Abstract
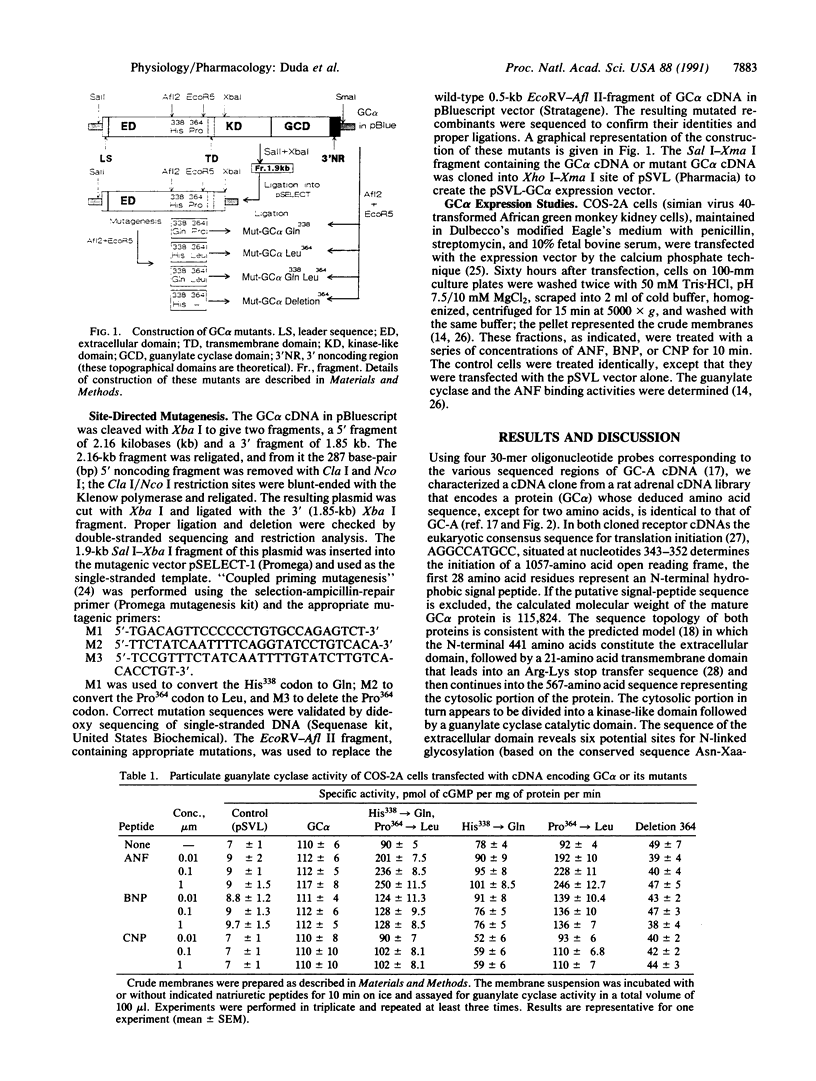
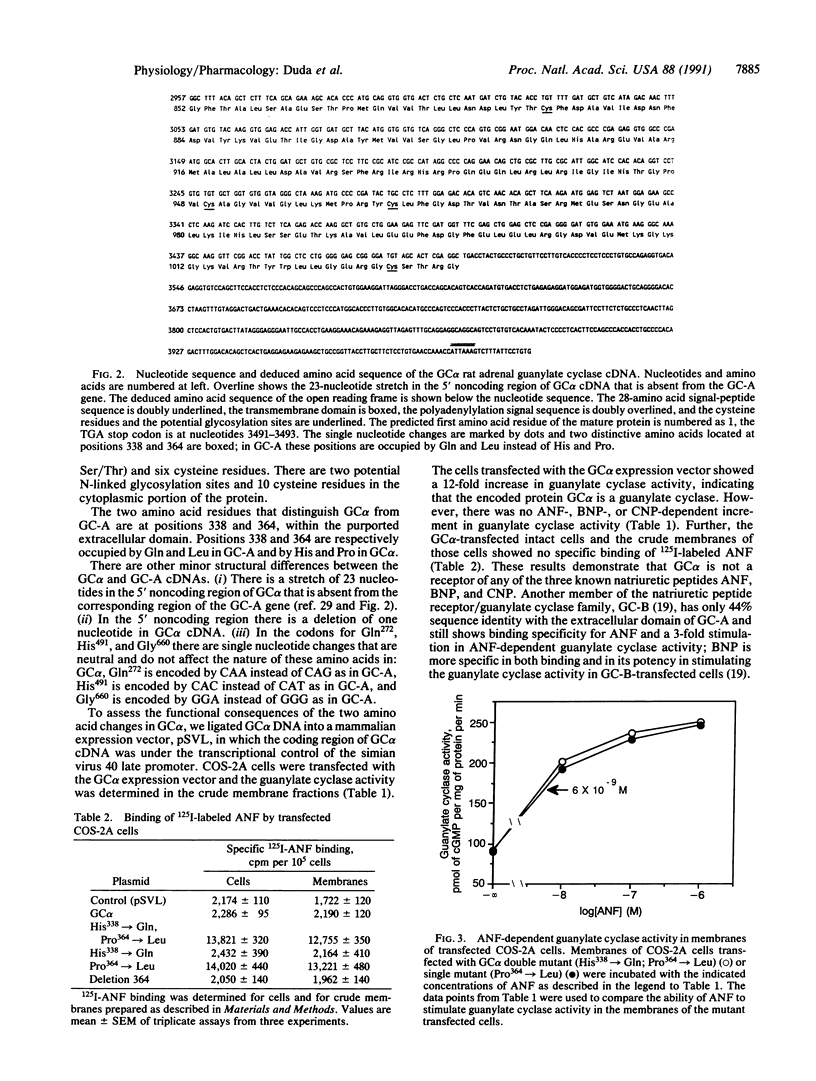
Natriuretic peptides are structurally related hormones that regulate hemodynamics of the physiological processes of diuresis, water balance, and blood pressure. One of the second messengers of these hormones is cGMP, and the type of receptor that is involved in the generation of cGMP is also a guanylate cyclase. Recent genetic evidence has revealed such a receptor family; two family members, GC-A and GC-B, have been cloned. We now describe the molecular cloning, sequencing, and expression of a cDNA clone from rat adrenal gland that encodes a membrane guanylate cyclase, GC alpha, that, with the exception of two amino acids, is structurally identical to GC-A and conforms to the purported topographical model of GC-A. The two amino acid changes are the substitutions Gln338----His338 and Leu364----Pro364, involving single nucleotide changes, CAG----CAC and CTG----CCG, respectively. Expression studies indicate that GC alpha cyclase activity is independent of the known natriuretic peptides, and direct binding studies demonstrate that GC alpha is not an ANF receptor. To determine the importance of Gln338 and Leu364 in ANF signaling, the GC alpha cDNA regions encoding amino acid residues 338 and 364 were remodeled by oligonucleotide-directed mutagenesis. A double mutant encoding Gln338 and Leu364, and a single-substitution mutant encoding Leu364 expressed both ANF binding and ANF-dependent cyclase activities, but the mutant encoding Gln338 and a deletion mutant lacking residue 364 did not express either of the above activities. These results define the critical role of Leu364 in ANF signal transduction.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Benton W. D., Davis R. W. Screening lambdagt recombinant clones by hybridization to single plaques in situ. Science. 1977 Apr 8;196(4286):180–182. doi: 10.1126/science.322279. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carter P. Improved oligonucleotide-directed mutagenesis using M13 vectors. Methods Enzymol. 1987;154:382–403. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)54086-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang M. S., Lowe D. G., Lewis M., Hellmiss R., Chen E., Goeddel D. V. Differential activation by atrial and brain natriuretic peptides of two different receptor guanylate cyclases. Nature. 1989 Sep 7;341(6237):68–72. doi: 10.1038/341068a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chinkers M., Garbers D. L., Chang M. S., Lowe D. G., Chin H. M., Goeddel D. V., Schulz S. A membrane form of guanylate cyclase is an atrial natriuretic peptide receptor. Nature. 1989 Mar 2;338(6210):78–83. doi: 10.1038/338078a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flynn T. G., Brar A., Tremblay L., Sarda I., Lyons C., Jennings D. B. Isolation and characterization of iso-rANP, a new natriuretic peptide from rat atria. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1989 Jun 15;161(2):830–837. