Abstract
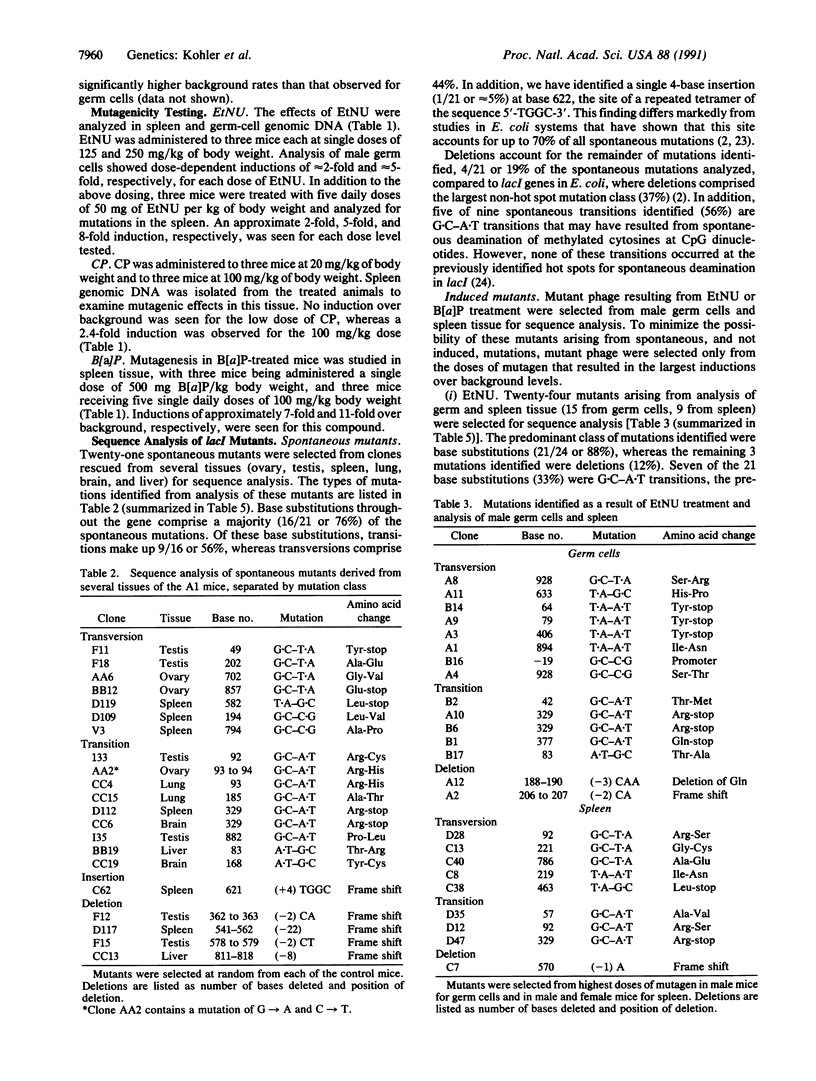
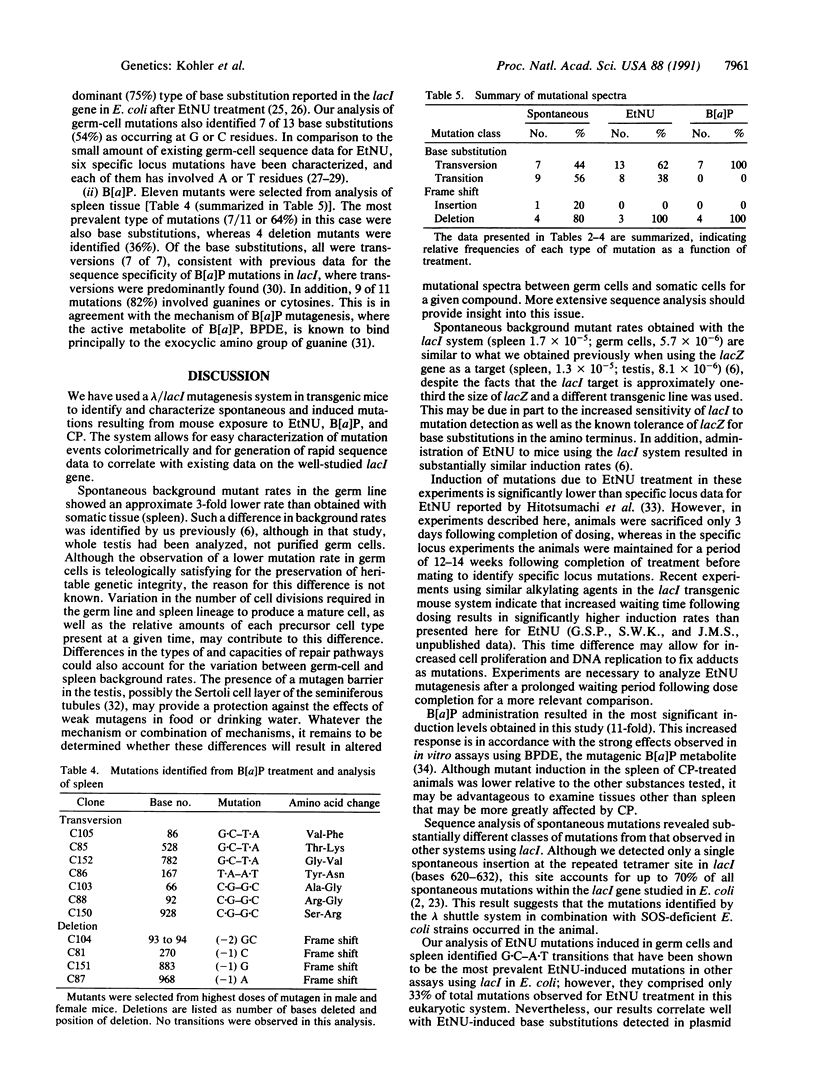
Transgenic mice with a lambda shuttle vector containing a lacI target gene were generated for use as a short-term, in vivo mutagenesis assay. The gene is recovered from the treated mice by exposing mouse genomic DNA to in vitro packaging extracts and plating the rescued phage on agar plates containing 5-bromo-4-chloro-3-indolyl beta-D-galactopyranoside (X-Gal). Phage with mutations in the lacI gene form blue plaques, whereas phage with a nonmutated lacI form colorless plaques. Spontaneous background mutant rates using this system range from 0.6 x 10(-5) to 1.7 x 10(-5), depending upon tissue analyzed, with germ cells exhibiting less than one-third the background rate of somatic tissue. Treatment of the mice with N-ethyl-N-nitrosourea (EtNU), benzo[a]pyrene (B[a]P), or cyclophosphamide caused an induction of mutations over background. Recovery of the lacI target for sequence analysis was performed by genetic excision of a plasmid from the phage using partial filamentous phage origins. The predominant mutations identified from untreated and treated populations were base substitutions. Although it has been shown by others that 70% of all spontaneous mutations within the lacI gene, when replicated in Escherichia coli, occur at a hot spot located at bases 620-632, only 1 of 21 spontaneous mutations has been identified in this region in the transgenic mouse system. In addition, 5 of 9 spontaneous transitions analyzed occur at CpG dinucleotides, whereas no transition mutations were identified at the prokaryotic deamination hot spots occurring at dcm sites (CCA/TGG) within the lacI gene. For EtNU, approximately equal amounts of transitions and transversions were observed, contrasting with B[a]P-induced mutations, in which only transversions were obtained. In addition, B[a]P mutagenesis showed a predominance of mutations (81%) involving cytosines and/or guanines, consistent with its known mode of action. The discovery of a spontaneous mutation spectrum different from that of bacterial assays, coupled with the concordance of EtNU and B[a]P base mutations with the known mechanisms of activity for these mutagens, suggests that this transgenic system will be useful as a short-term, in vivo system for mutagen assessment and analysis of mechanisms leading to mutations.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bellvé A. R., Millette C. F., Bhatnagar Y. M., O'Brien D. A. Dissociation of the mouse testis and characterization of isolated spermatogenic cells. J Histochem Cytochem. 1977 Jul;25(7):480–494. doi: 10.1177/25.7.893996. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coulondre C., Miller J. H., Farabaugh P. J., Gilbert W. Molecular basis of base substitution hotspots in Escherichia coli. Nature. 1978 Aug 24;274(5673):775–780. doi: 10.1038/274775a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crespi C. L., Seixas G. M., Turner T., Penman B. W. Sodium fluoride is a less efficient human cell mutagen at low concentrations. Environ Mol Mutagen. 1990;15(2):71–77. doi: 10.1002/em.2850150203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DuBridge R. B., Tang P., Hsia H. C., Leong P. M., Miller J. H., Calos M. P. Analysis of mutation in human cells by using an Epstein-Barr virus shuttle system. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Jan;7(1):379–387. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.1.379. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eckert K. A., Ingle C. A., Klinedinst D. K., Drinkwater N. R. Molecular analysis of mutations induced in human cells by N-ethyl-N-nitrosourea. Mol Carcinog. 