Abstract
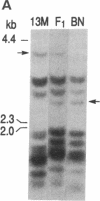
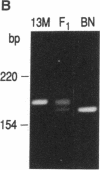
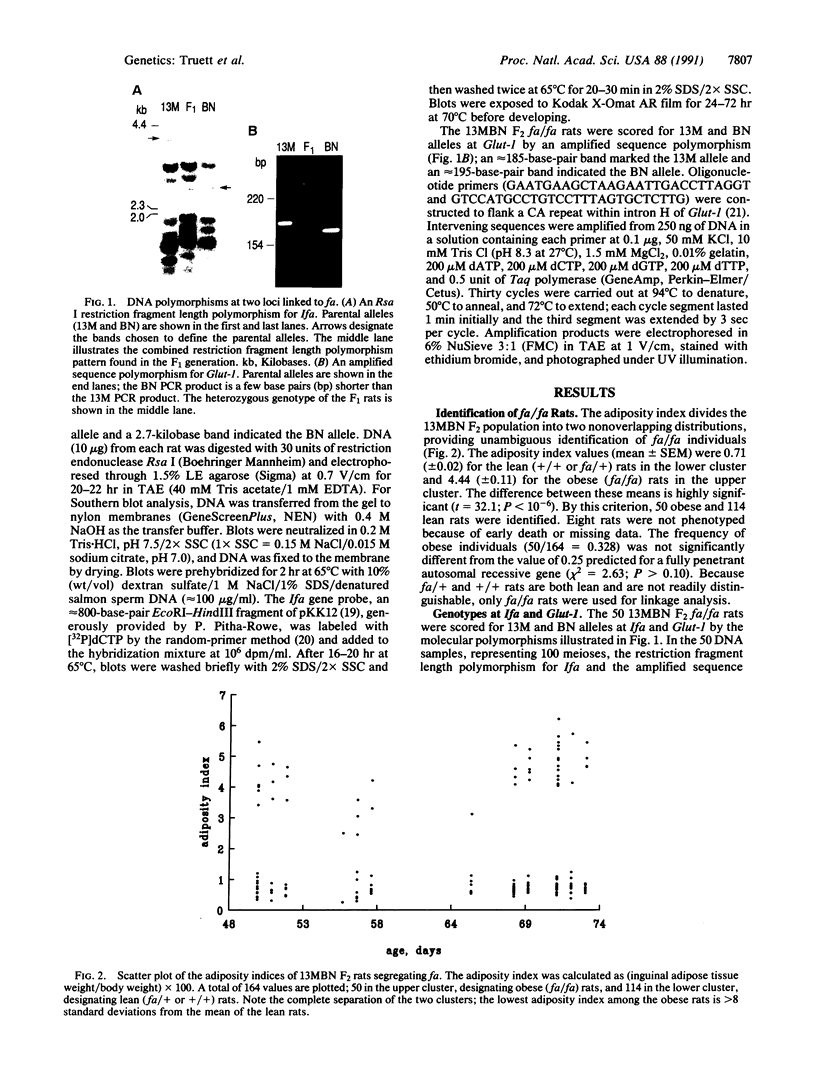
The autosomal recessive mutations fa (rat) and db (mouse) cause obesity syndromes that develop early and ultimately become severe. Although both fa/fa rats and db/db mice have been studied extensively as models of human obesity and diabetes, the molecular bases of these phenotypes remain unknown. We have mapped fa in 50 fa/fa (obese) offspring of a (13M x Brown Norway) F1 fa/+ intercross relative to two molecular markers, Ifa and Glut-1, which flank db on mouse chromosome 4 and which are located on rat chromosome 5. Ifa and Glut-1 are linked to fa, with a gene order, Ifa-fa-Glut-1, that is identical to that for the region around db in the mouse genome. These results place fa on rat chromosome 5 and suggest that db and fa are mutations in homologous genes.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Amar L. C., Arnaud D., Cambrou J., Guenet J. L., Avner P. R. Mapping of the mouse X chromosome using random genomic probes and an interspecific mouse cross. EMBO J. 1985 Dec 30;4(13B):3695–3700. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb04137.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bahary N., Leibel R. L., Joseph L., Friedman J. M. Molecular mapping of the mouse db mutation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Nov;87(21):8642–8646. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.21.8642. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barsh G. S., Epstein C. J. The long-range restriction map surrounding the mouse agouti locus reveals a disparity between physical and genetic distances. Genomics. 1989 Jul;5(1):9–18. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(89)90080-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boulangé A., Planche E., de Gasquet P. Onset of genetic obesity in the absence of hyperphagia during the first week of life in the Zucker rat (fa/fa). J Lipid Res. 1979 Sep;20(7):857–864. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bray G. A. The Zucker-fatty rat: a review. Fed Proc. 1977 Feb;36(2):148–153. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coleman D. L. Diabetes-obesity syndromes in mice. Diabetes. 1982;31(Suppl 1 Pt 2):1–6. doi: 10.2337/diab.31.1.s1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coleman D. L. Effects of parabiosis of obese with diabetes and normal mice. Diabetologia. 1973 Aug;9(4):294–298. doi: 10.1007/BF01221857. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coleman D. L., Eicher E. M. Fat (fat) and tubby (tub): two autosomal recessive mutations causing obesity syndromes in the mouse. J Hered. 1990 Nov-Dec;81(6):424–427. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jhered.a111019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coleman D. L., Hummel K. P. Studies with the mutation, diabetes, in the mouse. Diabetologia. 1967 Apr;3(2):238–248. doi: 10.1007/BF01222201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coleman D. L. Obese and diabetes: two mutant genes causing diabetes-obesity syndromes in mice. Diabetologia. 1978 Mar;14(3):141–148. doi: 10.1007/BF00429772. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deb S., Martin R. J., Hershberger T. V. Maintenance requirement and energetic efficiency of lean and obese Zucker rats. J Nutr. 1976 Feb;106(2):191–197. doi: 10.1093/jn/106.2.191. