Abstract
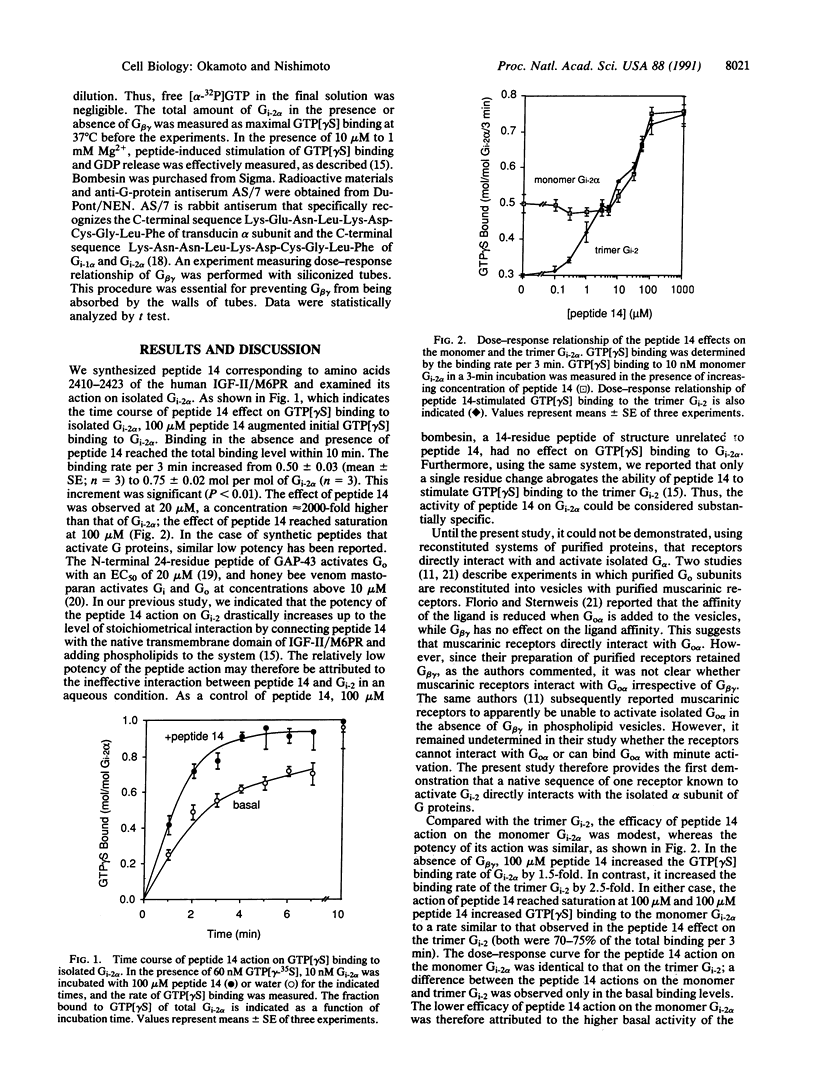
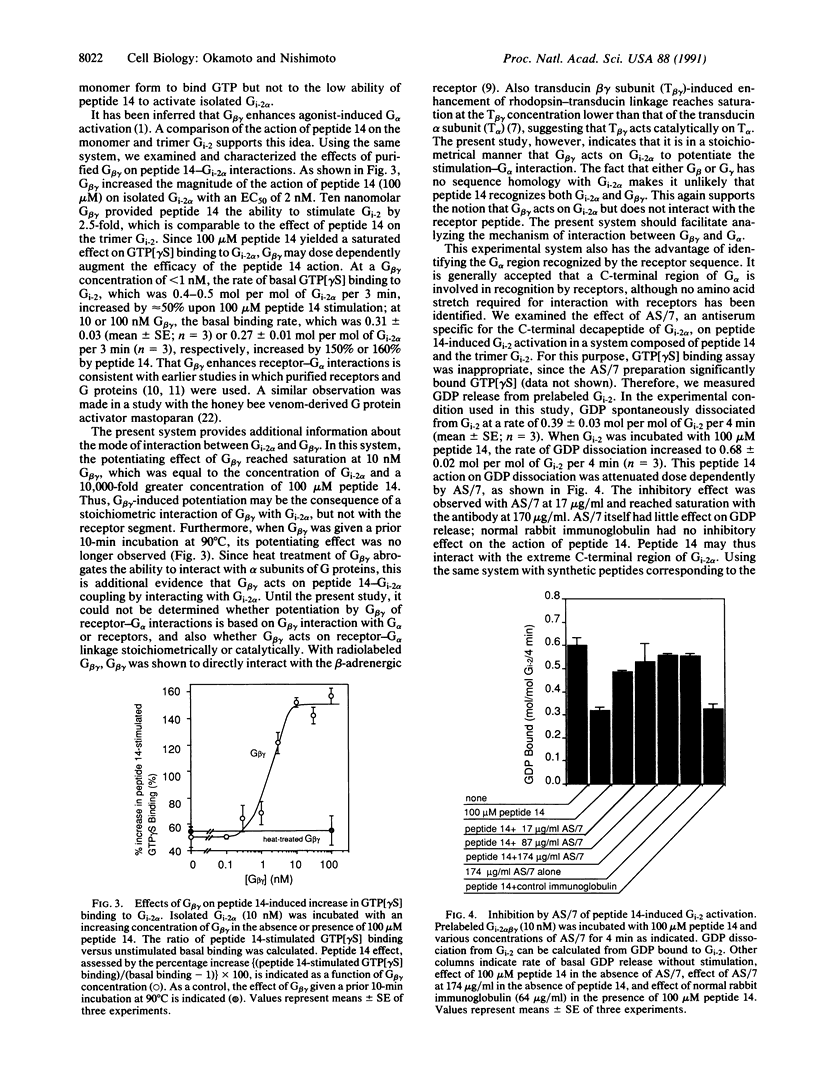
The peptide Arg2410-Lys2423 (peptide 14) of the human insulin-like growth factor II/mannose 6-phosphate receptor directly activates Gi-2, a GTP-binding protein (G protein), and is responsible for Gi-2 activating function of the receptor. To characterize the basic mechanism of couplings between receptor stimulation and subunits of G proteins, we constructed a system consisting of peptide 14 and alpha and beta gamma subunits of Gi-2 in aqueous solution. Peptide 14 significantly increased the rate of guanosine 5'-[gamma-thio]triphosphate binding to isolated Gi-2 alpha from 0.50 +/- 0.03 (mean +/- SE; n = 3) to 0.75 +/- 0.02 mol per mol of Gi-2 alpha per 3 min (n = 3) at 100 microM. In this system, G beta gamma does dependently potentiated the peptide 14 action on Gi-2 alpha; and G beta gamma-induced potentiation reached saturation at a concentration comparable to that of Gi-2 alpha. An antibody specific for the C-terminal decapeptide of Gi-2 alpha reduce peptide 14-stimulated GDP release from Gi-2 to the basal level. This simplified system indicates that (i) the receptor sequence directly interacts with isolated Gi-2 alpha at its C-terminal region and (ii) G beta gamma potentiates the stimulation-G alpha coupling in a stoichiometrical manner for G alpha.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Asano T., Morishita R., Semba R., Itoh H., Kaziro Y., Kato K. Identification of lung major GTP-binding protein as Gi2 and its distribution in various rat tissues determined by immunoassay. Biochemistry. 1989 May 30;28(11):4749–4754. doi: 10.1021/bi00437a035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Florio V. A., Sternweis P. C. Mechanisms of muscarinic receptor action on Go in reconstituted phospholipid vesicles. J Biol Chem. 1989 Mar 5;264(7):3909–3915. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Florio V. A., Sternweis P. C. Reconstitution of resolved muscarinic cholinergic receptors with purified GTP-binding proteins. J Biol Chem. 1985 Mar 25;260(6):3477–3483. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fung B. K. Characterization of transducin from bovine retinal rod outer segments. I. Separation and reconstitution of the subunits. J Biol Chem. 1983 Sep 10;258(17):10495–10502. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fung B. K., Nash C. R. Characterization of transducin from bovine retinal rod outer segments. II. Evidence for distinct binding sites and conformational changes revealed by limited proteolysis with trypsin. J Biol Chem. 1983 Sep 10;258(17):10503–10510. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilman A. G. G proteins: transducers of receptor-generated signals. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:615–649. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.56.070187.003151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hekman M., Feder D., Keenan A. K., Gal A., Klein H. W., Pfeuffer T., Levitzki A., Helmreich E. J. Reconstitution of beta-adrenergic receptor with components of adenylate cyclase. EMBO J. 1984 Dec 20;3(13):3339–3345. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02301.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higashijima T., Burnier J., Ross E. M. Regulation of Gi and Go by mastoparan, related amphiphilic peptides, and hydrophobic amines. Mechanism and structural determinants of activity. J Biol Chem. 1990 Aug 25;265(24):14176–14186. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higashijima T., Uzu S., Nakajima T., Ross E. M. Mastoparan, a peptide toxin from wasp venom, mimics receptors by activating GTP-binding regulatory proteins (G proteins). J Biol Chem. 1988 May 15;263(14):6491–6494. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Im M. J., Holzhöfer A., Böttinger H., Pfeuffer T., Helmreich E. J. Interactions of pure beta gamma-subunits of G-proteins with purified beta 1-adrenoceptor. FEBS Lett. 1988 Jan 25;227(2):225–229. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(88)80903-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katada T., Oinuma M., Kusakabe K., Ui M. A new GTP-binding protein in brain tissues serving as the specific substrate of islet-activating protein, pertussis toxin. FEBS Lett. 1987 Mar 23;213(2):353–358. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(87)81521-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masters S. B., Sullivan K. A., Miller R. T., Beiderman B., Lopez N. G., Ramachandran J., Bourne H. R. Carboxyl terminal domain of Gs alpha specifies coupling of receptors to stimulation of adenylyl cyclase. Science. 1988 Jul 22;241(4864):448–451. doi: 10.1126/science.2899356. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murayama Y., Okamoto T., Ogata E., Asano T., Iiri T., Katada T., Ui M., Grubb J. H., Sly W. S., Nishimoto I. Distinctive regulation of the functional linkage between the human cation-independent mannose 6-phosphate receptor and GTP-binding proteins by insulin-like growth factor II and mannose 6-phosphate. J Biol Chem. 1990 Oct 15;265(29):17456–17462. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishimoto I., Murayama Y., Katada T., Ui M., Ogata E. Possible direct linkage of insulin-like growth factor-II receptor with guanine nucleotide-binding proteins. J Biol Chem. 1989 Aug 25;264(24):14029–14038. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishimoto I., Ogata E., Okamoto T. Guanine nucleotide-binding protein interacting but unstimulating sequence located in insulin-like growth factor II receptor. Its autoinhibitory characteristics and structural determinants. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jul 5;266(19):12747–12751. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okamoto T., Asano T., Harada S., Ogata E., Nishimoto I. Regulation of transmembrane signal transduction of insulin-like growth factor II by competence type growth factors or viral ras p21. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jan 15;266(2):1085–1091. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okamoto T., Katada T., Murayama Y., Ui M., Ogata E., Nishimoto I. A simple structure encodes G protein-activating function of the IGF-II/mannose 6-phosphate receptor. Cell. 1990 Aug 24;62(4):709–717. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90116-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okamoto T., Nishimoto I., Murayama Y., Ohkuni Y., Ogata E. Insulin-like growth factor-II/mannose 6-phosphate receptor is incapable of activating GTP-binding proteins in response to mannose 6-phosphate, but capable in response to insulin-like growth factor-II. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1990 May 16;168(3):1201–1210. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(90)91156-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osawa S., Dhanasekaran N., Woon C. W., Johnson G. L. G alpha i-G alpha s chimeras define the function of alpha chain domains in control of G protein activation and beta gamma subunit complex interactions. Cell. 1990 Nov 16;63(4):697–706. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90136-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rall T., Harris B. A. Identification of the lesion in the stimulatory GTP-binding protein of the uncoupled S49 lymphoma. FEBS Lett. 1987 Nov 30;224(2):365–371. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(87)80486-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simonds W. F., Goldsmith P. K., Codina J., Unson C. G., Spiegel A. M. Gi2 mediates alpha 2-adrenergic inhibition of adenylyl cyclase in platelet membranes: in situ identification with G alpha C-terminal antibodies. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Oct;86(20):7809–7813. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.20.7809. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strittmatter S. M., Valenzuela D., Kennedy T. E., Neer E. J., Fishman M. C. G0 is a major growth cone protein subject to regulation by GAP-43. Nature. 1990 Apr 26;344(6269):836–841. doi: 10.1038/344836a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sullivan K. A., Miller R. T., Masters S. B., Beiderman B., Heideman W., Bourne H. R. Identification of receptor contact site involved in receptor-G protein coupling. Nature. 1987 Dec 24;330(6150):758–760. doi: 10.1038/330758a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ui M., Katada T., Murayama T., Kurose H., Yajima M., Tamura M., Nakamura T., Nogimori K. Islet-activating protein, pertussis toxin: a specific uncoupler of receptor-mediated inhibition of adenylate cyclase. Adv Cyclic Nucleotide Protein Phosphorylation Res. 1984;17:145–151. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



