Abstract
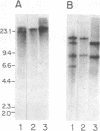
Mucoid strains of group A Streptococcus have been associated with recent outbreaks of acute rheumatic fever. The mucoid colony morphology of these strains is a result of abundant production of capsular polysaccharide, which is composed of hyaluronic acid. To study the role of the hyaluronic acid capsule in virulence, we derived an acapsular mutant from a mucoid strain of group A Streptococcus by transposon mutagenesis. M protein expression was not altered in the mutant strain. The mucoid wild-type strain grew in fresh human blood and was resistant to phagocytic killing in vitro. In contrast, the acapsular mutant failed to grow in fresh human blood and was sensitive to phagocytic killing in vitro. Loss of capsule was associated with a 100-fold reduction in virulence of the organisms in mice. We conclude that the hyaluronic acid capsule protects mucoid group A streptococci from phagocytosis and has an important role in virulence.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baltimore R. S., Kasper D. L., Baker C. J., Goroff D. K. Antigenic specificity of opsonophagocytic antibodies in rabbit anti-sera to group B streptococci. J Immunol. 1977 Feb;118(2):673–678. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caparon M. G., Scott J. R. Identification of a gene that regulates expression of M protein, the major virulence determinant of group A streptococci. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Dec;84(23):8677–8681. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.23.8677. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiRita V. J., Mekalanos J. J. Genetic regulation of bacterial virulence. Annu Rev Genet. 1989;23:455–482. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.23.120189.002323. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gawron-Burke C., Clewell D. B. A transposon in Streptococcus faecalis with fertility properties. Nature. 1982 Nov 18;300(5889):281–284. doi: 10.1038/300281a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gawron-Burke C., Clewell D. B. Regeneration of insertionally inactivated streptococcal DNA fragments after excision of transposon Tn916 in Escherichia coli: strategy for targeting and cloning of genes from gram-positive bacteria. J Bacteriol. 1984 Jul;159(1):214–221. doi: 10.1128/jb.159.1.214-221.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hosier D. M., Craenen J. M., Teske D. W., Wheller J. J. Resurgence of acute rheumatic fever. Am J Dis Child. 1987 Jul;141(7):730–733. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1987.04460070032015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan E. L., Johnson D. R., Cleary P. P. Group A streptococcal serotypes isolated from patients and sibling contacts during the resurgence of rheumatic fever in the United States in the mid-1980s. J Infect Dis. 1989 Jan;159(1):101–103. doi: 10.1093/infdis/159.1.101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knutson C. A., Jeanes A. A new modification of the carbazole analysis: application to heteropolysaccharides. Anal Biochem. 1968 Sep;24(3):470–481. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(68)90154-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LANCEFIELD R. C. Current knowledge of type-specific M antigens of group A streptococci. J Immunol. 1962 Sep;89:307–313. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LANCEFIELD R. C. Differentiation of group A streptococci with a common R antigen into three serological types, with special reference to the bactericidal test. J Exp Med. 1957 Oct 1;106(4):525–544. doi: 10.1084/jem.106.4.525. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Connor S. P., Cleary P. P. In vivo Streptococcus pyogenes C5a peptidase activity: analysis using transposon- and nitrosoguanidine-induced mutants. J Infect Dis. 1987 Sep;156(3):495–504. doi: 10.1093/infdis/156.3.495. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OUCHTERLONY O. Diffusion-in-gel methods for immunological analysis. Prog Allergy. 1958;5:1–78. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby P. W., Dieckmann M., Rhodes C., Berg P. Labeling deoxyribonucleic acid to high specific activity in vitro by nick translation with DNA polymerase I. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 15;113(1):237–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandson J., Hamerman D., Janis R., Rojkind M. Immunologic and chemical similarities between the streptococcus and human connective tissue. Trans Assoc Am Physicians. 1968;81:249–257. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simpson W. J., LaPenta D., Chen C., Cleary P. P. Coregulation of type 12 M protein and streptococcal C5a peptidase genes in group A streptococci: evidence for a virulence regulon controlled by the virR locus. J Bacteriol. 1990 Feb;172(2):696–700. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.2.696-700.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevens D. L., Tanner M. H., Winship J., Swarts R., Ries K. M., Schlievert P. M., Kaplan E. Severe group A streptococcal infections associated with a toxic shock-like syndrome and scarlet fever toxin A. N Engl J Med. 1989 Jul 6;321(1):1–7. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198907063210101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WILSON A. T. The relative importance of the capsule and the M-antigen in determining colony form of group A streptococci. J Exp Med. 1959 Mar 1;109(3):257–270. doi: 10.1084/jem.109.3.257. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wald E. R., Dashefsky B., Feidt C., Chiponis D., Byers C. Acute rheumatic fever in western Pennsylvania and the tristate area. Pediatrics. 1987 Sep;80(3):371–374. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wannamaker L. W. Virulence factors in streptococci. Scand J Infect Dis Suppl. 1982;31:22–27. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westlake R. M., Graham T. P., Edwards K. M. An outbreak of acute rheumatic fever in Tennessee. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 1990 Feb;9(2):97–100. doi: 10.1097/00006454-199002000-00007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitnack E., Bisno A. L., Beachey E. H. Hyaluronate capsule prevents attachment of group A streptococci to mouse peritoneal macrophages. Infect Immun. 1981 Mar;31(3):985–991. doi: 10.1128/iai.31.3.985-991.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]