Abstract
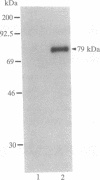
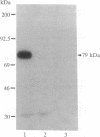
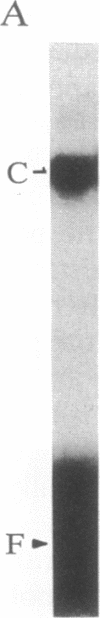
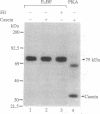
We previously described the purification and characterization of E1BF, a rat rRNA gene core promoter-binding factor that consists of two polypeptides of 89 and 79 kDa. When this factor was incubated in the absence of any exogenous protein kinase under conditions optimal for protein phosphorylation, the 79-kDa polypeptide of E1BF was selectively phosphorylated. The labeled phosphate could be removed from the E1BF polypeptide by treatment with calf intestinal alkaline phosphatase or potato acid phosphatase. Elution of the protein from the E1BF-promoter complex formed in an electrophoretic mobility-shift assay followed by incubation of the concentrated eluent with [gamma-32P] ATP resulted in the selective labeling of the 79-kDa band. The E1BF-associated protein kinase did not phosphorylate casein or histone H1. Fraction DE-B, a preparation containing RNA polymerase I and all polymerase I transcription factors (including E1BF), lost polymerase I transcriptional activity when treated with phosphatase. The phosphatase-induced inactivation of polymerase I activity associated with fraction DE-B could be reversed by the addition of purified E1BF. Treatment of purified E1BF with heat, SDS, or an ATP affinity analog eliminated its capacity to reactivate dephosphorylated fraction DE-B. These data demonstrate that (i) polymerase I promoter-binding factor E1BF contains an intrinsic substrate-specific protein kinase and (ii) E1BF is an essential polymerase I transcription factor that can modulate rRNA gene transcription by protein phosphorylation. Further, these studies have provided a direct means to identify a protein kinase or any other enzyme that can interact with a specific DNA sequence.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Basu M., Biswas R., Das M. 42,000-molecular weight EGF receptor has protein kinase activity. Nature. 1984 Oct 4;311(5985):477–480. doi: 10.1038/311477a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyle W. J., Smeal T., Defize L. H., Angel P., Woodgett J. R., Karin M., Hunter T. Activation of protein kinase C decreases phosphorylation of c-Jun at sites that negatively regulate its DNA-binding activity. Cell. 1991 Feb 8;64(3):573–584. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90241-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carter T., Vancurová I., Sun I., Lou W., DeLeon S. A DNA-activated protein kinase from HeLa cell nuclei. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Dec;10(12):6460–6471. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.12.6460. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cherry J. R., Johnson T. R., Dollard C., Shuster J. R., Denis C. L. Cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase phosphorylates and inactivates the yeast transcriptional activator ADR1. Cell. 1989 Feb 10;56(3):409–419. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90244-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dixit A., Garg L. C., Chao W., Jacob S. T. An enhancer element in the far upstream spacer region of rat ribosomal RNA gene. J Biol Chem. 1987 Aug 25;262(24):11616–11622. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duceman B. W., Rose K. M., Jacob S. T. Activation of purified hepatoma RNA polymerase I by homologous protein kinase NII. J Biol Chem. 1981 Nov 10;256(21):10755–10758. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garg L. C., Dixit A., Jacob S. T. A 37-base pair element in the far upstream spacer region can enhance transcription of rat rDNA in vitro and can bind to the core promoter-binding factor(s). J Biol Chem. 1989 Jan 5;264(1):220–224. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonzalez G. A., Montminy M. R. Cyclic AMP stimulates somatostatin gene transcription by phosphorylation of CREB at serine 133. Cell. 1989 Nov 17;59(4):675–680. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90013-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunter T., Cooper J. A. Protein-tyrosine kinases. Annu Rev Biochem. 1985;54:897–930. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.54.070185.004341. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson S. P., MacDonald J. J., Lees-Miller S., Tjian R. GC box binding induces phosphorylation of Sp1 by a DNA-dependent protein kinase. Cell. 1990 Oct 5;63(1):155–165. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90296-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurl R. N., Rothblum L. I., Jacob S. T. A purified fraction containing RNA polymerase I that can accurately transcribe rat ribosomal RNA gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Nov;81(21):6672–6675. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.21.6672. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lopez V., Stevens T., Lindquist R. N. Vanadium ion inhibition of alkaline phosphatase-catalyzed phosphate ester hydrolysis. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1976 Jul;175(1):31–38. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(76)90482-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raychaudhuri P., Bagchi S., Nevins J. R. DNA-binding activity of the adenovirus-induced E4F transcription factor is regulated by phosphorylation. Genes Dev. 1989 May;3(5):620–627. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.5.620. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rose K. M., Bell L. E., Siefken D. A., Jacob S. T. A heparin-sensitive nuclear protein kinase. Purification, properties, and increased activity in rat hepatoma relative to liver. J Biol Chem. 1981 Jul 25;256(14):7468–7477. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothblum L. I., Reddy R., Cassidy B. Transcription initiation site of rat ribosomal DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Nov 25;10(22):7345–7362. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.22.7345. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schnapp A., Pfleiderer C., Rosenbauer H., Grummt I. A growth-dependent transcription initiation factor (TIF-IA) interacting with RNA polymerase I regulates mouse ribosomal RNA synthesis. EMBO J. 1990 Sep;9(9):2857–2863. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07475.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seargeant L. E., Stinson R. A. Inhibition of human alkaline phosphatases by vanadate. Biochem J. 1979 Jul 1;181(1):247–250. doi: 10.1042/bj1810247. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sollner-Webb B., Tower J. Transcription of cloned eukaryotic ribosomal RNA genes. Annu Rev Biochem. 1986;55:801–830. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.55.070186.004101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sorger P. K., Pelham H. R. Yeast heat shock factor is an essential DNA-binding protein that exhibits temperature-dependent phosphorylation. Cell. 1988 Sep 9;54(6):855–864. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(88)91219-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka M., Herr W. Differential transcriptional activation by Oct-1 and Oct-2: interdependent activation domains induce Oct-2 phosphorylation. Cell. 1990 Feb 9;60(3):375–386. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90589-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu J. Y., Zhou Z. Y., Judd A., Cartwright C. A., Robinson W. S. The hepatitis B virus-encoded transcriptional trans-activator hbx appears to be a novel protein serine/threonine kinase. Cell. 1990 Nov 16;63(4):687–695. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90135-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yarden Y., Ullrich A. Growth factor receptor tyrosine kinases. Annu Rev Biochem. 1988;57:443–478. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.57.070188.002303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang J., Jacob S. T. Purification and characterization of a novel factor which stimulates rat ribosomal gene transcription in vitro by interacting with enhancer and core promoter elements. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Oct;10(10):5177–5186. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.10.5177. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zoller M. J., Taylor S. S. Affinity labeling of the nucleotide binding site of the catalytic subunit of cAMP-dependent protein kinase using p-fluorosulfonyl-[14C]benzoyl 5'-adenosine. Identification of a modified lysine residue. J Biol Chem. 1979 Sep 10;254(17):8363–8368. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]