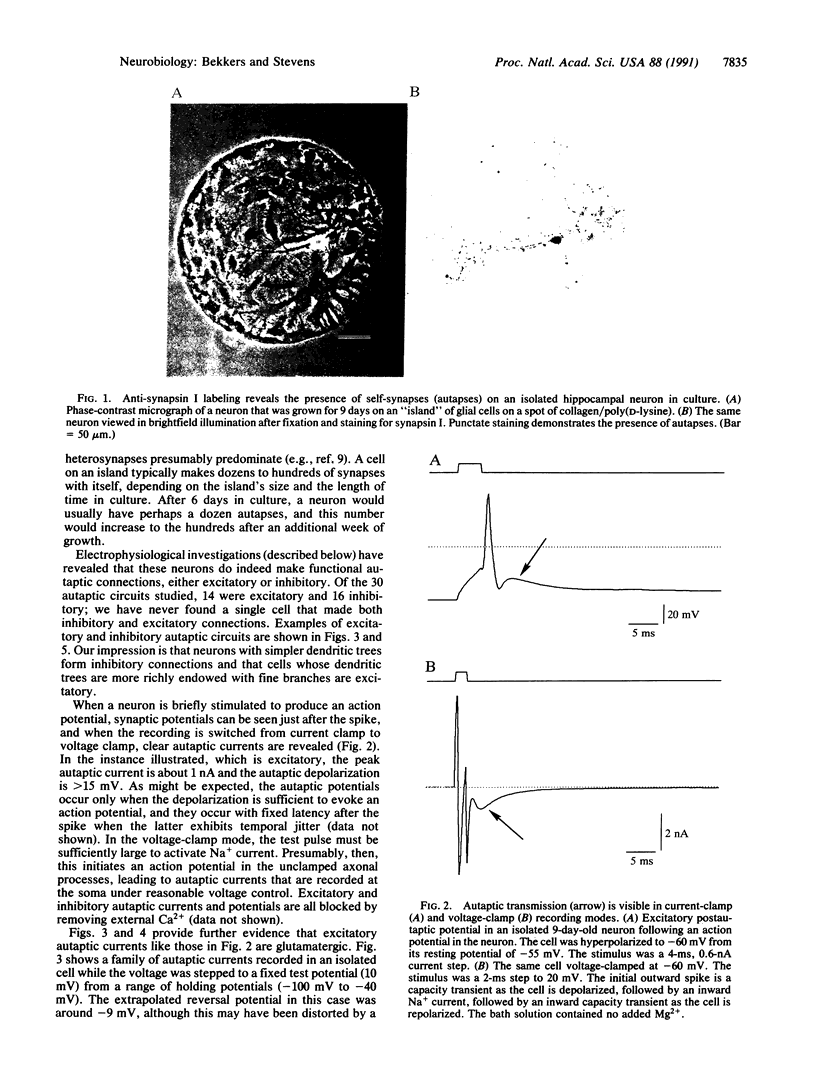
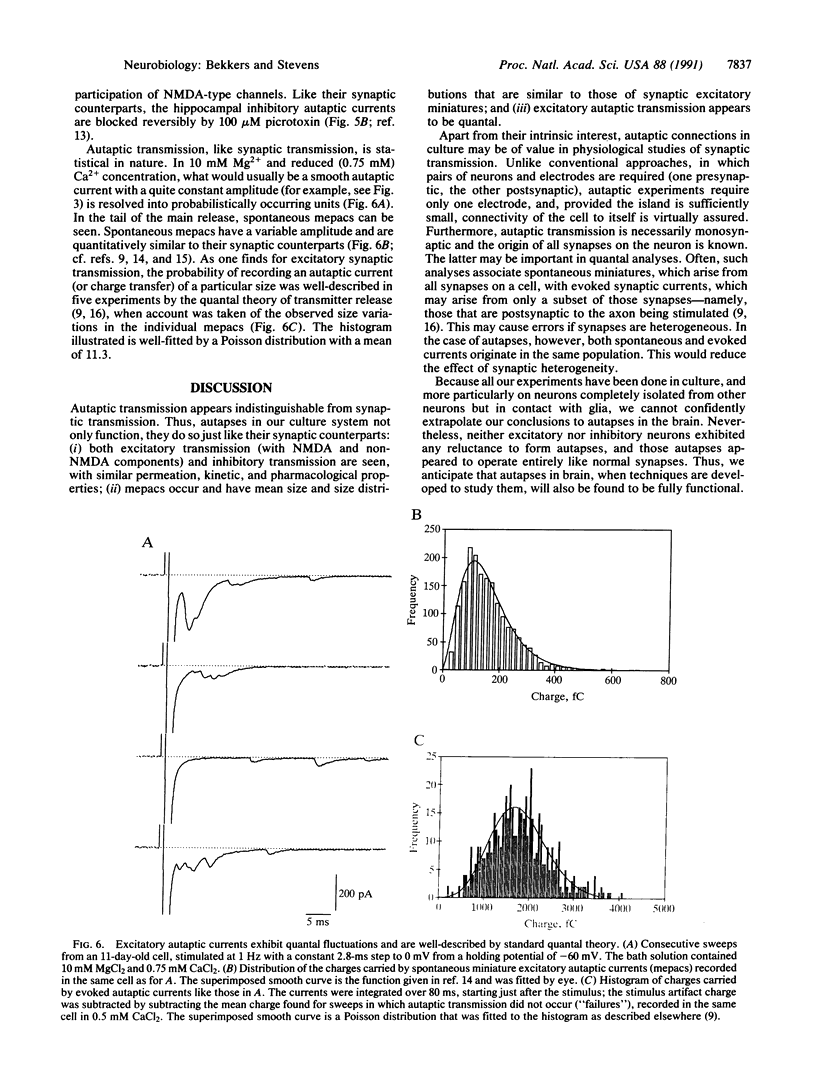
Abstract
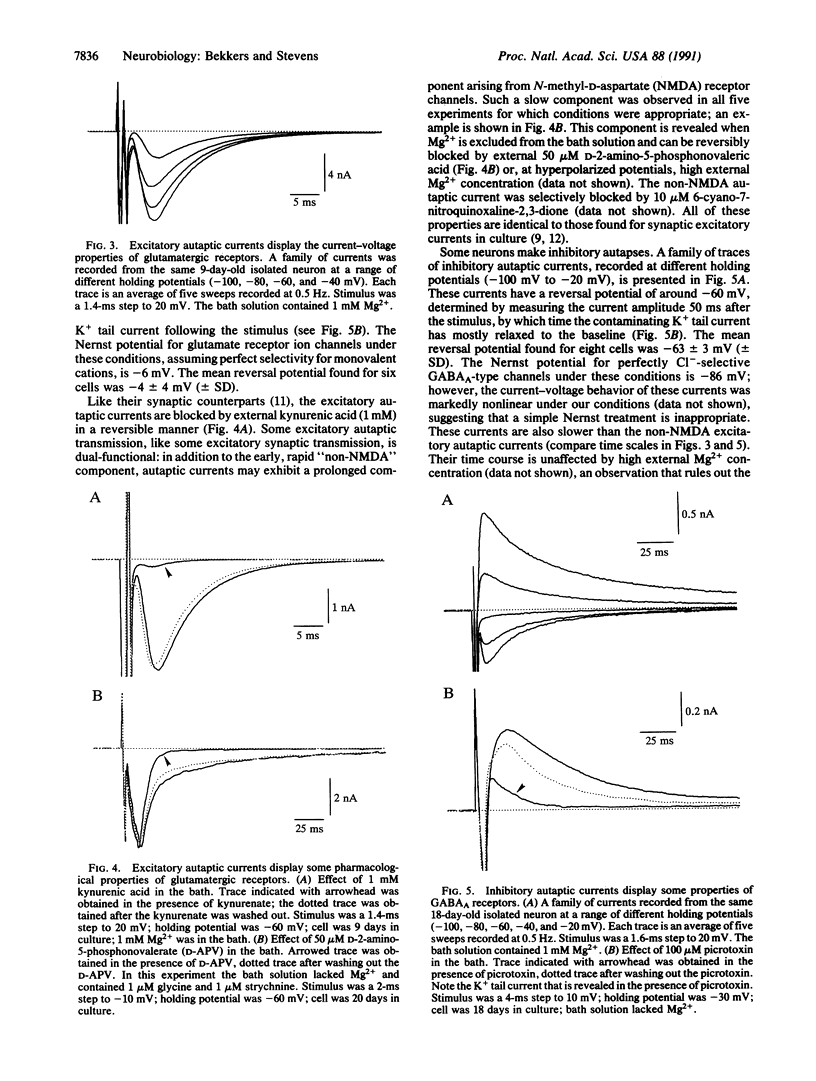
Individual rat hippocampal neurons, grown in isolation from other neurons on small spots of permissive substrate, were studied in order to characterize the electrical properties of the synapses that such cells formed with themselves (autapses). Excitatory (probably glutamatergic) or inhibitory (probably type A gamma-aminobutyratergic) autapses were frequently found. Excitatory autaptic currents reversed near the potential expected for monovalent cations were blocked by the glutamatergic antagonist kynurenic acid, and possessed a slow component with the pharmacological profile of N-methyl-D-aspartate-type channels. These currents also exhibited trial-to-trial statistical fluctuations in their amplitudes, this being well-described by quantal analysis. Inhibitory autaptic currents reversed at hyperpolarized potentials, as expected for chloride-permeable pores and were blocked by picrotoxin, a type A gamma-aminobutyric receptor antagonist. It is concluded that autaptic currents in culture are identical to those found at synapses.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bekkers J. M., Richerson G. B., Stevens C. F. Origin of variability in quantal size in cultured hippocampal neurons and hippocampal slices. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jul;87(14):5359–5362. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.14.5359. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bekkers J. M., Stevens C. F. NMDA and non-NMDA receptors are co-localized at individual excitatory synapses in cultured rat hippocampus. Nature. 1989 Sep 21;341(6239):230–233. doi: 10.1038/341230a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DEL CASTILLO J., KATZ B. Statistical factors involved in neuromuscular facilitation and depression. J Physiol. 