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(89)92675-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuller F., Porter J. G., Arfsten A. E., Miller J., Schilling J. W., Scarborough R. M., Lewicki J. A., Schenk D. B. Atrial natriuretic peptide clearance receptor. Complete sequence and functional expression of cDNA clones. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jul 5;263(19):9395–9401. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamet P., Tremblay J., Pang S. C., Garcia R., Thibault G., Gutkowska J., Cantin M., Genest J. Effect of native and synthetic atrial natriuretic factor on cyclic GMP. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984 Sep 17;123(2):515–527. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(84)90260-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hashiguchi T., Higuchi K., Ohashi M., Minamino N., Kangawa K., Matsuo H., Nawata H. Porcine brain natriuretic peptide, another modulator of bovine adrenocortical steroidogenesis. FEBS Lett. 1988 Aug 29;236(2):455–461. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(88)80076-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inagami T. Atrial natriuretic factor. J Biol Chem. 1989 Feb 25;264(6):3043–3046. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kambayashi Y., Nakao K., Itoh H., Hosoda K., Saito Y., Yamada T., Mukoyama M., Arai H., Shirakami G., Suga S. Isolation and sequence determination of rat cardiac natriuretic peptide. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1989 Aug 30;163(1):233–240. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(89)92126-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. The scanning model for translation: an update. J Cell Biol. 1989 Feb;108(2):229–241. doi: 10.1083/jcb.108.2.229. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuno T., Andresen J. W., Kamisaki Y., Waldman S. A., Chang L. Y., Saheki S., Leitman D. C., Nakane M., Murad F. Co-purification of an atrial natriuretic factor receptor and particulate guanylate cyclase from rat lung. J Biol Chem. 1986 May 5;261(13):5817–5823. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meloche S., McNicoll N., Liu B., Ong H., De Léan A. Atrial natriuretic factor R1 receptor from bovine adrenal zona glomerulosa: purification, characterization, and modulation by amiloride. Biochemistry. 1988 Oct 18;27(21):8151–8158. doi: 10.1021/bi00421a025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paul A. K., Marala R. B., Jaiswal R. K., Sharma R. K. Coexistence of guanylate cyclase and atrial natriuretic factor receptor in a 180-kD protein. Science. 1987 Mar 6;235(4793):1224–1226. doi: 10.1126/science.2881352. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perchellet J. P., Sharma R. K. Mediatory role of calcium and guanosine 3', 5'-monophosphate in adrenocorticotropin-induced steroidogenesis by adrenal cells. Science. 1979 Mar 23;203(4386):1259–1261. doi: 10.1126/science.34216. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sabatini D. D., Kreibich G., Morimoto T., Adesnik M. Mechanisms for the incorporation of proteins in membranes and organelles. J Cell Biol. 1982 Jan;92(1):1–22. doi: 10.1083/jcb.92.