1988;1(1):50–56. doi: 10.1002/mc.2940010111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenstadt E., Warren A. J., Porter J., Atkins D., Miller J. H. Carcinogenic epoxides of benzo[a]pyrene and cyclopenta[cd]pyrene induce base substitutions via specific transversions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Mar;79(6):1945–1949. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.6.1945. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farabaugh P. J., Schmeissner U., Hofer M., Miller J. H. Genetic studies of the lac repressor. VII. On the molecular nature of spontaneous hotspots in the lacI gene of Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1978 Dec 25;126(4):847–857. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90023-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gossen J. A., de Leeuw W. J., Tan C. H., Zwarthoff E. C., Berends F., Lohman P. H., Knook D. L., Vijg J. Efficient rescue of integrated shuttle vectors from transgenic mice: a model for studying mutations in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Oct;86(20):7971–7975. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.20.7971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirko M. K., Schmidt S. P., Hunter T. J., Evancho M. M., Sharp W. V., Donovan D. L. Endothelial cell seeding improves 4 mm PTFE vascular graft performance in antiplatelet medicated dogs. Artery. 1987;14(3):137–153. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hitotsumachi S., Carpenter D. A., Russell W. L. Dose-repetition increases the mutagenic effectiveness of N-ethyl-N-nitrosourea in mouse spermatogonia. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Oct;82(19):6619–6621. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.19.6619. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horsfall M. J., Gordon A. J., Burns P. A., Zielenska M., van der Vliet G. M., Glickman B. W. Mutational specificity of alkylating agents and the influence of DNA repair. Environ Mol Mutagen. 1990;15(2):107–122. doi: 10.1002/em.2850150208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hu Y. C., Guttenplan J. B. Evidence for a major premutagenic ethyldeoxythymidine-DNA adduct in an in vivo system: N-nitroso-N-ethylurea-treated Salmonella typhimurium. Carcinogenesis. 1985 Oct;6(10):1513–1516. doi: 10.1093/carcin/6.10.1513. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohler S. W., Provost G. S., Kretz P. L., Dycaico M. J., Sorge J. A., Short J. M. Development of a short-term, in vivo mutagenesis assay: the effects of methylation on the recovery of a lambda phage shuttle vector from transgenic mice. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 May 25;18(10):3007–3013. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.10.3007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohler S. W., Provost G. S., Kretz P. L., Fieck A., Sorge J. A., Short J. M. The use of transgenic mice for short-term, in vivo mutagenicity testing. Genet Anal Tech Appl. 1990 Dec;7(8):212–218. doi: 10.1016/0735-0651(90)90003-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kretz P. L., Kohler S. W., Short J. M. Identification and characterization of a gene responsible for inhibiting propagation of methylated DNA sequences in mcrA mcrB1 Escherichia coli strains. J Bacteriol. 1991 Aug;173(15):4707–4716. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.15.4707-4716.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langley K. E., Zabin I. beta-Galactosidase alpha complementation: properties of the complemented enzyme and mechanism of the complementation reaction. Biochemistry. 