1954 Jun 28;124(3):574–585. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1954.sp005130. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Camilli P., Cameron R., Greengard P. Synapsin I (protein I), a nerve terminal-specific phosphoprotein. I. Its general distribution in synapses of the central and peripheral nervous system demonstrated by immunofluorescence in frozen and plastic sections. J Cell Biol. 1983 May;96(5):1337–1354. doi: 10.1083/jcb.96.5.1337. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiFiglia M., Pasik P., Pasik T. A Golgi study of neuronal types in the neostriatum of monkeys. Brain Res. 1976 Sep 17;114(2):245–256. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(76)90669-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finch D. M., Fisher R. S., Jackson M. B. Miniature excitatory synaptic currents in cultured hippocampal neurons. Brain Res. 1990 Jun 4;518(1-2):257–268. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(90)90978-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forsythe I. D., Westbrook G. L. Slow excitatory postsynaptic currents mediated by N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors on cultured mouse central neurones. J Physiol. 1988 Feb;396:515–533. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1988.sp016975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furshpan E. J., Landis S. C., Matsumoto S. G., Potter D. D. Synaptic functions in rat sympathetic neurons in microcultures. I. Secretion of norepinephrine and acetylcholine. J Neurosci. 1986 Apr;6(4):1061–1079. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.06-04-01061.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furshpan E. J., MacLeish P. R., O'Lague P. H., Potter D. D. Chemical transmission between rat sympathetic neurons and cardiac myocytes developing in microcultures: evidence for cholinergic, adrenergic, and dual-function neurons. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Nov;73(11):4225–4229. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.11.4225. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jahr C. E., Jessell T. M. Synaptic transmission between dorsal root ganglion and dorsal horn neurons in culture: antagonism of monosynaptic excitatory postsynaptic potentials and glutamate excitation by kynurenate. J Neurosci. 1985 Aug;5(8):2281–2289. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.05-08-02281.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karabelas A. B., Purpura D. P. Evidence for autapses in the substantia nigra. Brain Res. 1980 Nov 3;200(2):467–473. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(80)90935-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Segal M. M. Epileptiform activity in microcultures containing one excitatory hippocampal neuron. J Neurophysiol. 1991 Apr;65(4):761–770. doi: 10.1152/jn.1991.65.4.761. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Segal M. M., Furshpan E. J. Epileptiform activity in microcultures containing small numbers of hippocampal neurons. J Neurophysiol. 1990 Nov;64(5):1390–1399. doi: 10.1152/jn.1990.64.5.1390. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Segal M., Barker J. L. Rat hippocampal neurons in culture: voltage-clamp analysis of inhibitory synaptic connections. J Neurophysiol. 1984 Sep;52(3):469–487. doi: 10.1152/jn.1984.52.3.469. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van der Loos H., Glaser E. M. Autapses in neocortex cerebri: synapses between a pyramidal cell's axon and its own dendrites. Brain Res. 1972 Dec 24;48:355–360. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(72)90189-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]