Abstract
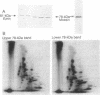
Moesin (membrane-organizing extension spike protein, pronounced mó ez in) has previously been isolated from bovine uterus and characterized as a possible receptor protein for heparan sulfate. We now have cloned and sequenced its complete cDNA, which represents a single 4.2-kilobase mRNA encoding a protein of 577 amino acids. It contains no apparent signal peptide or transmembrane domain. In addition, the protein shows significant sequence identity (72%) to ezrin (cytovillin, p81), as well as similarity to protein 4.1 and talin. All of the latter proteins have been postulated to serve as structural links between the plasma membrane and the cytoskeleton. A similar role for moesin is implied by structure and domain predictions derived from the cDNA-deduced peptide sequence. Furthermore, our data indicate that moesin is identical to the 77-kDa band that copurifies with ezrin in its isolation from human placenta [Bretscher, A. (1989) J. Cell Biol. 108, 921-930].
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson R. A., Marchesi V. T. Regulation of the association of membrane skeletal protein 4.1 with glycophorin by a polyphosphoinositide. Nature. 1985 Nov 21;318(6043):295–298. doi: 10.1038/318295a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birgbauer E., Solomon F. A marginal band-associated protein has properties of both microtubule- and microfilament-associated proteins. J Cell Biol. 1989 Oct;109(4 Pt 1):1609–1620. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.4.1609. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bretscher A. Purification of an 80,000-dalton protein that is a component of the isolated microvillus cytoskeleton, and its localization in nonmuscle cells. J Cell Biol. 1983 Aug;97(2):425–432. doi: 10.1083/jcb.97.2.425. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bretscher A. Rapid phosphorylation and reorganization of ezrin and spectrin accompany morphological changes induced in A-431 cells by epidermal growth factor. J Cell Biol. 1989 Mar;108(3):921–930. doi: 10.1083/jcb.108.3.921. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burridge K., Mangeat P. An interaction between vinculin and talin. Nature. 1984 Apr 19;308(5961):744–746. doi: 10.1038/308744a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cardin A. D., Weintraub H. J. Molecular modeling of protein-glycosaminoglycan interactions. Arteriosclerosis. 1989 Jan-Feb;9(1):21–32. doi: 10.1161/01.atv.9.1.21. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christmas P., Callaway J., Fallon J., Jones J., Haigler H. T. Selective secretion of annexin 1, a protein without a signal sequence, by the human prostate gland. J Biol Chem. 1991 Feb 5;266(4):2499–2507. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conboy J., Kan Y. W., Shohet S. B., Mohandas N. Molecular cloning of protein 4.1, a major structural element of the human erythrocyte membrane skeleton. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Dec;83(24):9512–9516. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.24.9512. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Correas I., Leto T. L., Speicher D. W., Marchesi V. T. Identification of the functional site of erythrocyte protein 4.1 involved in spectrin-actin associations. J Biol Chem. 1986 Mar 5;261(7):3310–3315. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devereux J., Haeberli P., Smithies O. A comprehensive set of sequence analysis programs for the VAX. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 11;12(1 Pt 1):387–395. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.1part1.387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forte J. G., Hanzel D. K., Okamoto C., Chow D., Urushidani T. Membrane and protein recycling associated with gastric HCl secretion. J Intern Med Suppl. 1990;732:17–26. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2796.1990.tb01467.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gould K. L., Bretscher A., Esch F. S., Hunter T. cDNA cloning and sequencing of the protein-tyrosine kinase substrate, ezrin, reveals homology to band 4.1. EMBO J. 1989 Dec 20;8(13):4133–4142. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08598.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gould K. L., Cooper J. A., Bretscher A., Hunter T. The protein-tyrosine kinase substrate, p81, is homologous to a chicken microvillar core protein. J Cell Biol. 1986 Feb;102(2):660–669. doi: 10.1083/jcb.102.2.660. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hay E. D. Theory for epithelial-mesenchymal transformation based on the "fixed cortex" cell motility model. Cell Motil Cytoskeleton. 1989;14(4):455–457. doi: 10.1002/cm.970140403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. Compilation and analysis of sequences upstream from the translational start site in eukaryotic mRNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 25;12(2):857–872. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.2.857. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lankes W., Griesmacher A., Grünwald J., Schwartz-Albiez R., Keller R. A heparin-binding protein involved in inhibition of smooth-muscle cell proliferation. Biochem J. 1988 May 1;251(3):831–842. doi: 10.1042/bj2510831. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lomax K. J., Leto T. L., Nunoi H., Gallin J. I., Malech H. L. Recombinant 47-kilodalton cytosol factor restores NADPH oxidase in chronic granulomatous disease. Science. 1989 Jul 28;245(4916):409–412. doi: 10.1126/science.2547247. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muesch A., Hartmann E., Rohde K., Rubartelli A., Sitia R., Rapoport T. A. A novel pathway for secretory proteins? Trends Biochem Sci. 1990 Mar;15(3):86–88. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(90)90186-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pakkanen R., Hedman K., Turunen O., Wahlström T., Vaheri A. Microvillus-specific Mr 75,000 plasma membrane protein of human choriocarcinoma cells. J Histochem Cytochem. 1987 Aug;35(8):809–816. doi: 10.1177/35.8.3298422. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pakkanen R. Immunofluorescent and immunochemical evidence for the expression of cytovillin in the microvilli of a wide range of cultured human cells. J Cell Biochem. 1988 Sep;38(1):65–75. doi: 10.1002/jcb.240380107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rees D. J., Ades S. E., Singer S. J., Hynes R. O. Sequence and domain structure of talin. Nature. 1990 Oct 18;347(6294):685–689. doi: 10.1038/347685a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubartelli A., Cozzolino F., Talio M., Sitia R. A novel secretory pathway for interleukin-1 beta, a protein lacking a signal sequence. EMBO J. 1990 May;9(5):1503–1510. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08268.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saku T., Furthmayr H. Characterization of the major heparan sulfate proteoglycan secreted by bovine aortic endothelial cells in culture. Homology to the large molecular weight molecule of basement membranes. J Biol Chem. 1989 Feb 25;264(6):3514–3523. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwab M., Alitalo K., Varmus H. E., Bishop J. M., George D. A cellular oncogene (c-Ki-ras) is amplified, overexpressed, and located within karyotypic abnormalities in mouse adrenocortical tumour cells. Nature. 1983 Jun 9;303(5917):497–501. doi: 10.1038/303497a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TAYLOR A. C., ROBBINS E. Observations on microextensions from the surface of isolated vertebrate cells. Dev Biol. 1963 Mar;6:660–673. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(63)90150-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tang T. K., Qin Z., Leto T., Marchesi V. T., Benz E. J., Jr Heterogeneity of mRNA and protein products arising from the protein 4.1 gene in erythroid and nonerythroid tissues. J Cell Biol. 1990 Mar;110(3):617–624. doi: 10.1083/jcb.110.3.617. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turunen O., Winqvist R., Pakkanen R., Grzeschik K. H., Wahlström T., Vaheri A. Cytovillin, a microvillar Mr 75,000 protein. cDNA sequence, prokaryotic expression, and chromosomal localization. J Biol Chem. 1989 Oct 5;264(28):16727–16732. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]