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schulz S., Singh S., Bellet R. A., Singh G., Tubb D. J., Chin H., Garbers D. L. The primary structure of a plasma membrane guanylate cyclase demonstrates diversity within this new receptor family. Cell. 1989 Sep 22;58(6):1155–1162. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90513-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz D., Geller D. M., Manning P. T., Siegel N. R., Fok K. F., Smith C. E., Needleman P. Ser-Leu-Arg-Arg-atriopeptin III: the major circulating form of atrial peptide. Science. 1985 Jul 26;229(4711):397–400. doi: 10.1126/science.3160114. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharma R. K., Marala R. B., Duda T. M. Purification and characterization of the 180-kDa membrane guanylate cyclase containing atrial natriuretic factor receptor from rat adrenal gland and its regulation by protein kinase C. Steroids. 1989 Mar-May;53(3-5):437–460. doi: 10.1016/0039-128x(89)90024-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Short J. M., Fernandez J. M., Sorge J. A., Huse W. D. Lambda ZAP: a bacteriophage lambda expression vector with in vivo excision properties. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Aug 11;16(15):7583–7600. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.15.7583. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sudoh T., Kangawa K., Minamino N., Matsuo H. A new natriuretic peptide in porcine brain. Nature. 1988 Mar 3;332(6159):78–81. doi: 10.1038/332078a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sudoh T., Minamino N., Kangawa K., Matsuo H. C-type natriuretic peptide (CNP): a new member of natriuretic peptide family identified in porcine brain. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1990 Apr 30;168(2):863–870. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(90)92401-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takayanagi R., Snajdar R. M., Imada T., Tamura M., Pandey K. N., Misono K. S., Inagami T. Purification and characterization of two types of atrial natriuretic factor receptors from bovine adrenal cortex: guanylate cyclase-linked and cyclase-free receptors. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1987 Apr 14;144(1):244–250. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(87)80502-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waldman S. A., Rapoport R. M., Murad F. Atrial natriuretic factor selectively activates particulate guanylate cyclase and elevates cyclic GMP in rat tissues. J Biol Chem. 1984 Dec 10;259(23):14332–14334. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamaguchi M., Rutledge L. J., Garbers D. L. The primary structure of the rat guanylyl cyclase A/atrial natriuretic peptide receptor gene. J Biol Chem. 1990 Nov 25;265(33):20414–20420. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Bold A. J. Atrial natriuretic factor: a hormone produced by the heart. Science. 1985 Nov 15;230(4727):767–770. doi: 10.1126/science.2932797. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




