A., Puglisi J., Grosjean H., Ebel J. P., Florentz C., Giegé R. Conformation in solution of yeast tRNA(Asp) transcripts deprived of modified nucleotides. Biochimie. 1990 Oct;72(10):735–743. doi: 10.1016/0300-9084(90)90158-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pütz J., Puglisi J. D., Florentz C., Giegé R. Additive, cooperative and anti-cooperative effects between identity nucleotides of a tRNA. EMBO J. 1993 Jul;12(7):2949–2957. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05957.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pütz J., Puglisi J. D., Florentz C., Giegé R. Identity elements for specific aminoacylation of yeast tRNA(Asp) by cognate aspartyl-tRNA synthetase. Science. 1991 Jun 21;252(5013):1696–1699. doi: 10.1126/science.2047878. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogers K. C., Söll D. Discrimination among tRNAs intermediate in glutamate and glutamine acceptor identity. Biochemistry. 1993 Dec 28;32(51):14210–14219. doi: 10.1021/bi00214a021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rould M. A., Perona J. J., Söll D., Steitz T. A. Structure of E. coli glutaminyl-tRNA synthetase complexed with tRNA(Gln) and ATP at 2.8 A resolution. Science. 1989 Dec 1;246(4934):1135–1142. doi: 10.1126/science.2479982. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rudinger J., Florentz C., Dreher T., Giegé R. Efficient mischarging of a viral tRNA-like structure and aminoacylation of a minihelix containing a pseudoknot: histidinylation of turnip yellow mosaic virus RNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Apr 25;20(8):1865–1870. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.8.1865. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruff M., Krishnaswamy S., Boeglin M., Poterszman A., Mitschler A., Podjarny A., Rees B., Thierry J. C., Moras D. Class II aminoacyl transfer RNA synthetases: crystal structure of yeast aspartyl-tRNA synthetase complexed with tRNA(Asp). Science. 1991 Jun 21;252(5013):1682–1689. doi: 10.1126/science.2047877. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saks M. E., Sampson J. R., Abelson J. N. The transfer RNA identity problem: a search for rules. Science. 1994 Jan 14;263(5144):191–197. doi: 10.1126/science.7506844. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sampson J. R., DiRenzo A. B., Behlen L. S., Uhlenbeck O. C. Nucleotides in yeast tRNAPhe required for the specific recognition by its cognate synthetase. Science. 1989 Mar 10;243(4896):1363–1366. doi: 10.1126/science.2646717. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sampson J. R., Uhlenbeck O. C. Biochemical and physical characterization of an unmodified yeast phenylalanine transfer RNA transcribed in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Feb;85(4):1033–1037. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.4.1033. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schulman L. H., Pelka H. Anticodon switching changes the identity of methionine and valine transfer RNAs. Science. 1988 Nov 4;242(4879):765–768. doi: 10.1126/science.3055296. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinberg S., Misch A., Sprinzl M. Compilation of tRNA sequences and sequences of tRNA genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993 Jul 1;21(13):3011–3015. doi: 10.1093/nar/21.13.3011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wyatt J. R., Chastain M., Puglisi J. D. Synthesis and purification of large amounts of RNA oligonucleotides. Biotechniques. 1991 Dec;11(6):764–769. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yan W., Francklyn C. Cytosine 73 is a discriminator nucleotide in vivo for histidyl-tRNA in Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1994 Apr 1;269(13):10022–10027. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