1976 Nov 2;15(22):4866–4875. doi: 10.1021/bi00667a018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lebkowski J. S., Clancy S., Miller J. H., Calos M. P. The lacI shuttle: rapid analysis of the mutagenic specificity of ultraviolet light in human cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(24):8606–8610. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.24.8606. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis S. E., Johnson F. M., Skow L. C., Popp D., Barnett L. B., Popp R. A. A mutation in the beta-globin gene detected in the progeny of a female mouse treated with ethylnitrosourea. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Sep;82(17):5829–5831. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.17.5829. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meehan T., Straub K., Calvin M. Benzo[alpha]pyrene diol epoxide covalently binds to deoxyguanosine and deoxyadenosine in DNA. Nature. 1977 Oct 20;269(5630):725–727. doi: 10.1038/269725a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller J. H., Coulondre C., Farabaugh P. J. Correlation of nonsense sites in the lacI gene with specific codons in the nucleotide sequence. Nature. 1978 Aug 24;274(5673):770–775. doi: 10.1038/274770a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mirkes P. E. Cyclophosphamide teratogenesis: a review. Teratog Carcinog Mutagen. 1985;5(2):75–88. doi: 10.1002/tcm.1770050202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller-Hill B., Crapo L., Gilbert W. Mutants that make more lac repressor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Apr;59(4):1259–1264. doi: 10.1073/pnas.59.4.1259. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newman M. A., Hee S. S., Schoeny R. S. Mutagenesis assays on urines produced by patients administered adriamycin and cyclophosphamide. Environ Mol Mutagen. 1990;16(3):189–203. doi: 10.1002/em.2850160307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peters J., Andrews S. J., Loutit J. F., Clegg J. B. A mouse beta-globin mutant that is an exact model of hemoglobin Rainier in man. Genetics. 1985 Aug;110(4):709–721. doi: 10.1093/genetics/110.4.709. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Popp R. A., Bailiff E. G., Skow L. C., Johnson F. M., Lewis S. E. Analysis of a mouse alpha-globin gene mutation induced by ethylnitrosourea. Genetics. 1983 Sep;105(1):157–167. doi: 10.1093/genetics/105.1.157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richardson K. K., Richardson F. C., Crosby R. M., Swenberg J. A., Skopek T. R. DNA base changes and alkylation following in vivo exposure of Escherichia coli to N-methyl-N-nitrosourea or N-ethyl-N-nitrosourea. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jan;84(2):344–348. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.2.344. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaaper R. M., Danforth B. N., Glickman B. W. Mechanisms of spontaneous mutagenesis: an analysis of the spectrum of spontaneous mutation in the Escherichia coli lacI gene. J Mol Biol. 1986 May 20;189(2):273–284. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90509-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Short J. M., Fernandez J. M., Sorge J. A., Huse W. D. Lambda ZAP: a bacteriophage lambda expression vector with in vivo excision properties. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Aug 11;16(15):7583–7600. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.15.7583. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yatagai F., Glickman B. W. Specificity of spontaneous mutation in the lacI gene cloned into bacteriophage M13. Mutat Res. 1990 Jan;243(1):21–28. doi: 10.1016/0165-7992(90)90118-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]