Abstract
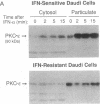
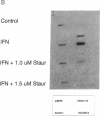
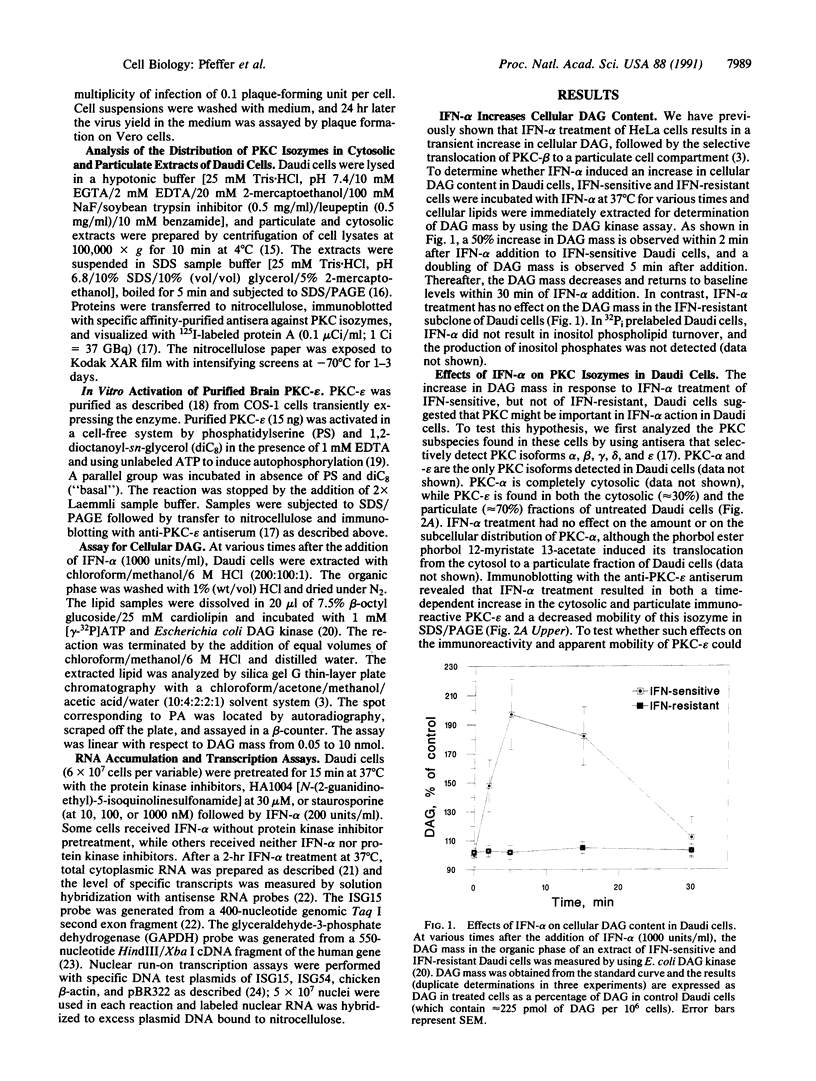
The early events that occur after treatment of the highly interferon alpha (IFN-alpha)-sensitive human lymphoblastoid Daudi cell line with human leukocyte IFN-alpha have been examined. IFN-alpha treatment of Daudi cells results in a rapid and transient increase in the cellular content of diacylglycerol, which occurs in the absence of inositol phospholipid turnover, or an increase in intracellular calcium concentration. Furthermore, IFN-alpha treatment results in a selective, time-dependent activation of the Ca(2+)-independent epsilon isoform of protein kinase C (PKC), while the alpha isoform is unaffected by IFN-alpha treatment. In contrast, IFN-alpha treatment of an IFN-resistant subclone of Daudi cells had no effect on the diacylglycerol content of cells and on the activation of PKC-epsilon. The selective PKC inhibitor staurosporine blocked the transcriptional activation of IFN-alpha-stimulated genes, the cytoplasmic accumulation of mRNAs for these genes, and the induction of antiviral activity by IFN-alpha against vesicular stomatitis virus in IFN-sensitive cells. These observations suggest that transmembrane signaling of IFN-alpha involves diacylglycerol production and activation of PKC-epsilon in Daudi cells.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Branca A. A., Faltynek C. R., D'Alessandro S. B., Baglioni C. Interaction of interferon with cellular receptors. Internalization and degradation of cell-bound interferon. J Biol Chem. 1982 Nov 25;257(22):13291–13296. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daniel-Issakani S., Spiegel A. M., Strulovici B. Lipopolysaccharide response is linked to the GTP binding protein, Gi2, in the promonocytic cell line U937. J Biol Chem. 1989 Dec 5;264(34):20240–20247. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faltynek C. R., Princler G. L., Gusella G. L., Varesio L., Radzioch D. A functional protein kinase C is required for induction of 2-5A synthetase by recombinant interferon-alpha A in Daudi cells. J Biol Chem. 1989 Aug 25;264(24):14305–14311. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang K. P., Chan K. F., Singh T. J., Nakabayashi H., Huang F. L. Autophosphorylation of rat brain Ca2+-activated and phospholipid-dependent protein kinase. J Biol Chem. 1986 Sep 15;261(26):12134–12140. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kessler D. S., Pine R., Pfeffer L. M., Levy D. E., Darnell J. E., Jr Cells resistant to interferon are defective in activation of a promoter-binding factor. EMBO J. 1988 Dec 1;7(12):3779–3783. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03262.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knopf J. L., Lee M. H., Sultzman L. A., Kriz R. W., Loomis C. R., Hewick R. M., Bell R. M. Cloning and expression of multiple protein kinase C cDNAs. Cell. 1986 Aug 15;46(4):491–502. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90874-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larner A. C., Jonak G., Cheng Y. S., Korant B., Knight E., Darnell J. E., Jr Transcriptional induction of two genes in human cells by beta interferon. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Nov;81(21):6733–6737. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.21.6733. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nachshen D. A., Pfeffer L. M., Tamm I. Effect of anti-Ig on cytosolic Ca2+ in Daudi lymphoblastoid cells. J Biol Chem. 1986 Nov 15;261(32):15134–15139. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishizuka Y. Studies and prospectives of the protein kinase c family for cellular regulation. Cancer. 1989 May 15;63(10):1892–1903. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19890515)63:10<1892::aid-cncr2820631005>3.0.co;2-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ono Y., Fujii T., Ogita K., Kikkawa U., Igarashi K., Nishizuka Y. The structure, expression, and properties of additional members of the protein kinase C family. J Biol Chem. 1988 May 15;263(14):6927–6932. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osada S., Mizuno K., Saido T. C., Akita Y., Suzuki K., Kuroki T., Ohno S. A phorbol ester receptor/protein kinase, nPKC eta, a new member of the protein kinase C family predominantly expressed in lung and skin. J Biol Chem. 1990 Dec 25;265(36):22434–22440. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker P. J., Kour G., Marais R. M., Mitchell F., Pears C., Schaap D., Stabel S., Webster C. Protein kinase C--a family affair. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 1989 Aug;65(1-2):1–11. doi: 10.1016/0303-7207(89)90159-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfeffer L. M., Stebbing N., Donner D. B. Cytoskeletal association of human alpha-interferon-receptor complexes in interferon-sensitive and -resistant lymphoblastoid cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 May;84(10):3249–3253. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.10.3249. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfeffer L. M., Strulovici B., Saltiel A. R. Interferon-alpha selectively activates the beta isoform of protein kinase C through phosphatidylcholine hydrolysis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Sep;87(17):6537–6541. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.17.6537. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preiss J., Loomis C. R., Bishop W. R., Stein R., Niedel J. E., Bell R. M. Quantitative measurement of sn-1,2-diacylglycerols present in platelets, hepatocytes, and ras- and sis-transformed normal rat kidney cells. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jul 5;261(19):8597–8600. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reich N. C., Pfeffer L. M. Evidence for involvement of protein kinase C in the cellular response to interferon alpha. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Nov;87(22):8761–8765. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.22.8761. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reich N., Evans B., Levy D., Fahey D., Knight E., Jr, Darnell J. E., Jr Interferon-induced transcription of a gene encoding a 15-kDa protein depends on an upstream enhancer element. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Sep;84(18):6394–6398. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.18.6394. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaap D., Parker P. J., Bristol A., Kriz R., Knopf J. Unique substrate specificity and regulatory properties of PKC-epsilon: a rationale for diversity. FEBS Lett. 1989 Jan 30;243(2):351–357. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(89)80160-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaap D., Parker P. J. Expression, purification, and characterization of protein kinase C-epsilon. J Biol Chem. 1990 May 5;265(13):7301–7307. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strulovici B., Daniel-Issakani S., Baxter G., Knopf J., Sultzman L., Cherwinski H., Nestor J., Jr, Webb D. R., Ransom J. Distinct mechanisms of regulation of protein kinase C epsilon by hormones and phorbol diesters. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jan 5;266(1):168–173. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strulovici B., Daniel-Issakani S., Oto E., Nestor J., Jr, Chan H., Tsou A. P. Activation of distinct protein kinase C isozymes by phorbol esters: correlation with induction of interleukin 1 beta gene expression. Biochemistry. 1989 Apr 18;28(8):3569–3576. doi: 10.1021/bi00434a063. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tiwari R. K., Kusari J., Kumar R., Sen G. C. Gene induction by interferons and double-stranded RNA: selective inhibition by 2-aminopurine. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Oct;8(10):4289–4294. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.10.4289. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tso J. Y., Sun X. H., Kao T. H., Reece K. S., Wu R. Isolation and characterization of rat and human glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase cDNAs: genomic complexity and molecular evolution of the gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Apr 11;13(7):2485–2502. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.7.2485. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wathelet M. G., Clauss I. M., Paillard F. C., Huez G. A. 2-Aminopurine selectively blocks the transcriptional activation of cellular genes by virus, double-stranded RNA and interferons in human cells. Eur J Biochem. 1989 Oct 1;184(3):503–509. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1989.tb15043.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yap W. H., Teo T. S., Tan Y. H. An early event in the interferon-induced transmembrane signaling process. Science. 1986 Oct 17;234(4774):355–358. doi: 10.1126/science.2429366. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]