Abstract
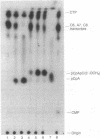
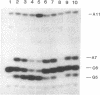
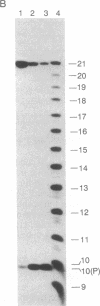
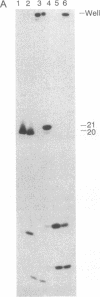
Ternary complexes of RNA polymerase, bearing the nascent RNA transcript, are intermediates in the synthesis of all RNAs and are regulatory targets of factors that control RNA chain elongation and termination. To study the catalytic and regulatory properties of RNA polymerases during elongation, we have developed methods for the preparation of these intermediates halted at defined positions along a DNA template. To our surprise, some of these halted complexes undergo a reaction in which the RNA transcript is cleaved up to 10 nucleotides from its 3'-terminal growing point. The 5'-terminal fragment, bearing a free 3'-OH residue, remains bound to the RNA polymerase-DNA complex and can resume elongation, whereas the 3'-terminal oligonucleotide of 2-10 nucleotides, bearing a 5'-phosphate, is released. RNA cleavage occurs only in the ternary complex and requires a divalent metal ion such as Mg2+. Since RNA polymerases are believed to have a single catalytic site for nucleotide addition, this reaction is unlikely to be due to hydrolysis catalyzed by this site comparable to the 3'----5' exonuclease activity associated with the catalytic center found for some DNA polymerases. Nor is this reaction easily explained by models for transcription elongation that postulate a 12-base-pair DNA.RNA hybrid as intermediate. Instead, we suggest that this is an unusual kind of protein-facilitated reaction in which tight binding of the RNA product to the enzyme strains the RNA phosphodiester linkage, resulting in cleavage of the RNA well away from the catalytic center. By this model, the nascent RNA enters a product binding site beginning 3 or 4 nucleotides from the growing point at the 3' terminus. This RNA binding site extends for up to 16 nucleotides along the protein surface. The stress brought about by this binding appears to vary considerably for different ternary complexes and may play a role in driving the translocation of the RNA polymerase along the DNA.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arndt K. M., Chamberlin M. J. RNA chain elongation by Escherichia coli RNA polymerase. Factors affecting the stability of elongating ternary complexes. J Mol Biol. 1990 May 5;213(1):79–108. doi: 10.1016/S0022-2836(05)80123-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bean B. L., Koren R., Mildvan A. S. Magnetic resonance studies of the conformation of enzyme-bound adenylyl(3' leads to 5')uridine and adenosine 5'-triphosphate on RNA polymerase from Esherichia coli. Biochemistry. 1977 Jul 26;16(15):3322–3333. doi: 10.1021/bi00634a007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bedale W. A., Inman R. B., Cox M. M. RecA protein-facilitated DNA strand breaks. A mechanism for bypassing DNA structural barriers during strand exchange. J Biol Chem. 1991 Apr 5;266(10):6499–6510. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Busby S., Spassky A., Buc H. On the binding of tRNA to Escherichia coli RNA polymerase. Interactions between the core enzyme, DNA and tRNA. Eur J Biochem. 1981 Sep 1;118(3):443–451. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1981.tb05540.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chamberlin M. J., Nierman W. C., Wiggs J., Neff N. A quantitative assay for bacterial RNA polymerases. J Biol Chem. 1979 Oct 25;254(20):10061–10069. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman D. I., Imperiale M. J., Adhya S. L. RNA 3' end formation in the control of gene expression. Annu Rev Genet. 1987;21:453–488. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.21.120187.002321. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gamper H. B., Hearst J. E. A topological model for transcription based on unwinding angle analysis of E. coli RNA polymerase binary, initiation and ternary complexes. Cell. 1982 May;29(1):81–90. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90092-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonzalez N., Wiggs J., Chamberlin M. J. A simple procedure for resolution of Escherichia coli RNA polymerase holoenzyme from core polymerase. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1977 Aug;182(2):404–408. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(77)90521-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guerrier-Takada C., Altman S. Catalytic activity of an RNA molecule prepared by transcription in vitro. Science. 1984 Jan 20;223(4633):285–286. doi: 10.1126/science.6199841. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guerrier-Takada C., Gardiner K., Marsh T., Pace N., Altman S. The RNA moiety of ribonuclease P is the catalytic subunit of the enzyme. Cell. 1983 Dec;35(3 Pt 2):849–857. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90117-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guerrier-Takada C., van Belkum A., Pleij C. W., Altman S. Novel reactions of RNAase P with a tRNA-like structure in turnip yellow mosaic virus RNA. Cell. 1988 Apr 22;53(2):267–272. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90388-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Handschin J. C., Wehrli W. On the kinetics of the rifampicin-RNA-polymerase complex. Differences between crude and purified enzyme fractions. Eur J Biochem. 1976 Jul 1;66(2):309–317. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1976.tb10520.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higuchi R., Krummel B., Saiki R. K. A general method of in vitro preparation and specific mutagenesis of DNA fragments: study of protein and DNA interactions. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Aug 11;16(15):7351–7367. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.15.7351. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krummel B., Chamberlin M. J. RNA chain initiation by Escherichia coli RNA polymerase. Structural transitions of the enzyme in early ternary complexes. Biochemistry. 1989 Sep 19;28(19):7829–7842. doi: 10.1021/bi00445a045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kumar S. A., Krakow J. S. Studies on the product binding sites of the Azotobacter vinelandii ribonucleic acid polymerase. J Biol Chem. 1975 Apr 25;250(8):2878–2884. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kumar S. A. The structure and mechanism of action of bacterial DNA-dependent RNA polymerase. Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 1981;38(3):165–210. doi: 10.1016/0079-6107(81)90013-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levin J. R., Krummel B., Chamberlin M. J. Isolation and properties of transcribing ternary complexes of Escherichia coli RNA polymerase positioned at a single template base. J Mol Biol. 1987 Jul 5;196(1):85–100. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90512-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McClain W. H., Guerrier-Takada C., Altman S. Model substrates for an RNA enzyme. Science. 1987 Oct 23;238(4826):527–530. doi: 10.1126/science.2443980. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rice G. A., Kane C. M., Chamberlin M. J. Footprinting analysis of mammalian RNA polymerase II along its transcript: an alternative view of transcription elongation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 May 15;88(10):4245–4249. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.10.4245. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stein P. J., Mildvan A. S. Magnetic resonance and kinetic studies of initiator-substrate distances on RNA polymerase from Escherichia coli. Biochemistry. 1978 Jun 27;17(13):2675–2684. doi: 10.1021/bi00606a034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Studier F. W., Rosenberg A. H. Genetic and physical mapping of the late region of bacteriophage T7 DNA by use of cloned fragments of T7 DNA. J Mol Biol. 1981 Dec 15;153(3):503–525. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90405-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zaug A. J., Kent J. R., Cech T. R. Reactions of the intervening sequence of the Tetrahymena ribosomal ribonucleic acid precursor: pH dependence of cyclization and site-specific hydrolysis. Biochemistry. 1985 Oct 22;24(22):6211–6218. doi: 10.1021/bi00343a027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Hippel P. H., Bear D. G., Morgan W. D., McSwiggen J. A. Protein-nucleic acid interactions in transcription: a molecular analysis. Annu Rev Biochem. 1984;53:389–446. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.53.070184.002133. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]