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris R. B., Hervey E., Hervey G. R., Tobin G. Body composition of lean and obese Zucker rats in parabiosis. Int J Obes. 1987;11(3):275–283. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hummel K. P., Coleman D. L., Lane P. W. The influence of genetic background on expression of mutations at the diabetes locus in the mouse. I. C57BL-KsJ and C57BL-6J strains. Biochem Genet. 1972 Aug;7(1):1–13. doi: 10.1007/BF00487005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikeda H., Shino A., Matsuo T., Iwatsuka H., Suzuoki Z. A new genetically obese-hyperglycemic rat (Wistar fatty). Diabetes. 1981 Dec;30(12):1045–1050. doi: 10.2337/diab.30.12.1045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelley K. A., Pitha P. M. Characterization of a mouse interferon gene locus I. Isolation of a cluster of four alpha interferon genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Feb 11;13(3):805–823. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.3.805. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koletsky S. Obese spontaneously hypertensive rats--a model for study of atherosclerosis. Exp Mol Pathol. 1973 Aug;19(1):53–60. doi: 10.1016/0014-4800(73)90040-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leibel R. L., Bahary N., Friedman J. M. Genetic variation and nutrition in obesity: approaches to the molecular genetics of obesity. World Rev Nutr Diet. 1990;63:90–101. doi: 10.1159/000418501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin R. J., Harris R. B., Jones D. D. Evidence for a central mechanism of obesity in the Zucker fatty rat (fa/fa). Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1986 Oct;183(1):1–10. doi: 10.3181/00379727-183-42380. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Searle A. G., Peters J., Lyon M. F., Hall J. G., Evans E. P., Edwards J. H., Buckle V. J. Chromosome maps of man and mouse. IV. Ann Hum Genet. 1989 May;53(Pt 2):89–140. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-1809.1989.tb01777.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szpirer C., Rivière M., Szpirer J., Genet M., Drèze P., Islam M. Q., Levan G. Assignment of 12 loci to rat chromosome 5: evidence that this chromosome is homologous to mouse chromosome 4 and to human chromosomes 9 and 1 (1p arm). Genomics. 1990 Apr;6(4):679–684. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(90)90504-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams S. A., Birnbaum M. J. The rat facilitated glucose transporter gene. Transformation and serum-stimulated transcription initiate from identical sites. J Biol Chem. 1988 Dec 25;263(36):19513–19518. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yen T. T., Shaw W. N., Yu P. L. Genetics of obesity of Zucker rats and Koletsky rats. Heredity (Edinb) 1977 Jun;38(3):373–377. doi: 10.1038/hdy.1977.100. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zucker L M. Two-Way Selection for Body Size in Rats, with Observations on Simultaneous Changes in Coat Color Pattern and Hood Size. Genetics. 1960 Apr;45(4):467–483. doi: 10.1093/genetics/45.4.467. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zucker L. M., Antoniades H. N. Insulin and obesity in the Zucker genetically obese rat "fatty". Endocrinology. 1972 May;90(5):1320–1330. doi: 10.1210/endo-90-5-1320. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]