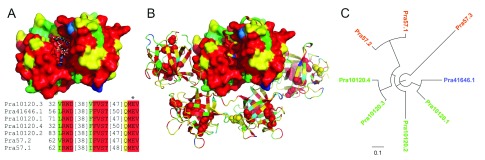
Figure 3. Pierisin conservation mapping to structure homolog and phylogenetic tree of the ricin domains.
An alignment of the MTX holotoxin (PDB 2vse) sequence with the Pieris rapae pierisins was used to map sequence conservations calculated for the pierisin sequences. Conservations were colored in rainbow from blue (variable) to red (conserved). ( A) The N-terminal ADP-ribosylation toxin domain (shown in surface representation) of the MTX holotoxin structure was superimposed with the cholera ADP-ribosylation toxin bound to its NAD+ substrate (shown in ball and stick) to highlight the NAD+ binding pocket. An alignment of residues that contribute to the binding pocket are depicted below the structure, highlighted according to conservation, with the catalytic E marked by an asterisk. ( B) The N-terminal ADP-ribosylation toxin domain (shown in surface representation) of the MTX holotoxin is inhibited by a conserved inhibitory linker region (shown in tube) that blocks the substrate binding pocket. The C-terminal ricin-like domains of the holotoxin are depicted in cartoon, with corresponding sidechains of QxW motifs depicted in sphere. ( C) Phylogenetic tree of ricin domains in 8 pierisins from Pieris rapae.