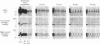Abstract
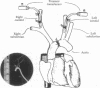
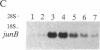
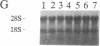
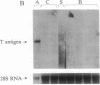
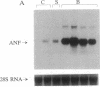
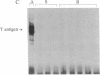
To study the mechanisms that activate expression of the atrial natriuretic factor (ANF) gene during pressure-induced hypertrophy, we have developed and characterized an in vivo murine model of myocardial cell hypertrophy. We employed microsurgical techniques to produce a stable 35- to 45-mmHg pressure gradient across the thoracic aorta of the mouse that is associated with rapid and transient expression of an immediate-early gene program (c-fos/c-jun/junB/Egr-1/nur-77), an increase in heart weight/body weight ratio, and up-regulation of the endogenous ANF gene. These responses that are identical to those in cultured cell and other in vivo models of hypertrophy. To determine whether tissue-specific and inducible expression of the ANF gene can be segregated, we used a transgenic mouse line in which 500 base pairs of the human ANF promoter region directs atrial-specific expression of the simian virus 40 large tumor antigen (T antigen), with no detectable expression in the ventricles. Thoracic aortic banding of these mice led to a 20-fold increase in the endogenous ANF mRNA in the ventricle but no detectable expression of the T-antigen marker gene. This result provides evidence that atrial-specific and inducible expression of the ANF gene can be segregated, suggesting that a distinct set of regulatory cis sequences may mediate the up-regulation of the ANF gene during in vivo pressure overload hypertrophy. This murine model demonstrates the utility of microsurgical techniques to study in vivo cardiac physiology in transgenic mice and should allow the application of genetic approaches to identify the mechanisms that activate ventricular expression of the ANF gene during in vivo hypertrophy.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arai H., Nakao K., Saito Y., Morii N., Sugawara A., Yamada T., Itoh H., Shiono S., Mukoyama M., Ohkubo H. Augmented expression of atrial natriuretic polypeptide gene in ventricles of spontaneously hypertensive rats (SHR) and SHR-stroke prone. Circ Res. 1988 May;62(5):926–930. doi: 10.1161/01.res.62.5.926. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bishopric N. H., Simpson P. C., Ordahl C. P. Induction of the skeletal alpha-actin gene in alpha 1-adrenoceptor-mediated hypertrophy of rat cardiac myocytes. J Clin Invest. 1987 Oct;80(4):1194–1199. doi: 10.1172/JCI113179. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiu R., Angel P., Karin M. Jun-B differs in its biological properties from, and is a negative regulator of, c-Jun. Cell. 1989 Dec 22;59(6):979–986. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90754-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen D. R., Curran T. fra-1: a serum-inducible, cellular immediate-early gene that encodes a fos-related antigen. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 May;8(5):2063–2069. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.5.2063. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Day M. L., Schwartz D., Wiegand R. C., Stockman P. T., Brunnert S. R., Tolunay H. E., Currie M. G., Standaert D. G., Needleman P. Ventricular atriopeptin. Unmasking of messenger RNA and peptide synthesis by hypertrophy or dexamethasone. Hypertension. 1987 May;9(5):485–491. doi: 10.1161/01.hyp.9.5.485. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwards B. S., Ackermann D. M., Lee M. E., Reeder G. S., Wold L. E., Burnett J. C., Jr Identification of atrial natriuretic factor within ventricular tissue in hamsters and humans with congestive heart failure. J Clin Invest. 1988 Jan;81(1):82–86. doi: 10.1172/JCI113314. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Field L. J. Atrial natriuretic factor-SV40 T antigen transgenes produce tumors and cardiac arrhythmias in mice. Science. 1988 Feb 26;239(4843):1029–1033. doi: 10.1126/science.2964082. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franch H. A., Dixon R. A., Blaine E. H., Siegl P. K. Ventricular atrial natriuretic factor in the cardiomyopathic hamster model of congestive heart failure. Circ Res. 1988 Jan;62(1):31–36. doi: 10.1161/01.res.62.1.31. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanahan D. Transgenic mice as probes into complex systems. Science. 1989 Dec 8;246(4935):1265–1275. doi: 10.1126/science.2686032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hazel T. G., Nathans D., Lau L. F. A gene inducible by serum growth factors encodes a member of the steroid and thyroid hormone receptor superfamily. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Nov;85(22):8444–8448. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.22.8444. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson S. A., Spencer M., Sen A., Kumar C., Siddiqui M. A., Chien K. R. Structure, organization, and expression of the rat cardiac myosin light chain-2 gene. Identification of a 250-base pair fragment which confers cardiac-specific expression. J Biol Chem. 1989 Oct 25;264(30):18142–18148. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isoyama S., Wei J. Y., Izumo S., Fort P., Schoen F. J., Grossman W. Effect of age on the development of cardiac hypertrophy produced by aortic constriction in the rat. Circ Res. 1987 Sep;61(3):337–345. doi: 10.1161/01.res.61.3.337. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iwaki K., Sukhatme V. P., Shubeita H. E., Chien K. R. Alpha- and beta-adrenergic stimulation induces distinct patterns of immediate early gene expression in neonatal rat myocardial cells. fos/jun expression is associated with sarcomere assembly; Egr-1 induction is primarily an alpha 1-mediated response. J Biol Chem. 1990 Aug 15;265(23):13809–13817. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Izumo S., Nadal-Ginard B., Mahdavi V. Protooncogene induction and reprogramming of cardiac gene expression produced by pressure overload. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jan;85(2):339–343. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.2.339. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Izumo S., Nadal-Ginard B., Mahdavi V. Protooncogene induction and reprogramming of cardiac gene expression produced by pressure overload. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jan;85(2):339–343. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.2.339. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson T., Allard M. F., Sreenan C. M., Doss L. K., Bishop S. P., Swain J. L. The c-myc proto-oncogene regulates cardiac development in transgenic mice. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Jul;10(7):3709–3716. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.7.3709. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knowlton K. U., Baracchini E., Ross R. S., Harris A. N., Henderson S. A., Evans S. M., Glembotski C. C., Chien K. R. Co-regulation of the atrial natriuretic factor and cardiac myosin light chain-2 genes during alpha-adrenergic stimulation of neonatal rat ventricular cells. Identification of cis sequences within an embryonic and a constitutive contractile protein gene which mediate inducible expression. J Biol Chem. 1991 Apr 25;266(12):7759–7768. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Komuro I., Kurabayashi M., Takaku F., Yazaki Y. Expression of cellular oncogenes in the myocardium during the developmental stage and pressure-overloaded hypertrophy of the rat heart. Circ Res. 1988 Jun;62(6):1075–1079. doi: 10.1161/01.res.62.6.1075. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lattion A. L., Michel J. B., Arnauld E., Corvol P., Soubrier F. Myocardial recruitment during ANF mRNA increase with volume overload in the rat. Am J Physiol. 1986 Nov;251(5 Pt 2):H890–H896. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1986.251.5.H890. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee H. R., Henderson S. A., Reynolds R., Dunnmon P., Yuan D., Chien K. R. Alpha 1-adrenergic stimulation of cardiac gene transcription in neonatal rat myocardial cells. Effects on myosin light chain-2 gene expression. J Biol Chem. 1988 May 25;263(15):7352–7358. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee R. T., Bloch K. D., Pfeffer J. M., Pfeffer M. A., Neer E. J., Seidman C. E. Atrial natriuretic factor gene expression in ventricles of rats with spontaneous biventricular hypertrophy. J Clin Invest. 1988 Feb;81(2):431–434. doi: 10.1172/JCI113337. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Long C. S., Ordahl C. P., Simpson P. C. Alpha 1-adrenergic receptor stimulation of sarcomeric actin isogene transcription in hypertrophy of cultured rat heart muscle cells. J Clin Invest. 1989 Mar;83(3):1078–1082. doi: 10.1172/JCI113951. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan H. E., Gordon E. E., Kira Y., Chua H. L., Russo L. A., Peterson C. J., McDermott P. J., Watson P. A. Biochemical mechanisms of cardiac hypertrophy. Annu Rev Physiol. 1987;49:533–543. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.49.030187.002533. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mulvagh S. L., Michael L. H., Perryman M. B., Roberts R., Schneider M. D. A hemodynamic load in vivo induces cardiac expression of the cellular oncogene, c-myc. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1987 Sep 15;147(2):627–636. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(87)90977-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nair K. G., Cutilletta A. F., Zak R., Koide T., Rabinowitz M. Biochemical correlates of cardiac hypertrophy. I. Experimental model; changes in heart weight, RNA content, and nuclear RNA polymerase activity. Circ Res. 1968 Sep;23(3):451–462. doi: 10.1161/01.res.23.3.451. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sen A., Dunnmon P., Henderson S. A., Gerard R. D., Chien K. R. Terminally differentiated neonatal rat myocardial cells proliferate and maintain specific differentiated functions following expression of SV40 large T antigen. J Biol Chem. 1988 Dec 15;263(35):19132–19136. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shubeita H. E., McDonough P. M., Harris A. N., Knowlton K. U., Glembotski C. C., Brown J. H., Chien K. R. Endothelin induction of inositol phospholipid hydrolysis, sarcomere assembly, and cardiac gene expression in ventricular myocytes. A paracrine mechanism for myocardial cell hypertrophy. J Biol Chem. 1990 Nov 25;265(33):20555–20562. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simpson P. Norepinephrine-stimulated hypertrophy of cultured rat myocardial cells is an alpha 1 adrenergic response. J Clin Invest. 1983 Aug;72(2):732–738. doi: 10.1172/JCI111023. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Starksen N. F., Simpson P. C., Bishopric N., Coughlin S. R., Lee W. M., Escobedo J. A., Williams L. T. Cardiac myocyte hypertrophy is associated with c-myc protooncogene expression. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Nov;83(21):8348–8350. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.21.8348. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waspe L. E., Ordahl C. P., Simpson P. C. The cardiac beta-myosin heavy chain isogene is induced selectively in alpha 1-adrenergic receptor-stimulated hypertrophy of cultured rat heart myocytes. J Clin Invest. 1990 Apr;85(4):1206–1214. doi: 10.1172/JCI114554. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zeller R., Bloch K. D., Williams B. S., Arceci R. J., Seidman C. E. Localized expression of the atrial natriuretic factor gene during cardiac embryogenesis. Genes Dev. 1987 Sep;1(7):693–698. doi: 10.1101/gad.1.7.693. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhu H., Garcia A. V., Ross R. S., Evans S. M., Chien K. R. A conserved 28-base-pair element (HF-1) in the rat cardiac myosin light-chain-2 gene confers cardiac-specific and alpha-adrenergic-inducible expression in cultured neonatal rat myocardial cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Apr;11(4):2273–2281. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.4.2273. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]